G. Tires and Tubes
1. Tires
Bicycle tires ar e avai lable in many designs and sp ecifications, ranging from gen
eral-purpose designs to tires desig ned to
perform best under very specific weather or terrain conditions. If, once you’ve gained experience with your new bike, you feel that
a different tire might better suit your riding needs, your dealer can help you select the most appropriate design.
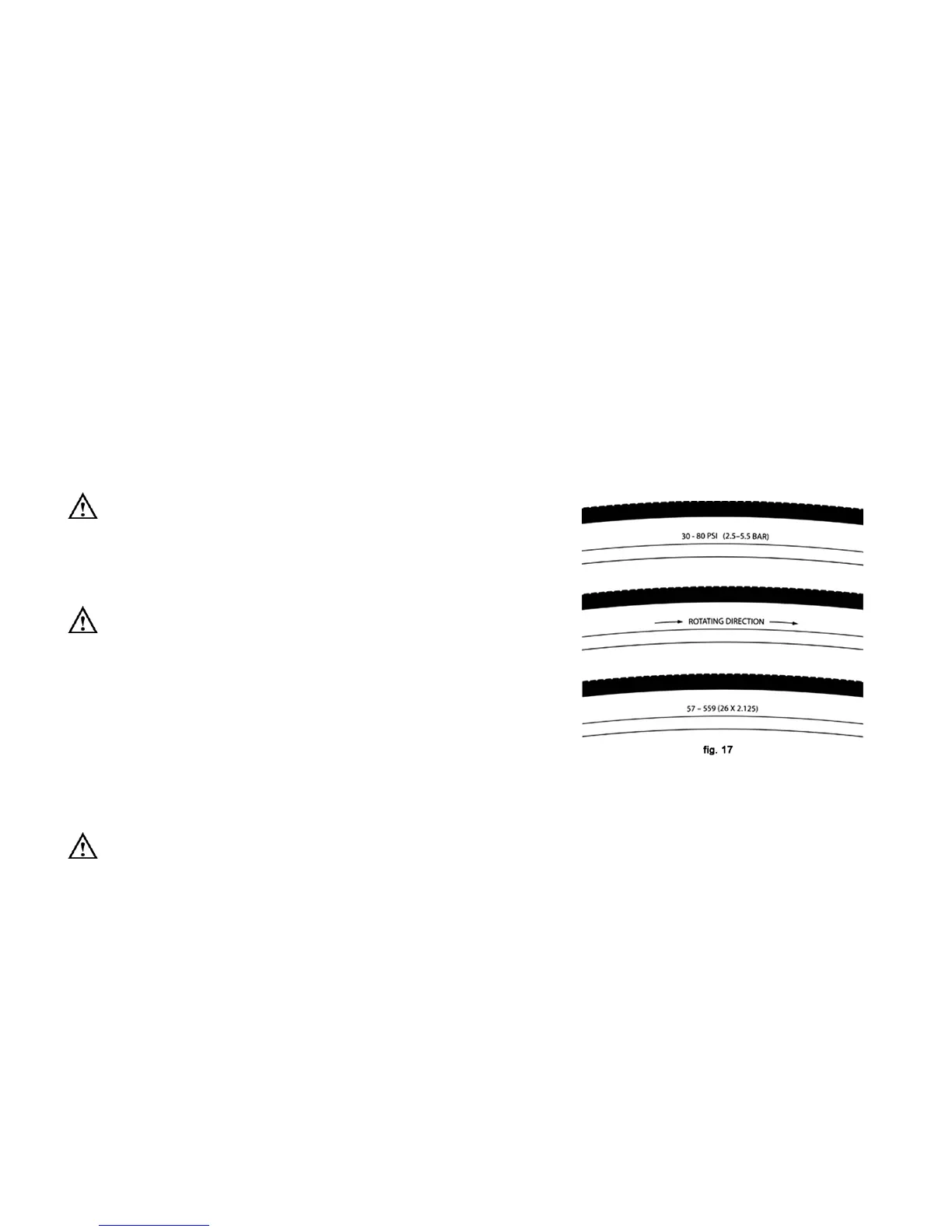
The size, pressure rating, and on some high-performance tires the specific recommended use, are marked on the side
wall of
the tire (see fig. 17). The part of this information which is most important to you is Tire Pressure.
WARNING: Ne ver in flate a tire b eyond th e maximum p ressure
marked on the tire’ s
sidewall. Exceeding t he recommended
maximum pre ssure m ay bl ow the t ire off the rim, which could c ause
damage to the bike and injury to the rider and bystanders.
The best and safest way to inflate a bic ycle tire to the correct pressure is
with a bicycle pump which has a built-in pressure gauge.
WARNING: There is a safety risk in usin
g gas station air hoses or
other air co mpressors. T hey ar e not ma de fo r b icycle tires. T hey
move a la rge volume o f ai r very r apidly, an d will raise th e p ressure in
your tire very rapidly, which could cause the tube to explode.
Tire pressure is given either as maximum pressure or as a pressure range.
How a tir e pe rforms under different te rrain or weather cond itions de pends
largely on tire pressur e. Inflating the tire to near it s maxim um recommen ded
pressure gives the lo west roll ing resi stance; but also prod uces the hars hest
ride. High pressures work best on smooth, dry pavement.
Very low pressures, at the bot tom of the recommended pres
sure range, give the best perf ormance on smooth, slick ter rain
such as hard-packed clay, and on deep, loose surfaces such as deep, dry sand.
Tire pressure that is too low for your weight and the riding conditions can cause a puncture of the tube by allowing the tire to
deform sufficiently to pinch the inner tube between the rim and the riding surface.
CAUTION: Pencil ty pe automoti ve tire gauges can be in accurate an
d should not be relied upon for consistent,
accurate pressure readings. Instead, use a high quality dial gauge.
31
 Loading...
Loading...