41
A = 6.82
B = 1.44
(A and B are constants determined by a raindrop diameter of 1 mm and the
physical properties of air.)
Find the fall velocity at time t = 0, 1, 2, 5, 10, 15.
*As the calculations are continued, v approaches 6.82. Therefore, the
velocity of a raindrop is about 6.82 m/s (24.6 km/h) when it reaches the ground.
Note: The fall distance from time t = 0 to 15 [s] is given by the following equation.
(Calculation of integral)
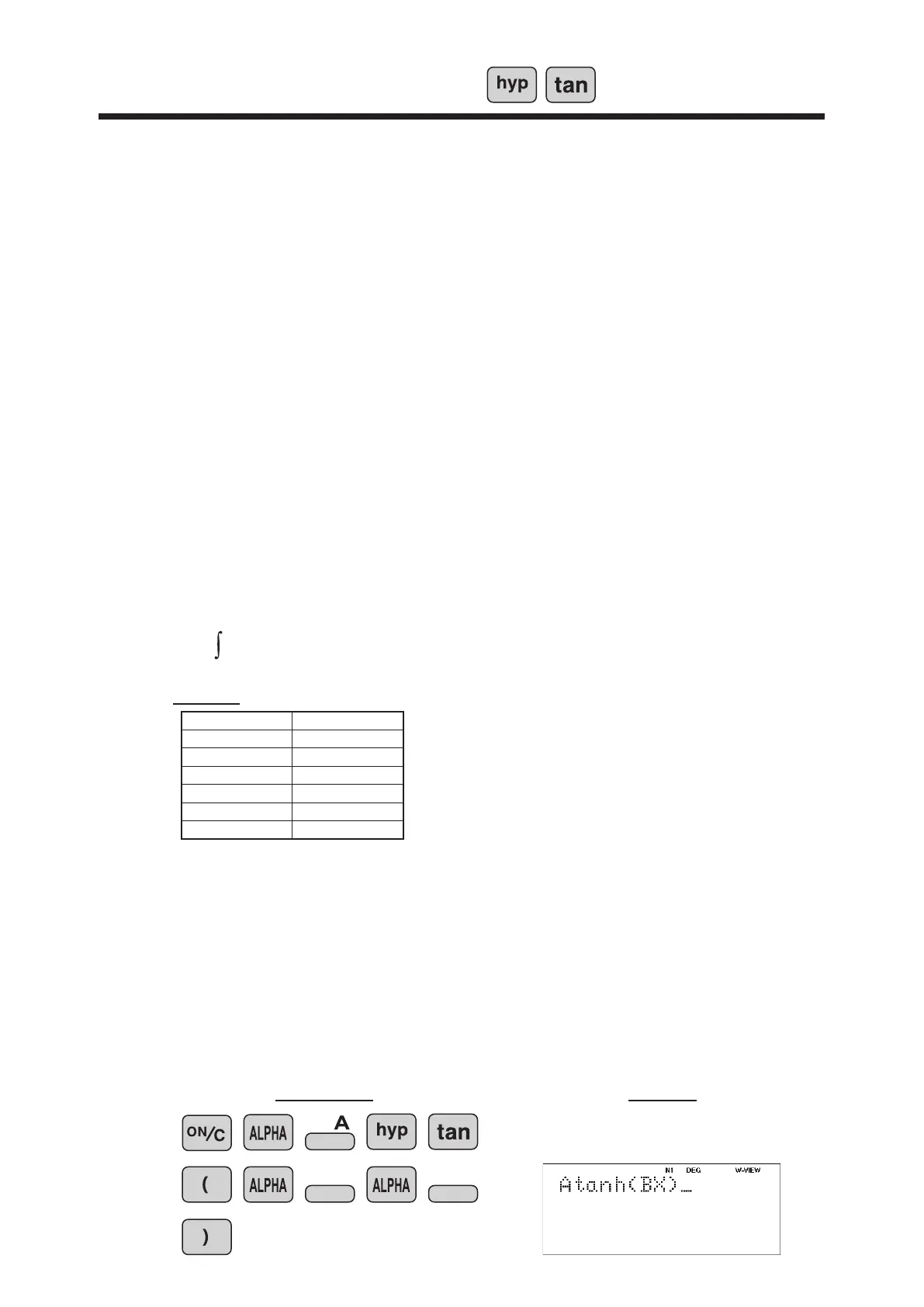
v = AtanhBt [m/s]
1. Enter Atanh(BX) (use the characters A, B, and X to enter)
[DEG mode]
Answer
Operation Display
<Example 2>
A drop of rain falls against an air resistance proportional to the square of the fall
velocity. The velocity v at time t seconds after the start of the fall is given by the
following equation:
B X
(6.82tanh(1.44x))dx = 99.01718518
15
0
x
0
1
2
5
10
15
v
0
6.0950185
6.777153851
6.819992397
6.82
6.82
Hyperbolic Functions
NOTE:
This example is solved by the Simulation calculation (ALGB)
.
EL-W516T has the Simulation calculation (ALGB)
.
This function is convenient for repeated calculations using varying values of X.
(This example is for EL-W516T only.)
 Loading...
Loading...











