DL06 Micro PLC User Manual, 3rd Edition, Rev. E
3-19
Chapter 3: CPU Specifications and Operation
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
A
B
C
D
Improving Response Time
There are a few things you can do to help improve throughput.
• You can choose instructions with faster execution times
• You can use immediate I/O instructions (which update the I/O points during the program
execution)
• You can use the HSIO Mode 50 Pulse Catch features designed to operate in high-speed
environments. See Appendix E for details on using this feature.
• You can change Mode 60 filter to 0 msec for X0, X1, X2, and X3.
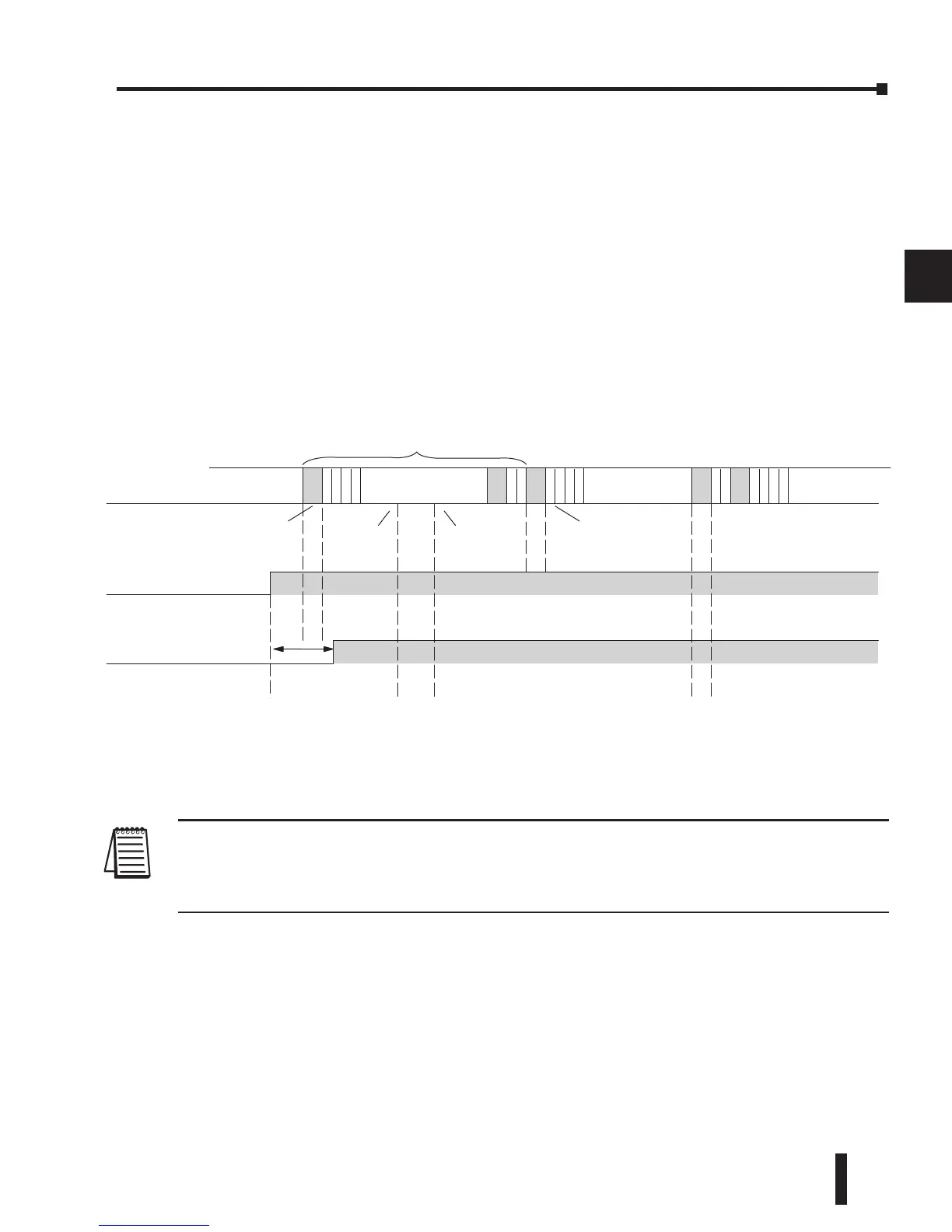
Of these three things the Immediate I/O instructions are probably the most important
and most useful. The following example shows how an immediate input instruction
and immediate output instruction would affect the response time.
In this case, you can calculate the response time by simply adding the following items.
Input Delay + Instruction Execution Time + Output Delay = Response Time
The instruction execution time would be calculated by adding the time for the immediate input
instruction, the immediate output instruction, and any other instructions in between the two.
NOTE: Even though the immediate instruction reads the most current status from I/O, it only uses
the results to solve that one instruction. It does not use the new status to update the image register.
Therefore, any regular instructions that follow will still use the image register values. Any immediate
instructions that follow will access the I/O again to update the status.
Chapter 3: CPU Specifications and Operation
Solve
Program
Read
Input
Immediate
Normal
Write
Outputs
Solve
Program
Scan
Solve
Program
Field Input
Input
Of
f/On Delay
 Loading...
Loading...