ENGINE
2.12
and rings. See Honing to Oversize in this
chapter. Inspect cylinder for out of round.
Piston Inspection
1. Inspect the piston for scoring or cracks in piston
crown or pin area. Excessive carbon buildup below
the ring land is an indication of piston, ring, or
cylinder wear. If damage is excessive, replace
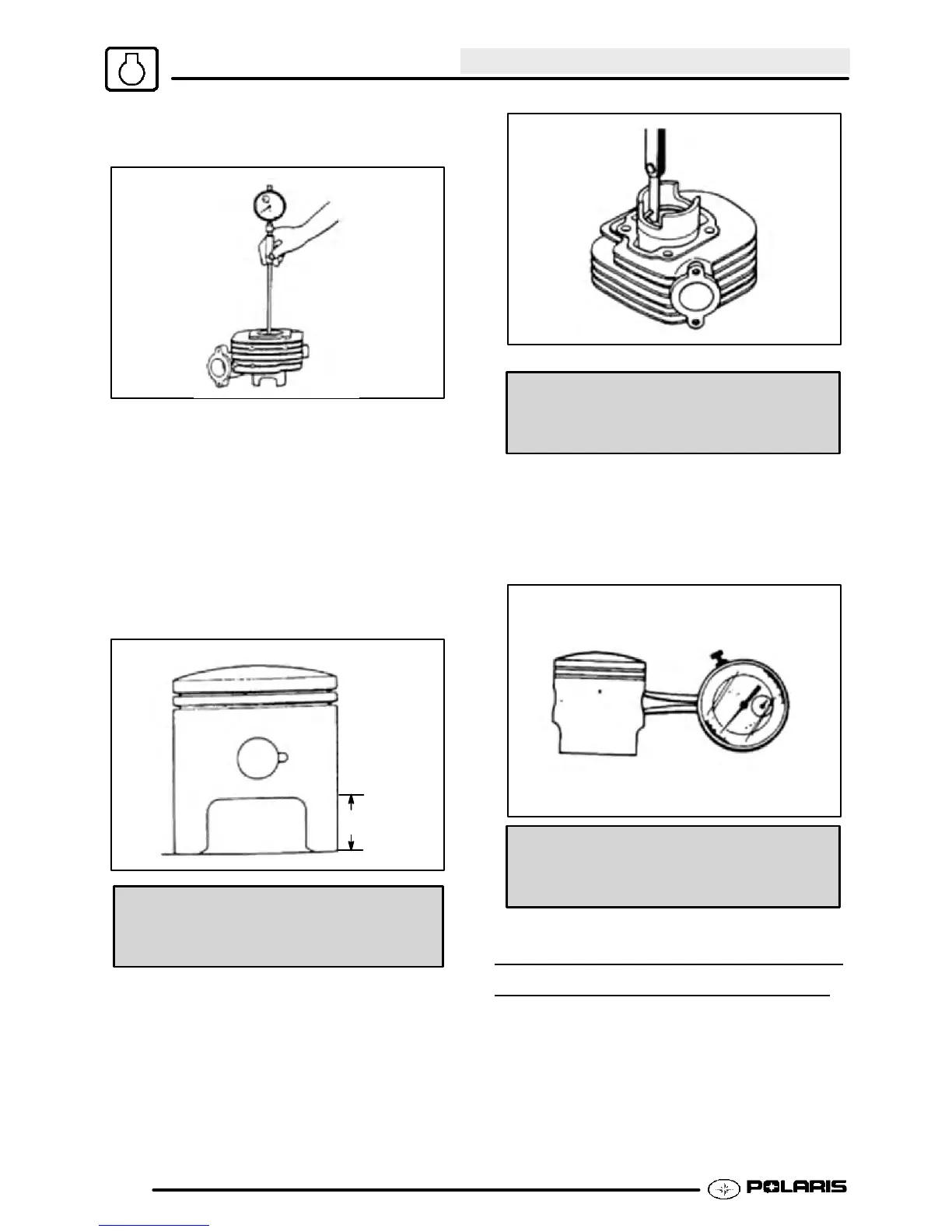
piston. Piston-to-cylinder clearance should not
exceed .0047² (0.12 mm). Measure the piston 5/8²
(15 mm) from bottom. Then measure inside
diameter of cylinder. The difference between these
measurements should not exceed .0047² (0.12
mm).
5/8² (15 mm)
Piston to Cylinder Clearance:
50 cc: .00138--.00177” (.035--.045 mm).
90 cc: .00118--.00197” (0.03 -- .05 mm)
Piston Ring Installed Gap
2. Position piston ring 1/2² (1.3cm) fromthetop of the
cylinder using the piston to push it squarely into
place. Measure installed gap with a feeler gauge
at both the top and bottom of the cylinder.
Replace rings if the installed end gap exceeds the
service limit.
Piston Ring Installed Gap
Service Limit:
.030I (0.75 mm)
Piston Pin Hole Inspection
1. Using a telescoping gauge or similar bore gauge,
measure the inside diameter of the piston pin hole
on both sides of the piston. Replace if diameter
exceeds .395² (10.03 mm)
Piston Pin Hole
Service Limit:
.395I (10.03 mm)
HONING ---- CYLINDER HONE
SELECTION &
PROCEDURE
Polaris recommends using only a rigid hone or arbor
honing machine which has the capability of
oversizing. Selecting a hone which will straighten as
well as remove material from the cylinder is very
important. Using a common spring loaded glaze
breaker for honing is never advised.
Enfocus Software - Customer Support
 Loading...
Loading...











