SX243: Parts Breakdown & Operating Manual 4 Rev. 09/20/11
deposits in the tool may cut power and may be corrected by
cleaning the air strainer and flushing out the tool with gum
solvent oil or an equal mixture of SAE #10 and kerosene. If outside
conditions are in order, disconnect tool from hose and take tool to
your nearest authorized service center.
Operation...
Always place a chisel in the hammer and hold the tool down to
the work before operating. Damage to the tool or the retainer may
result if this precaution is not followed.
The chisel retainers are not designed for complete safety against
accidental release of cutters or hammers. To avoid injury, the
throttle (trigger) must never be depressed unless the chisel is
held firmly against the work place. When tool is not in actual use,
the chisel must be removed. During operation, safety goggles
should ALWAYS be used to guard against flying rust and chips.
When using tool, regulate the speed so that the chisel is not being
driven out of the cylinder. If piston is allowed to strike the cylinder
wall, internal damage will result.
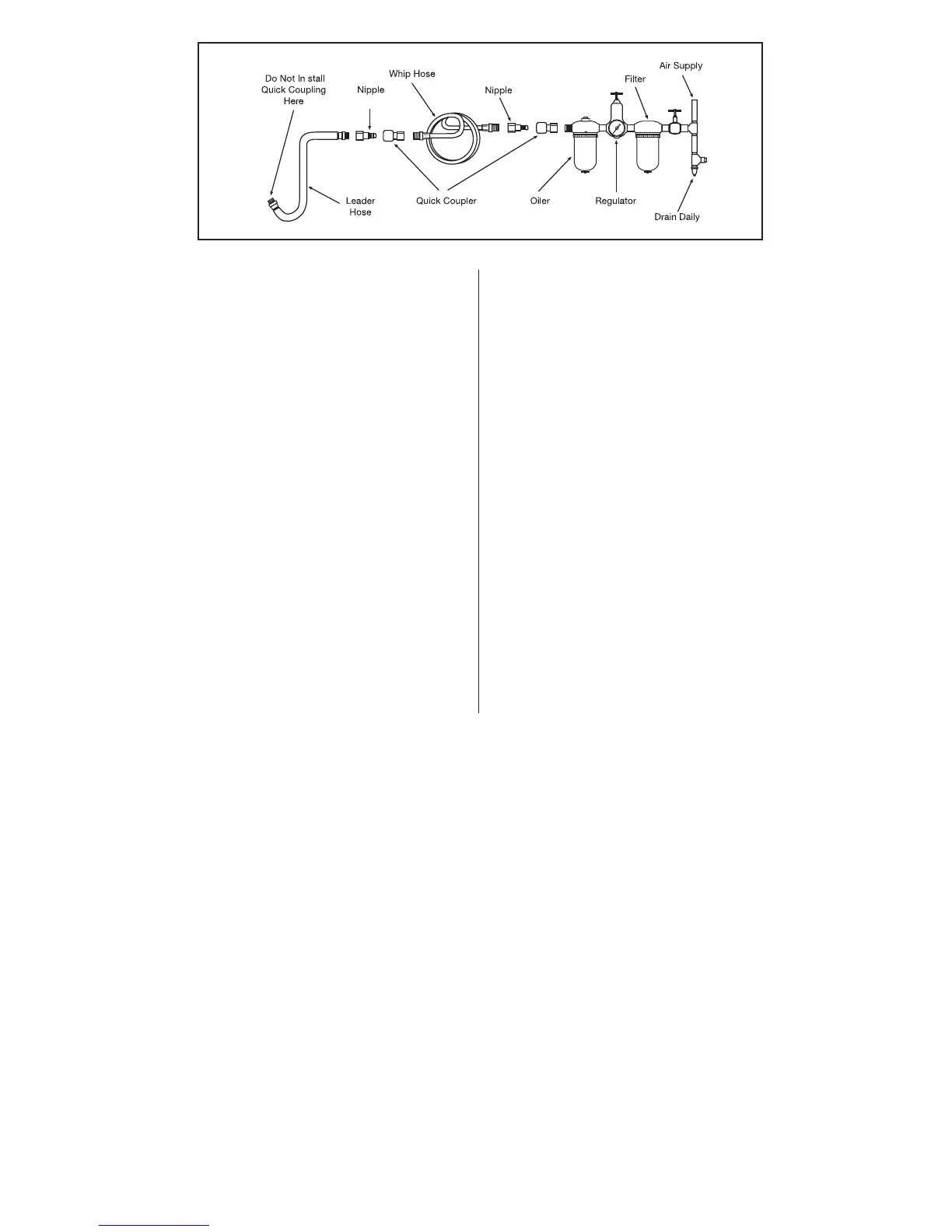
Air Supply...
Tools of this class operate on a wide range of air pres sures. It is
recommended that air pres sure of these tools mea sures 90 PSI at the
tool while running free. Higher pres sure (over 90 psig; 6.2 bar) will
short en the tool life and can cause accessory failure due to over speed.
Always use clean, dry air. Dust, corrosive fumes and/or water in the air
line will cause damage to the tool. Drain the air tank daily. Clean the
air inlet filter screen on at least a weekly schedule. The rec om mend ed
hookup pro ce dure can be viewed in figure 1.
Lubrication...
Lubricate the tool each day after use with quality SAE #10 air motor oil.
Add the oil to the air inlet or into the hose at the nearest connection to
the air supply then run the tool until all excess oil is expelled from the
exhaust. Total oil quantity needed for this procedure is approximately
1 ounce.
Troubleshooting...
Other factors outside the tool may cause loss of power or erratic
action. Reduced compressor output, excessive drain on the air line,
moisture or restrictions in air pipes or the use of hose connections of
improper size or poor conditions may reduce air supply. Grit or gum
FIGURE 1
Shop for other air tools & compressors on our website.
 Loading...
Loading...