7
ENGLISH
3.13 Removing the casing
To access the components inside, remove the casing as indicated below:
- nd and unscrew the 2 screws (A - g. 11) xing the casing to the boiler levering the two
xing clips (C - g. 11), detach the bottom part of the casing
- lift the casing upwards to release it from the top tabs (B - g. 11), then remove it.
WARNING
b
If removing the side panels, put them back in their initial position, referring to the
adhesive labels on their walls.
b
If the front panel is damaged it must be replaced.
b
The noise absorbing panels inside the front and side walls ensure the airtight seal for the
air supply duct in the installation environment.
b
It is therefore CRUCIAL after the dismantling operations to correctly reposition the
components to ensure the boiler's seal is effective.
3.14 Flue gas exhaust and combustion air suction (Fig. 12)
To evacuate the combustion products, refer to UNI 7129-7131. Always comply with
local standards of the Fire Department, the Gas Company and with possible municipal
dispositions. The evacuation of the combustion products is carried out by a centrifugal fan
and the control board constantly monitors that it is operating correctly. It is essential for
the evacuation of the ue gases and the adduction of the boiler's combustion air that only
original pipes be used (except C6) and that the connection is made correctly as shown in
the instructions provided with the ue gases accessories. A single ue can be connected
to several appliances provided that every appliance is the condensing type. The boiler is
a C-type appliance (with airtight chamber), and must therefore have a safe connection to
the ue gas discharge pipe and to the combustion air suction pipe; these both carry their
contents outside, and are essential for the operation of the appliance.
Both concentric and twin terminals are available.
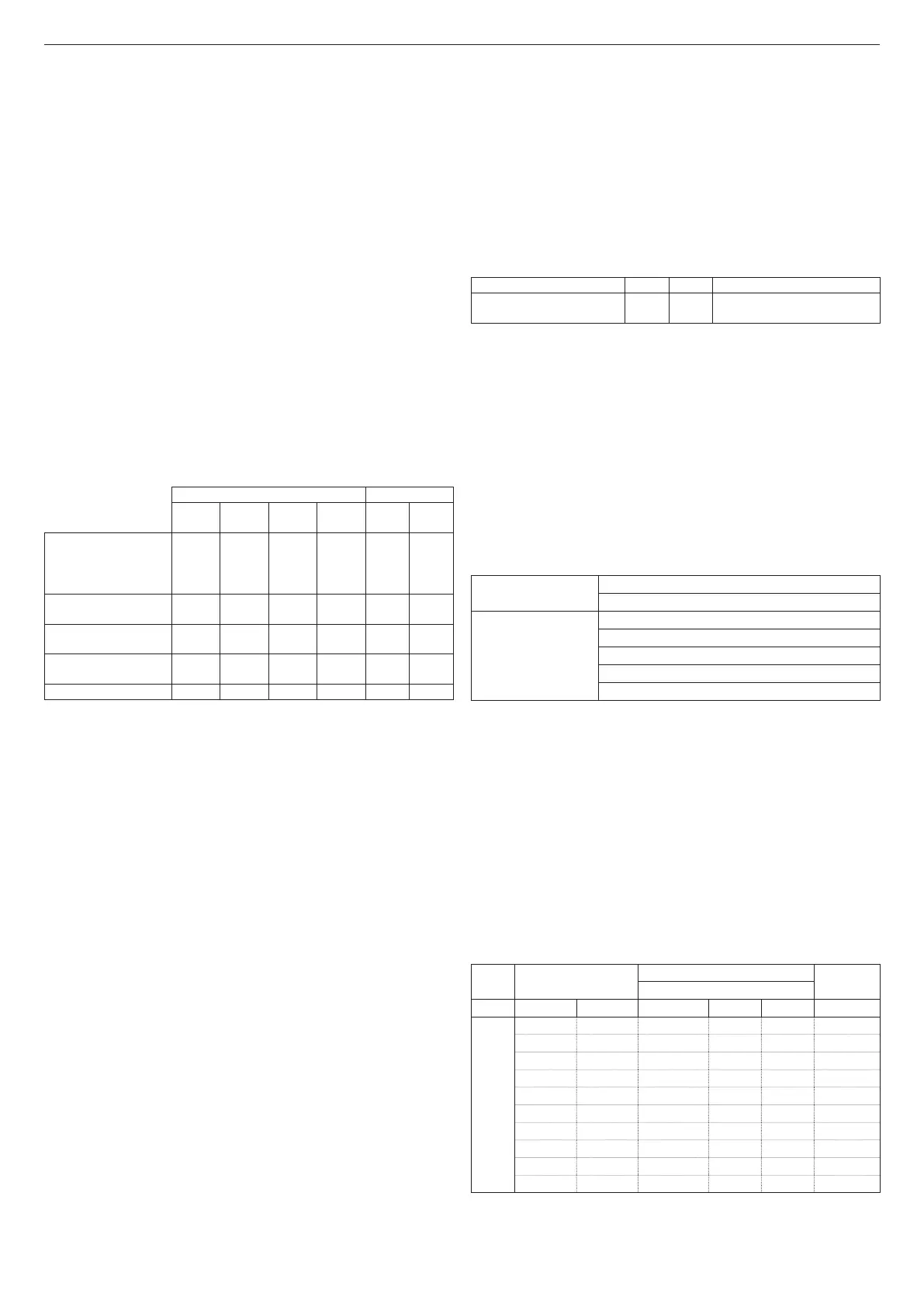
Suction/discharge pipes length table
Maximum straight length Pressure drop
25C 30C 35C 40C
Bend
45°
Bend
90°
Flue gases pipe
Ø 80 mm ("forced open”
installation)
(type B23P-B53P)
110 m 65m 65m 53m 1 m 1.5 m
Concentric pipe
Ø 60-100 mm (horizontal)
10 m 6 m 6 m 6 m 1.3m 1.6m
Concentric pipe
Ø 60-100 mm (vertical)
11 m 7 m 7 m 7 m 1.3m 1.6m
Concentric pipe
Ø 80-125 mm
25 m 15 m 15 m 15 m 1 m 1.5 m
Twin pipe Ø 80 mm
60+60 m 33+33 m 35+35 m 28+28 m 1 m 1.5 m
b
The straight length includes the rst bend (connection into the boiler), terminals
and joints. An exception is made for the vertical Ø 60-100 mm coaxial pipe, whose
straight length excludes bends.
b
The boiler is supplied without the ue gas exhaust/air suction kit, since it is possible
to use the accessories for condensing appliances that best t the installation
characteristics (see catalogue).
b
The maximum lengths of the pipes refer to the ue accessories available in the
catalogue.
b
It is compulsory to use specic pipes.
b
The non insulated ue gas outlet pipes are potential sources of danger.
b
The use of a longer pipe causes a loss of output of the boiler.
b
Make sure the ue gas discharge pipe is tilted 3° towards the boiler.
b
The exhaust pipes can face in the direction most suited to the installation
requirements.
b
As envisaged by current legislation, the boiler is designed to take in and dispose of
ue gas condensate and/or meteoric water condensate deriving from the ue gas
discharge system using its own siphon.
b
If a condensate relaunch pump is installed, check the technical data (provided by the
manufacturer) regarding output, to ensure it operates correctly.
“Forced open” installation (B23P-B53P) (Fig.13)
In this conguration the boiler is connected to the ø 80 mm ue gases discharge pipe by
means of an adaptor.
- Position the adaptor so that the Ø 60 pipe goes fully into the ue gases turret of the boiler.
- Once positioned, make sure that the 4 notches (A) on the ange connect to the groove
(B) on the Ø 100 of the adaptor.
- Fully tighten the screws (C) that tighten the two locking terminals of the ange so the
adaptor itself is restrained.
Coaxial pipes (ø 60-100 mm) (Fig. 14)
- Position the bend so that the Ø 60 pipe goes fully up against the ue gases turret of the
boiler.
- Once positioned, make sure that the 4 notches (A) on the ange connect to the groove
(B) on the Ø 100 of the bend.
- Fully tighten the screws (C) that tighten the two locking terminals of the ange so the
bend itself is restrained.
Twin pipes (ø 80 mm) (Fig. 15)
The combustion air suction pipe should be selected from the two inputs, remove the closing
plug xed with the screws and x the specic air deector.
- Position the adaptor on the ue gases pipe so that the Ø 60 pipe goes fully up against
the ue gases turret of the boiler.
- Once positioned, make sure that the 4 notches (A) on the ange connect to the groove
(B) on the Ø 100 of the adaptor.
- Fully tighten the screws (C) that tighten the two locking terminals of the ange so the
adaptor itself is restrained.
If the Ø 60-100 to Ø 80-80 splitter kit is used instead of the twin pipe system, there is a loss
in the maximum lengths as shown in the table (g. 15a).
- Place the splitter so that the Ø 60 pipe goes fully up against the ue gases turret of the
boiler.
- Once positioned, make sure that the 4 notches (A) on the ange connect to the groove
(B) on the Ø 100 of the splitter.
- Fully tighten the screws (C) that tighten the two locking terminals of the ange so the
adaptor itself is restrained.
Ø50 Ø60 Ø80
Loss of length (m) 0.5 1.2
5.5 for flue gases pipe
7.5 for air pipe
Coaxial pipes (ø 80-125 mm) (Fig. 16)
- Place the adaptor vertical attachment so that the Ø 60 pipe goes fully up against the ue
gases turret of the boiler.
- Once positioned, make sure that the 4 notches (A) on the ange connect to the groove
(B) on the Ø 100 of the adaptor.
- Fully tighten the screws (C) that tighten the two locking terminals of the ange so the
adaptor itself is restrained.
- Then t the Ø 80-125 adaptor kit on the vertical tting.
Twin pipes with Ø 80 pipework (Ø50 - Ø60 - Ø80) (Fig. 17)
Thanks to the boiler characteristics, a Ø80 ue gas exhaust pipe can be connected to
the Ø50 - Ø60 - Ø80 piping ranges.
b
For the pipe, you are advised to make a project calculation in order to respect the
relevant regulations in force.
The table shows the standard congurations allowed.
Table of standard pipe conguration (*)
Air suction
1 Bend 90° Ø 80
4.5m pipe Ø80
Flue gas discharge
1 Bend 90° Ø 80
4.5m pipe Ø80
Reduction from Ø80 to Ø50 from Ø80 to Ø60
Flue base bend 90°, Ø50 or Ø60 or Ø80
For ducting pipe lengths see table
(*) Use ue gas system accessories made of plastic (PP) for condensing boilers: Ø50
and Ø80 class H1 and Ø60 class P1.
The boilers are factory set to:
25C: 6,200 r.p.m. in heating mode and 7,600 in domestic hot water mode and the maximum
attainable length is 5m for Ø 50 pipe, 18m for Ø 60 pipe and 98m for Ø 80 pipe.
30C: 5,800 rpm in heating mode and 6,900 in domestic hot water mode, and the maximum
length that can be reached is 2m for Ø50, 11m for Ø60 pipe and 53m for Ø80 pipe.
35C: 6,900 rpm in heating mode and 7,800 in domestic hot water mode, and the maximum
length that can be reached is 2m for Ø50 pipe, 11m for Ø60 pipe and 57m for Ø80 pipe.
40C: 6,900 rpm in heating mode and 9,100 in domestic hot water mode, and the maximum
length that can be reached is 7m for Ø60 pipe and 42m for Ø80 pipe (not applicable for
Ø50 pipe).
Should greater lengths be required, compensate the pressure drop with an increase in the
r.p.m.of the fan, as shown in the adjustments table, to provide the rated heat input.
b
The minimum calibration should not be modied.
Table of adjustments
Fan rotations
r.p.m.
Pipework ducts
ΔP at boiler
outlet
Maximum length [m]
Heating DHW Ø 50 Ø 60 Ø 80 Pa
25C
6,200 7,600 5 18 98 174
6,300 7,700 7 (*) 23 (*) 125 (*) 213
6,400 7,800 9 (*) 28 (*) 153 (*) 253
6,500 7,900 11 (*) 33 (*) 181 (*) 292
6,600 8,000 13 (*) 38 (*) 208 (*) 332
6,700 8,100 15 (*) 43 (*) 236 (*) 371
6,800 8,200 17 (*) 48 (*) 263 (*) 410
6,900 8,300 19 (*) 53 (*) 291 (*) 450
7,000 8,400 22 (*) 58 (*) 319 (*) 489
7,100 8,500 24 (*) 63 (*) 346 (*) 528

 Loading...
Loading...











