Operating mode
The operating modes of relay outputs are three:
1 Immediate: the relay remains triggered until the radio signal is still on, that is to say
The relay output remains closed until the transmitter key is kept pressed,
2 Step-by-step: the relay stays triggered until a following controlsignal is given, that is to say when the transmitter key
is pressed again.
3 Time-based: once triggered, the relay remains on for a preset time from 3 seconds to 18 hours.
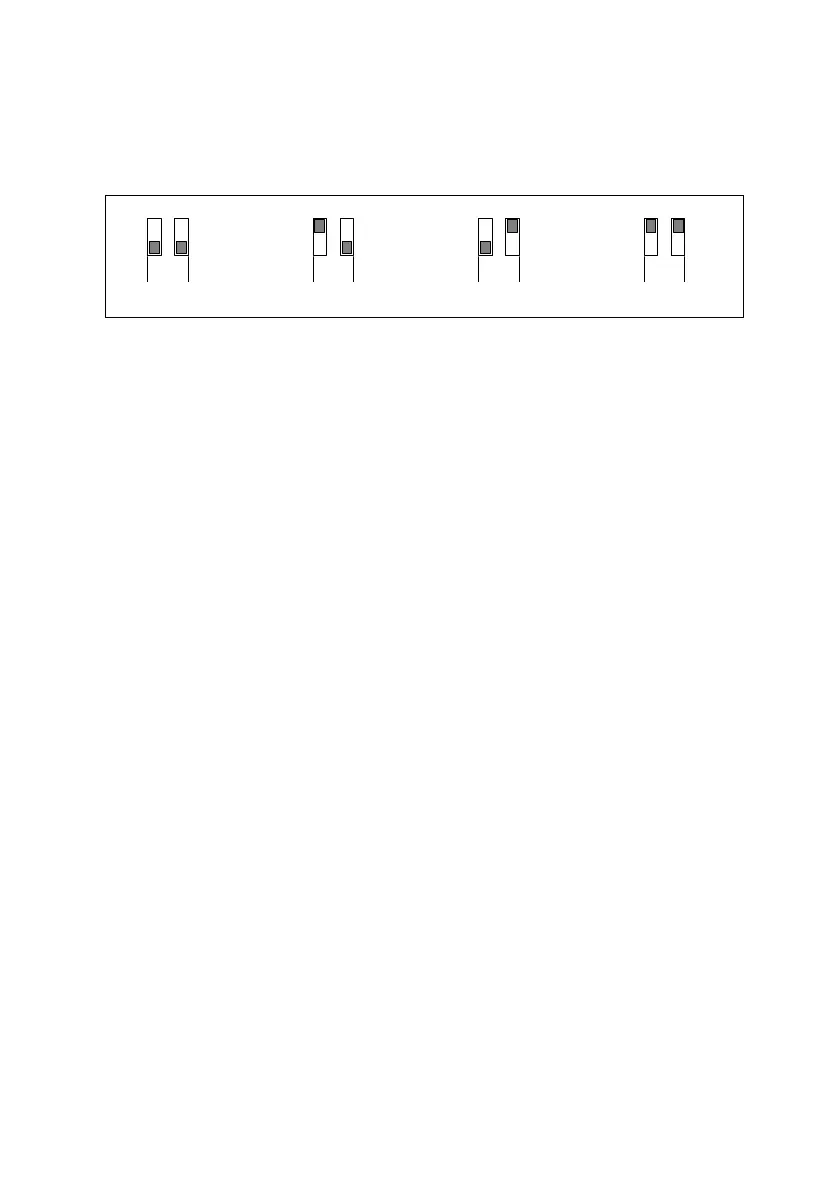
To select the desired operating mode, position the dip-switches 1-2 (channel 1) and 3-4 (channel 2) as follows:
Presetting of immediate and step-by-step operating mode
Each relay is matched to two dip-switches: dip-switch 1-2= relay 1, dip-switch 3-4= relay 2 (see Figure 2). To select the
Immediate operating mode position the dip-switched on position OFF (mode 1). If the Step-by-step mode is to be
selected, position the relevant dip-switches as in mode 2.
Operating mode with timer
To program the activation time of the relay, proceed as follows:
1 Cut off power supply to the receiver card.
2 Preset the two dip-switches relevant to the desired channel, dip 1-2 = channel 1, dip 3-4 = channel 2, both to position
ON, as per mode 4 (see table 1). To preset the same times of the two channels, position all 4 dip-switches on ON.
If the time should be programmed on only one channel, thus keeping the programming of second channel, preset the
dip-switches on mode 4 for the channel to be programmed, and on mode 3 for the remaining channel. If the dip-switch
of the remaining channel is positioned on mode 1, the corresponding relay time will be reset at the end of the pro-
gramming.
3 Power the receiver card to terminals 5 and 6.
4 Press the self-learning key and wait until the desired programming time has elapsed. At this point release the learning
key and store the above time in the memory module. The time learned is the same as the relay triggering time.
NOTE: Once the mode 4 has been selected, also for one channel, the only solution possible is to store the time
in memory. At the end of the learning function, remember to position the dip-switches to the normal operating
mode (1, 2 or 3).
Radio diagnosis
The receiver is provided with LED for the radio diagnosis: in fact, the installer is able to detect immediately if some radio
interference are present which may have a negative effect on the maximum range of the radio, thus impairing the correct
operation of the unit. Between two transmissions, check for any interference be present according to the table hereun-
der:
LED off= no interference
Flashing LED= slight interference
LED on with steady light= strong interference
Installation
Carry out the connections as per wire diagram. Power supply voltage is at 24V AC/DC to terminals 5 and 6 (in this case
keep to polarity by connecting the negative pole to terminal 5 and the positive pole to terminal 6). If more than one
receiver is required, position them at a distance of 3-4 metres one from the other to avoid any possible interference.
Position the antenna far from obstacles and metal structures, or above the latter if they are connected to ground (earth).
Connect the earth to terminal 9 and the antenna to terminal 10. The antenna is necessary to optimize the performance
of the unit. Conversely, the range would reduce to a few tenths of meters. If the cable supplied with the antenna is too
short, do not make joints but replace the cable with another one featuring the adequate length and 50 Ohm impedance
(type RG58). In any case, the cable must not exceed 10 metres length.
Warnings and advice
Before powering the receiver card select power supply voltage through the special voltage selection jumper. In case of
failure check the following:
• Power supply of the receiver.
• The battery good conditions of the transmitter.
• The correct installation of the antenna.
• The LED of radio reception should not be always on. Conversely, the LED indicates the presence of a very strong
interference, which might impair the correct operation of the system.
Mode1: Immediate
Off Off
a
Ch.
b
Mode2: Step-by-step
On Off
a
Ch.
b
Mode3: Time-based
Off On
a
Ch.
b
Mode4: Programming
of time in mode3
On On
a
Ch.
b

 Loading...
Loading...