immediately. Users can choose to continuously retrieve traces or manually request them one at
a time with the Single and Continuous buttons found on the Sweep Toolbar.
2.6.1.1 RBW/VBW limitations
Low RBW/VBW values increase the working memory footprint of an SM200/SM435 application
by increasing the FFT size and increasing buffer sizes for VBW averaging. For 32-bit applications
and Spike, this may limit the RBW/VBW in certain configurations.
When utilizing narrow spans (<5MHz) and low RBWs (<3Hz), a significant amount of processing
must be done in real-time for the measurement to be valid. Please see our recommended
processors if you are having issues with these types of sweeps.
2.6.2 Real-Time Spectrum Analysis
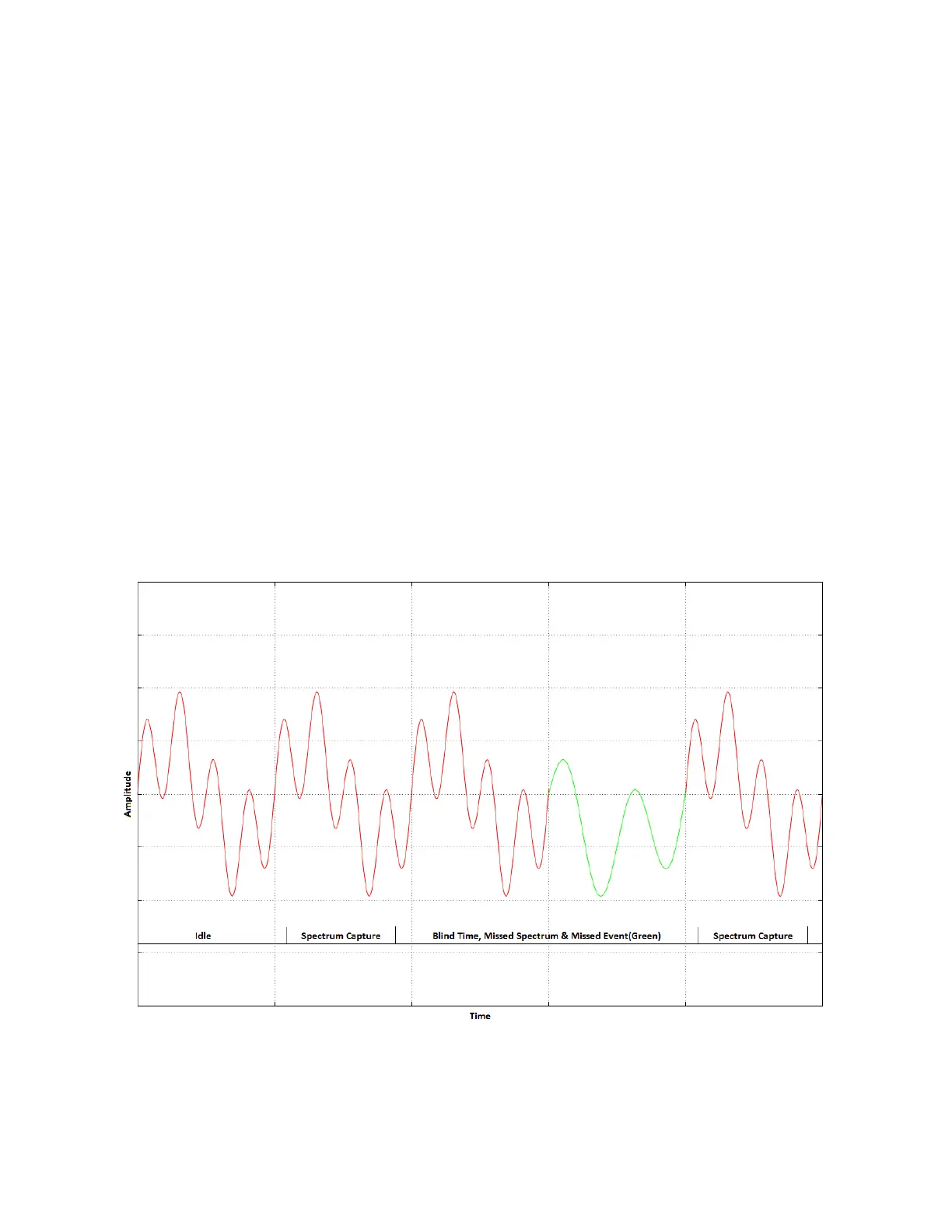
One of the issues with the standard sweep mode is the “blind time” between each trace. Blind
time refers to the time between spectrum sampling. During this time, we are processing the last
capture, or viewing the data. During this time, it is possible to miss an event. The picture below
shows a missed event in green.
In this image, we see an event missed due to the blind time between spectrum sampling. With
Real-Time spectrum analysis we can prevent this and capture ALL events.

 Loading...
Loading...