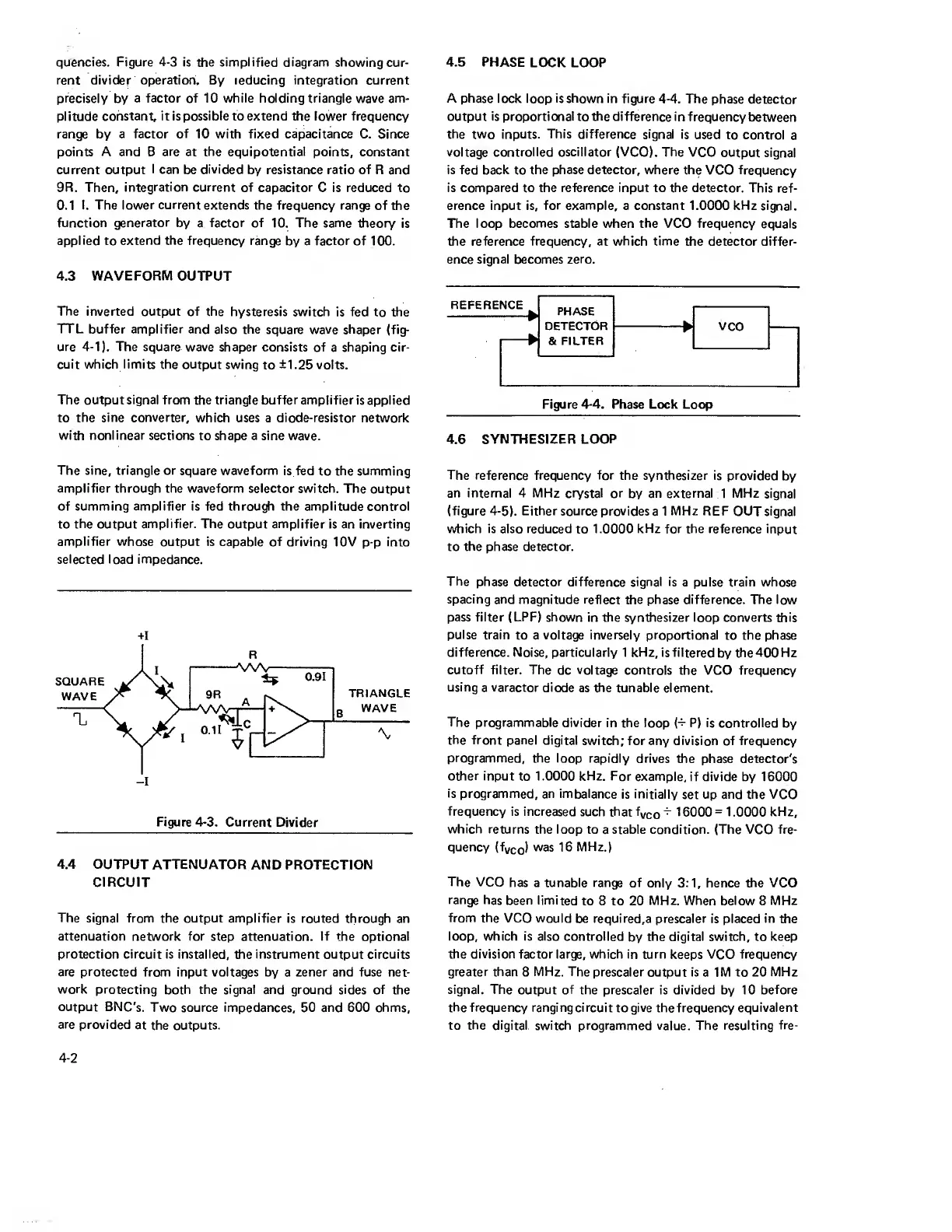
quencies. Figure
4-3
is the simplified diagram showing
cur-
rent divider operation. By reducing integration current
precisely
by
a factor of 10 while holding triangle
wave
am-
plitude
constant, it is possible to extend the
lower
frequency
range by a
factor of
10
with fixed
capacitance C. Since
points A
and
B
are
at
the equipotential
points, constant
current
output
I
can
be
divided
by
resistance
ratio
of
R and
9R. Then,
integration current
of capacitor
C is
reduced
to
0.1 I. The
lower current
extends the frequency range
of the
function generator by
a
factor of
10. The same theory
is
applied to
extend the
frequency range
by a
factor
of 100.
4.3
WAVEFORM OUTPUT
4.5 PHASE
LOCK LOOP
A phase
lock loop
is
shown in figure
4-4.
The
phase detector
output
is
proportional to the difference in
frequency
between
the
two inputs.
This difference
signal is
used
to
control
a
voltage
controlled oscillator (VCO). The
VCO
output signal
is fed back
to
the phase detector, where the
VCO frequency
is compared to the
reference
input to the detector.
This ref-
erence
input is,
for example,
a constant 1.0000 kHz
signal.
The loop
becomes
stable when the VCO frequency
equals
the reference
frequency,
at
which time
the detector differ-
ence signal becomes
zero.
The inverted output of the
hysteresis switch
is
fed
to the
TTL buffer
amplifier and also the
square wave shaper (fig-
ure
4-1).
The square wave shaper
consists of
a
shaping cir-
cuit which limits the output
swing
to
±1.25 volts.
The output signal from the triangle buffer amplifier
is applied
to
the sine converter, which
uses a diode-resistor network
with nonlinear sections
to shape a sine wave.
Figure
4-4.
Phase Lock Loop
4.6 SYNTHESIZER
LOOP
The sine, triangle or square waveform
is fed
to
the summing
amplifier
through the waveform selector switch.
The output
of
summing amplifier is
fed through the amplitude control
to
the
output
amplifier. The output amplifier is
an inverting
amplifier
whose output is capable of driving
10V
p-p
into
selected load impedance.
Figure
4-3.
Current Divider
4.4 OUTPUT
ATTENUATOR
AND PROTECTION
CIRCUIT
The
signal from the output amplifier
is routed through an
attenuation network for
step attenuation.
If
the optional
protection circuit is installed,
the
instrument
output
circuits
are protected
from
input
voltages by
a
zener and fuse net-
work
protecting both the signal and ground sides of the
output BNC's.
Two source impedances, 50 and 600 ohms,
are
provided
at
the
outputs.
The
reference frequency
for
the synthesizer is
provided
by
an
internal
4 MHz
crystal or
by
an external
1
MHz
signal
(figure 4-5). Either
source provides
a
1
MHz
REF
OUT signal
which is also reduced
to
1.0000 kHz for the reference
input
to the phase
detector.
The
phase detector
difference signal
is
a pulse train whose
spacing
and magnitude reflect the phase difference. The
low
pass filter (LPF) shown in
the synthesizer loop converts this
pulse
train
to a
voltage inversely
proportional
to
the phase
difference.
Noise, particularly 1 kHz, is
filtered
by
the 400 Hz
cutoff
filter. The
dc
voltage
controls the VCO frequency
using
a
varactor diode
as the tunable element.
The programmable divider
in the loop (± P) is controlled
by
the front panel
digital
switch; for any division of frequency
programmed, the
loop rapidly drives
the phase detector's
other input
to
1.0000 kHz.
For example, if divide
by 16000
is programmed,
an imbalance
is
initially
set
up and the VCO
frequency
is increased
such thatf
Vco
16000=
1.0000 kHz,
which returns
the
loop
to
a
stable condition. (The VCO fre-
quency (f
vco
)
was
16
MHz.)
The VCO
has a tunable range of
only
3:1,
hence
the
VCO
range
has been limited
to 8 to 20
MHz. When below
8
MHz
from
the VCO would
be required.a prescaler
is placed
in the
loop, which is also
controlled
by
the digital switch,
to
keep
the
division
factor large, which in turn
keeps VCO
frequency
greater than
8
MHz. The
prescaler output is
a
1M to 20 MHz
signal. The
output
of
the prescaler is divided by 10
before
the frequency ranging circuit
to
give
the frequency
equivalent
to
the
digital switch programmed
value.
The resulting
fre-
4-2
 Loading...
Loading...