21
Cross section of the battery cable
The cross section of the required battery cable depends on the resistance and the contact resistances in the
cable. To draw 5 kW from a 24 V battery, more than 200 amps of current ow through the cable. To keep losses
as low as possible, the cable must have a sufcient cross section.
Nedap recommends the following cable cross sections for the various PowerRouter versions:
5.0 kW system – Copper wire, 95 mm
2
3.7 kW system – Copper wire, 70 - 95 mm
2
3.0 kW system – Copper wire, 60 - 95 mm
2
Place the battery as close as possible to the PowerRouter to keep the cable as short as possible (≤ 2.5 m).
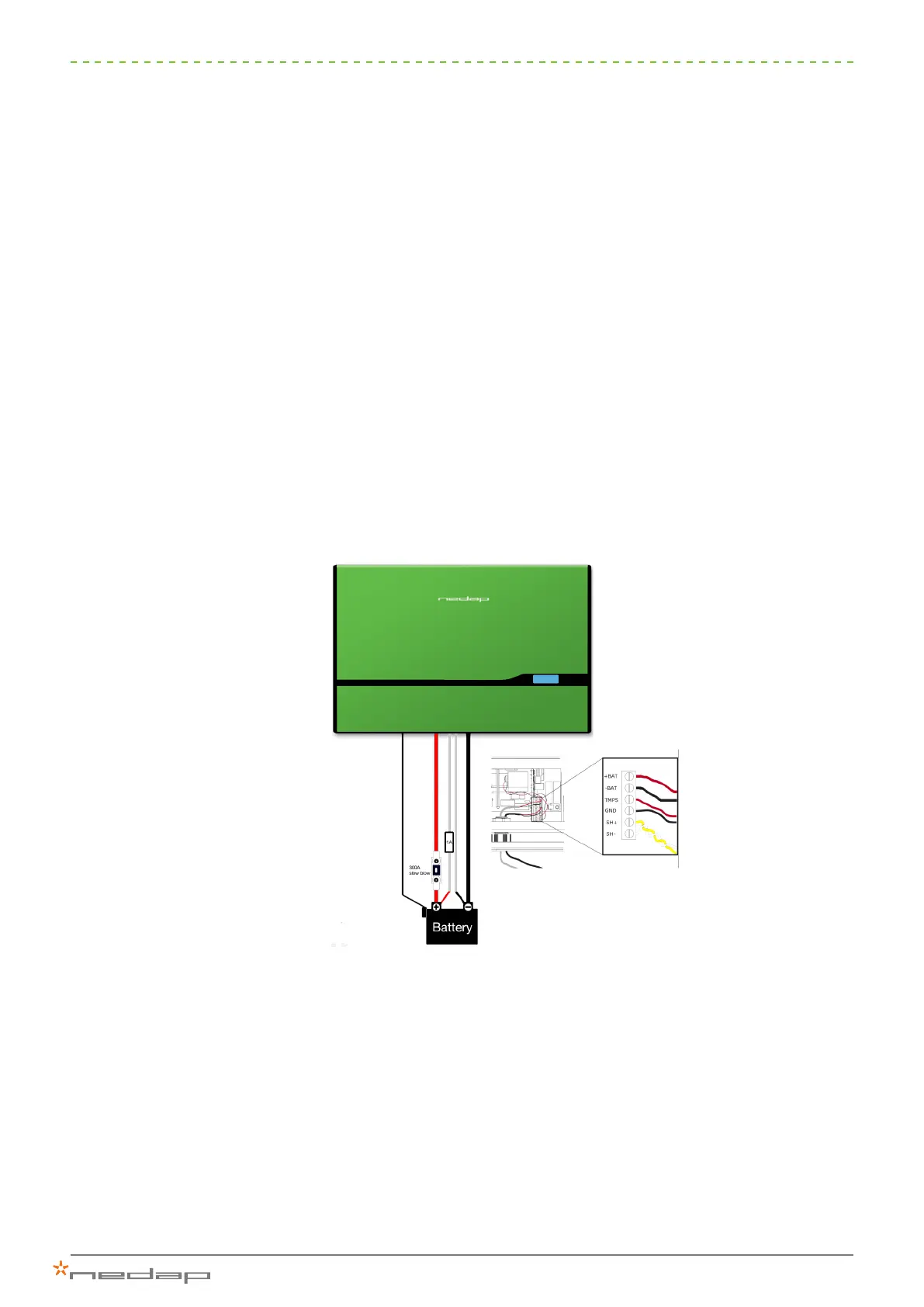
Voltage sense
When using longer battery cables (> 2.5m), Nedap recommends connecting sensor wires for voltage
compensation. This enables the PowerRouter to measure the voltage across the poles of the battery before any
voltage losses through the cables and connections. Connect a red wire with a 1 A fuse between the ‘+’ pole of
the battery and the +BAT terminal on the PowerRouter. Connect a black wire between the ‘-’ pole of the battery
and the -BAT terminal on the PowerRouter. We recommend you use stranded wire (not included).
Temperature sensor
The temperature sensor measures the temperature of the battery during charging. When the temperature
increases too rapidly, the PowerRouter will lower the charging current to protect the battery during charging. For
precise measurement, the sensor should be stuck onto one of the batteries near the ‘+’ pole. The rmware has
been programmed to automatically perform temperature compensation of 50 mV/°C. If the battery temperature
rises above 50 °C, charging/discharging is stopped to protect the battery.
Figure 28: Voltage Sense

 Loading...
Loading...