34
MAINTENANCE
Hydrometer
A hydrometer is used to test the state of charge of a battery cell. This is performed by
measuring the density of the electrolyte, which is accomplished by measuring the specific
gravity of the electrolyte. The greater the concentration of sulfuric acid, the more dense
the electrolyte becomes. The higher the density, the higher the state of charge.
To prevent battery explosion that could result in severe
personal injury or death, never insert a metal thermometer into a battery. Use a hydrometer with a built in thermometer
that is designed for testing batteries.
Specific gravity is the measurement of a liquid that is compared to a baseline. The baseline is water which is assigned a base number of 1.000. The concentra-
tion of sulfuric acid to water in a new golf car battery is 1.280 which means that the electrolyte weighs 1.280 times the weight of the same volume of water. A
fully charged battery will test at 1.275 - 1.280 while a discharged battery will read in the 1.140 range.
NOTICE: Do not perform a hydrometer test on a battery that has just been watered. The battery must go through at least one charge and discharge
cycle in order to permit the water to adequately mix with the electrolyte.
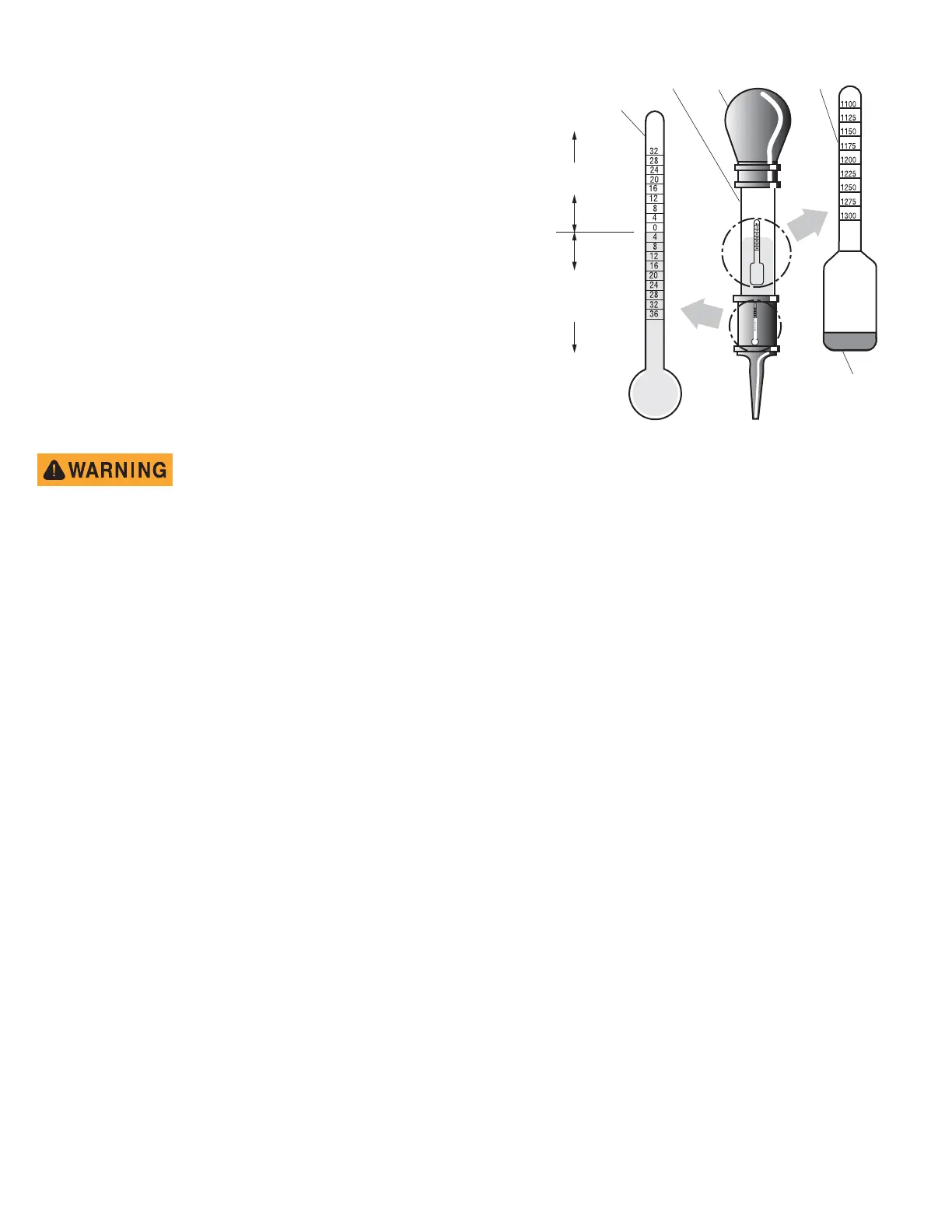
The temperature of the electrolyte is important since the hydrometer reading must be corrected to 80° F (27° C). High quality hydrometers are equipped with
an internal thermometer that will measure the temperature of the electrolyte and will include a conversion scale to correct the float reading. It is important to
recognize that the electrolyte temperature is significantly different from the ambient temperature if the vehicle has been operated.
FloatBulb
Cylinder
Thermometer
Add to Float
Reading
Subtract
from Float
Reading
Weight
Hydrometer
 Loading...
Loading...