Instruction book
12 6996 0224 30
2. General description
2.1 What is vacuum and how is flow rate understood
What is vacuum and how to denote
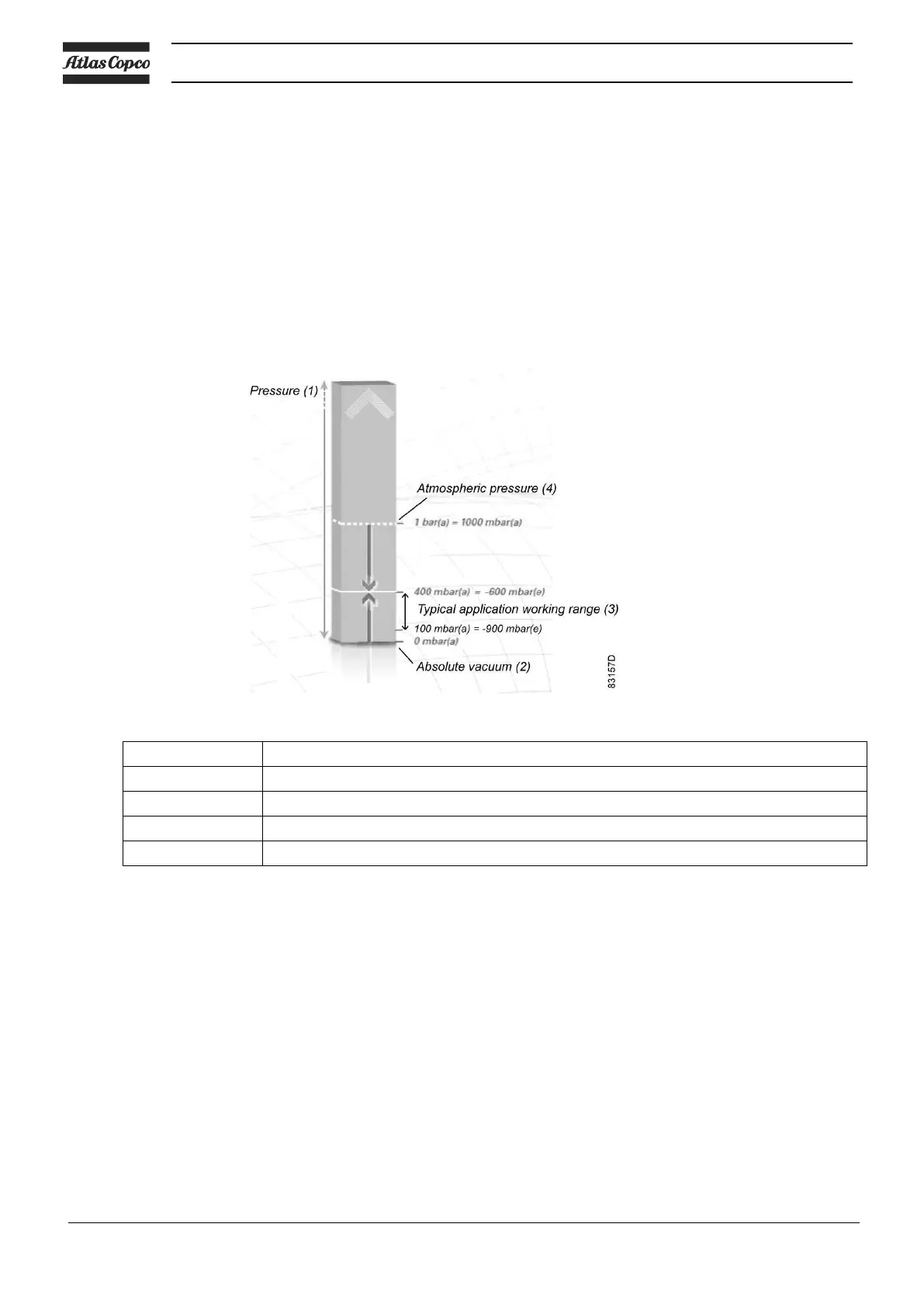
A vacuum is any pressure in a system that is below the ambient atmospheric pressure. It can be denoted
in absolute terms or in effective (gauge) terms:
mbar(a) – absolute pressure – denotes how much the pressure is above absolute zero vacuum.
(minus) mbar(e) – the effective or gauge pressure – denotes how much the pressure is below the local
atmospheric pressure.
Typical application working range
Atmospheric pressure at sea level is roughly 1 bar(a) or 1000 mbar(a) or 0 bar(e). The typical working
range for pump applications is 400 mbar(a) to 100 mbar(a), i.e. -600 mbar(e) to -900 mbar(e). This
operating pressure range is just indicative. The GVS A vacuum pumps are designed for continuous
operation between atmospheric pressure and their ultimate pressure.
It is important to understand which type of reference is required before selecting a pressure instrument
for measuring the vacuum.
It must be noted that the distinction doesn’t matter for a pressure difference (e.g. pressure loss), since
it is always the result of subtracting 2 pressures (whether stated as absolute or as effective pressures).

 Loading...
Loading...











