D
Oper.ujng
sysl:cms
ha\"C
rules
(Of
the
muimum
length
of
a
filename,
for
valid
first characters,
and
for
dUl'1leters
iliat
are
inv:illiid
no
nutler
where
they
appcu
in
the
n:arne.
The
most
common
rule for a filename
is
that
it
must be
unique
on
a particular
disk
or
within
a particular
subdirectory.
See Figure 4-10.
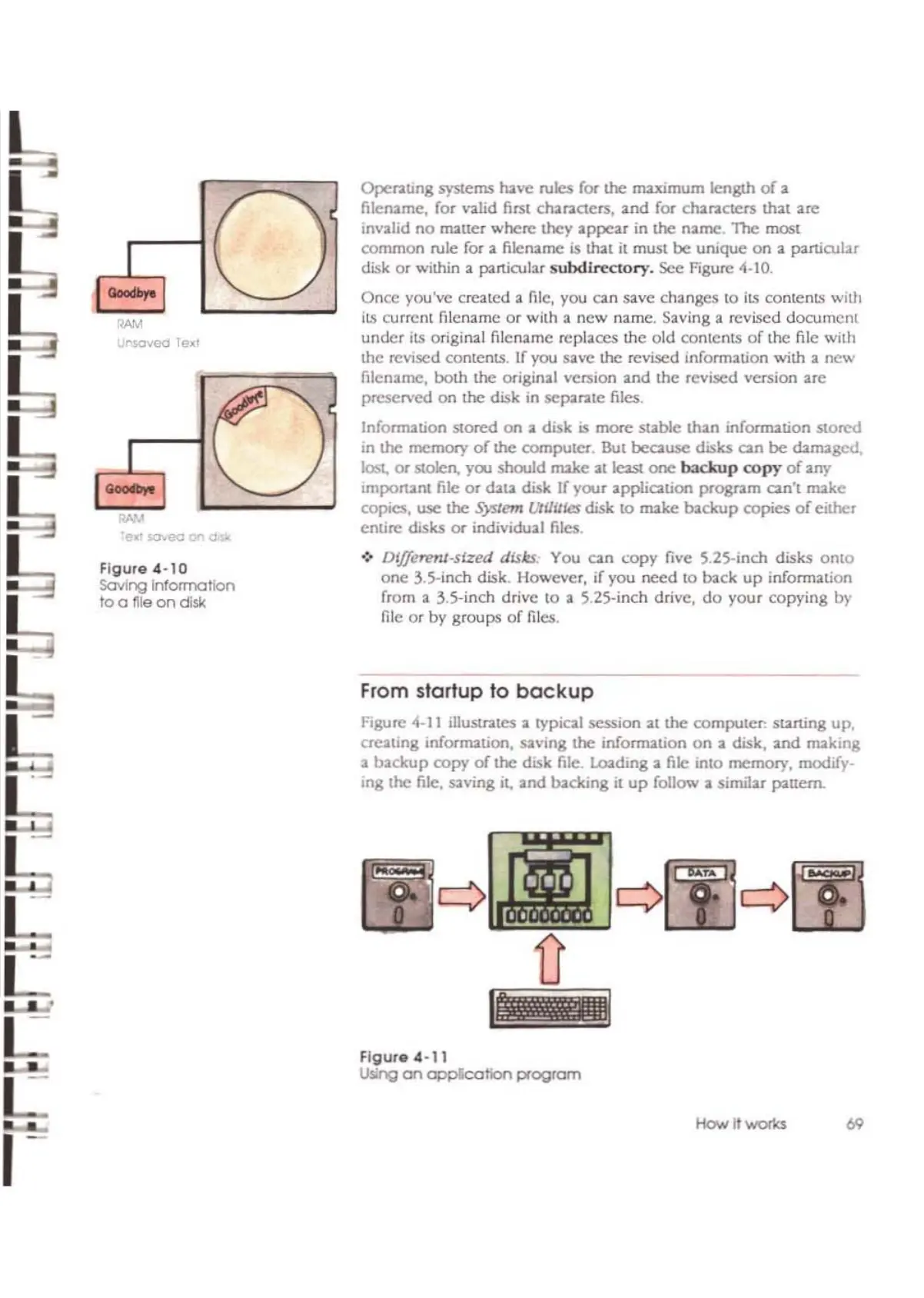
Onee you've created
:I.
me,
yO\.!
can save changes to
ilS
contents
with
ilS
current filename
or
with a
new
name. Saving a revised
document
under
its
original filename replaces
me
old
contents
of
the
file
with
the revised contents. If you
save
the revised information
with
a
new
filename,
both
the
original
version and
the
revised
version
are
preserved
on
the
disk
in sep'lrlltC files.
Information stored
on
a disk is
more
stable
than
infomution
MOre<!
in
the
memory
of
the computer. But because
disks
can
be
d:mugcd.
lost,
or
stolen,
yoo
should
make al least
one
b3ckup
copy
of
any
Important
file
or
d.lll.a
disk If
your
application
prognm
can't
make
copies, use the System lJtUilles disk
to
make
backup
copies
of
either
emirc disks
or
individual
nics
.
•:. DljJerent-sized disks. You
an
copy
five 5.25-inch disks
onto
onc
3.S-inch disk. However, if you
need
to back
up
infonnation
from a
3.5-inch drivc
to
a 5.25-inch drive,
do
your
copying
by
me
or
by
groups
or
files.
From startup to
backup
Figure 4-11 ilIUSlr.lICS a
Iypial
session
allhe
computer: starting up,
creatmg
mfonT12Lion,
saving
the
information
on
a disk,
and
making
a
backup
copy
of
the
disk file. Loading a file into
memory,
modify-
ing
the
file, saving it,
and
backing
il
up
follow a similar panern.
""'
1'I$Ovea
TexT
I
Figure
4-10
Soving
Information
to a tile
on
dlsk
,-
Figure
4-11
Using
on
opplcotlon
program
How it
W'Of1<s
69
 Loading...
Loading...