12
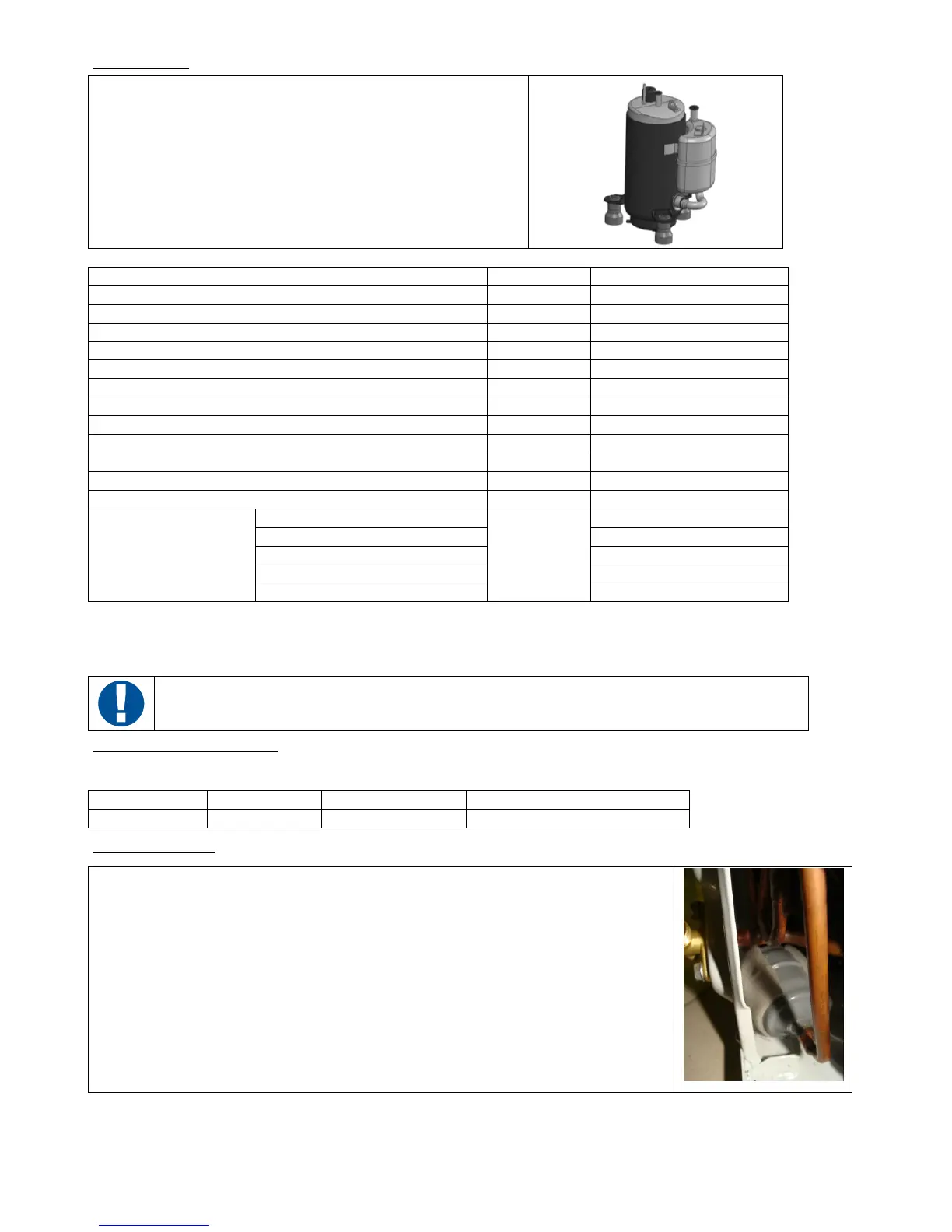
Compressor (*)
Inhales the gas from the evaporator and compresses it in the
condenser. Because of the job of compression, the vapor goes out of
the compressor with more pressure and strongly overheated.
Maintain the conditions of operation of the compressor within the
parameters brought in chart, if not respected, not only the
performances won't be optimal, but it could present malfunctions and
shortening of the life of the compressor.
Characteristic Unit Value
Compressor type - Rotary piston
N° motor poles Nr 2
displacement cm³ 12,2
Start condenser µF/V 15/400
Motor resistance Ω Main 5,84/Aux 7,62
Max quantity of refrigerant R-134a (CH2FCF3) kg 0,9
Oil NE032/L22E or equivalents ml 270 ±20
Mass (oil included) kg 9,2
Power supply 1ph. 220-240V 50Hz
Power consumption W 475/490
Current consumption A 2,3
Heating capacity W 1965/1980
Temperature conditions
Evaporation
°C
10
Condensation 55
Inlet gas 20
Ambient 35,0
Liquid 46,7
The followings conditions are considered possible cause of risks:
• In the case of high or low tension with high ambient temperature (ex. 43°C)
• Return of fluid in liquid phase in the compressor.
• Filling of the filter dehydrator.
Pipe stress: the copper pipeline in outlet of the compressor is subject to vibrations. To avoid breakups, the
constructor applies an insulating material that limits the oscillations (damper), make sure it is entire and is
not altered during maintenance/operations.
Compressor start-up capacitor
The march capacitor has the purpose to start the compressor.
Capacity (μF) Tension (V) Freq (Hz) Terminals
15 ± 5% 450 50/60 Faston 6.3mm
Dehydrator filter (*)
The filter has two functions:
1 - absorbs the contaminants of the circuit as water and acid,
2 - makes a physical filtering.
The ability to remove the water from the circuit is the principal function of the filter.

 Loading...
Loading...










