Selkirk College IATPL Program Manual
Beech 95 POH Effective September 1, 2005 Appendix 14 - 39
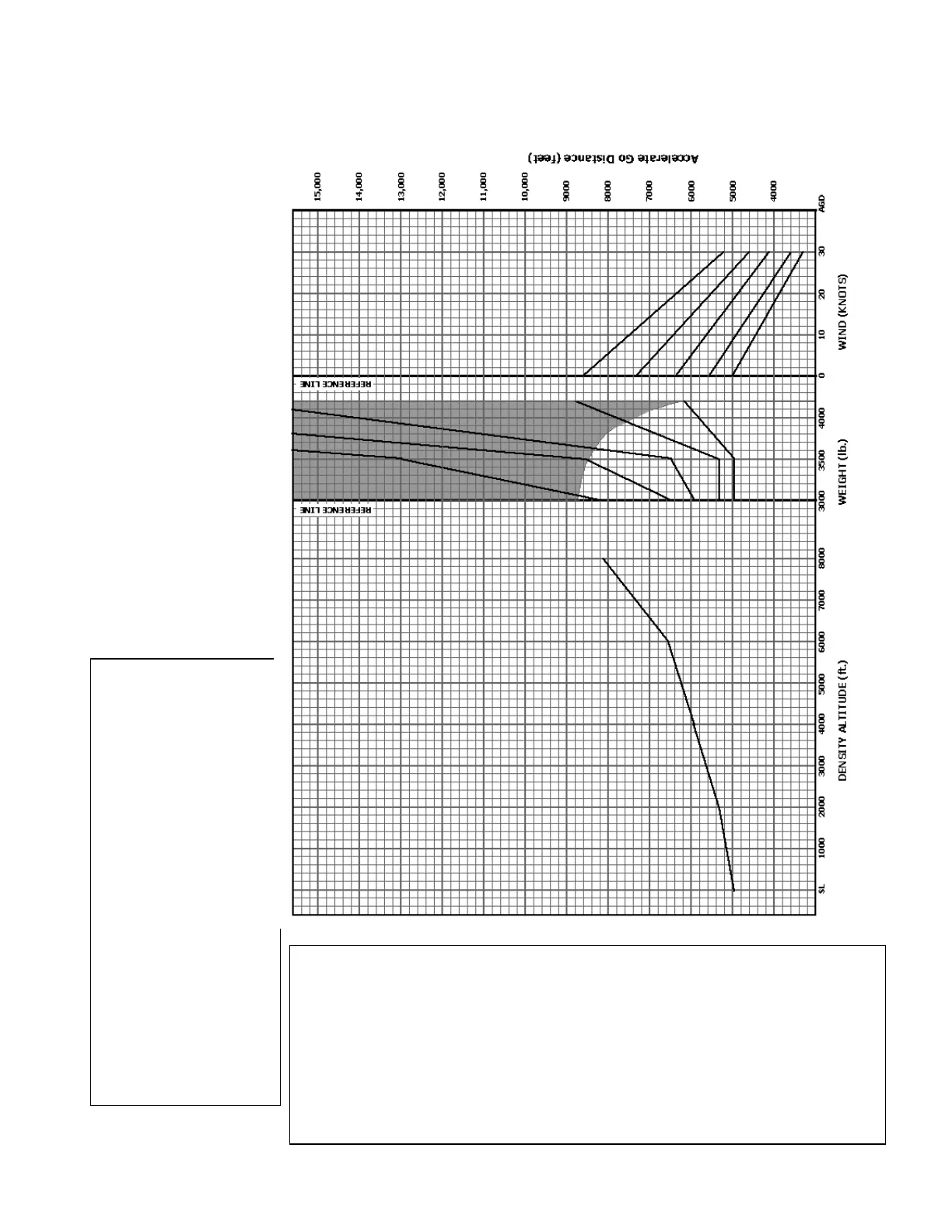
Accelerate Go Distance – B95
Graph gives minimum distance to 50’ agl following an engine failure at Vgo or
later
Vr, all weights – 74 KIAS
Vgo, all weights – 89 KIAS, or N/A (see notes)
Conditions:
Normal takeoff procedure. Paved level dry runway.
Engine failure at Vgo with gear up
Full power on operating engine with mixture leaned to appropriate
fuel flow
Failed engine propeller feathered immediately.
AGD distance is to reach 50 feet or complete feathering
procedure whichever is reached last.
NOTES: Produced by Selkirk College based on approved POH.
For use by Selkirk College Professional Aviation students and instructors only.
Distances calculated with this chart are an estimate based on the normal takeoff distance chart such that the
airplane is at 35’agl at 89KIAS, a 20 second time period is allowed to complete the engine failure drill during
which the assumed performance is gear down, propeller windmilling. A climb to 50 feet is then assumed based on
gear up and propeller feathered. The relevant charts are: Single Engine Emergency Rate of Climb chart (page 6-9)
and Normal Takeoff Distance (pages 6-2 and 6-3) Charts are in Beechcraft Travelair D95A Owner’s Manual.
Note that if calculations show that the airplane will strike the ground or come within 15 feet of the ground Vgo is
not considered to be a safe concept. In that situation pilots must determine a minimum safe altitude instead (refer
to single engine climb performance charts.) See notes on page 34 of this appendix.
 Loading...
Loading...










