6
There is a simple formula for calculating the magnication:
Focal width of the telescope tube / Focal width of the eyepiece
= Magnication
The magnication also depends on the focal width of the telescope tube. The telescope has a focal length of
500 mm. From this formula, we see that if you use an eyepiece with a focal width of 20 mm, you will get the
following magnication:
500 mm / 20 mm = 25X magnication
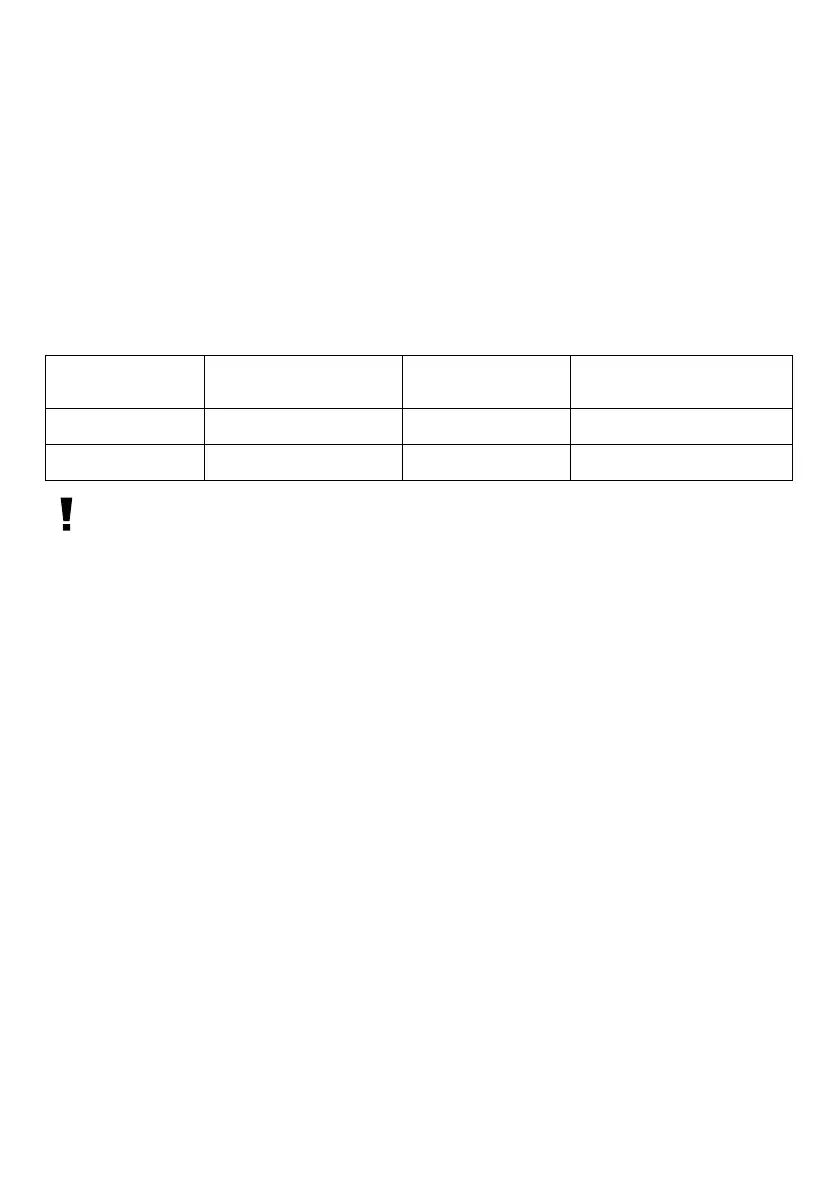
The table below shows some common magnications.
Telescope tube
focal width
Focal width of eyepiece Magnication Magnication with
2X Barlow lens
500 mm 20 mm 25X 50X
500 mm 6 mm 83X 167X
NOTES on cleaning
• Clean the eyepieces and lenses only with a soft, lint-free cloth, like a microbre cloth. Do not apply excess
pressure to the cloth to avoid scratching the lenses.
• To remove more stubborn dirt, moisten the cleaning cloth with an eyeglass-cleaning solution, and wipe the
lenses gently.
• Protect the device from dust and moisture. After use, particularly in high humidity, let the device acclimatise
for a short period of time, so that the residual moisture can dissipate before storing. Remove the dust cover
and store it in the included bag during use.
• To remove dust on the mirrors, use a ne brush or air blower (from your local camera shop or optician). Don’t
touch any mirror surface with your ngers — they may damage the coating.
Telescope ABC:
What do the following terms mean?
Barlow Lens:
The Barlow lens was named after its inventor, Peter Barlow, a British mathematician and physicist who lived
from 1776–1862. The lens can be used to increase the focal width of a telescope. Depending on the type of
lens, it is possible to double or even to triple the focal width. As a result, the magnication can also be in-
creased. Also, see Eyepiece.
Focal width:
Everything that magnies an object via an optic (lens/mirror) has a certain focal width. The focal width is the
length of the path the light travels from the surface of the lens/mirror to its focal point. The focal point is also
referred to as the focus. In focus, the image is clear. In the case of a telescope, the focal widths of the telescope
tube and the eyepieces are combined.
Mirror:
The mirror bends the light which falls on it in such a way that the light creates a clear image at the focal point,
after it has traveled a certain distance (focal width).
 Loading...
Loading...











