Chapter 3: System planning Data network planning
Page 3-28
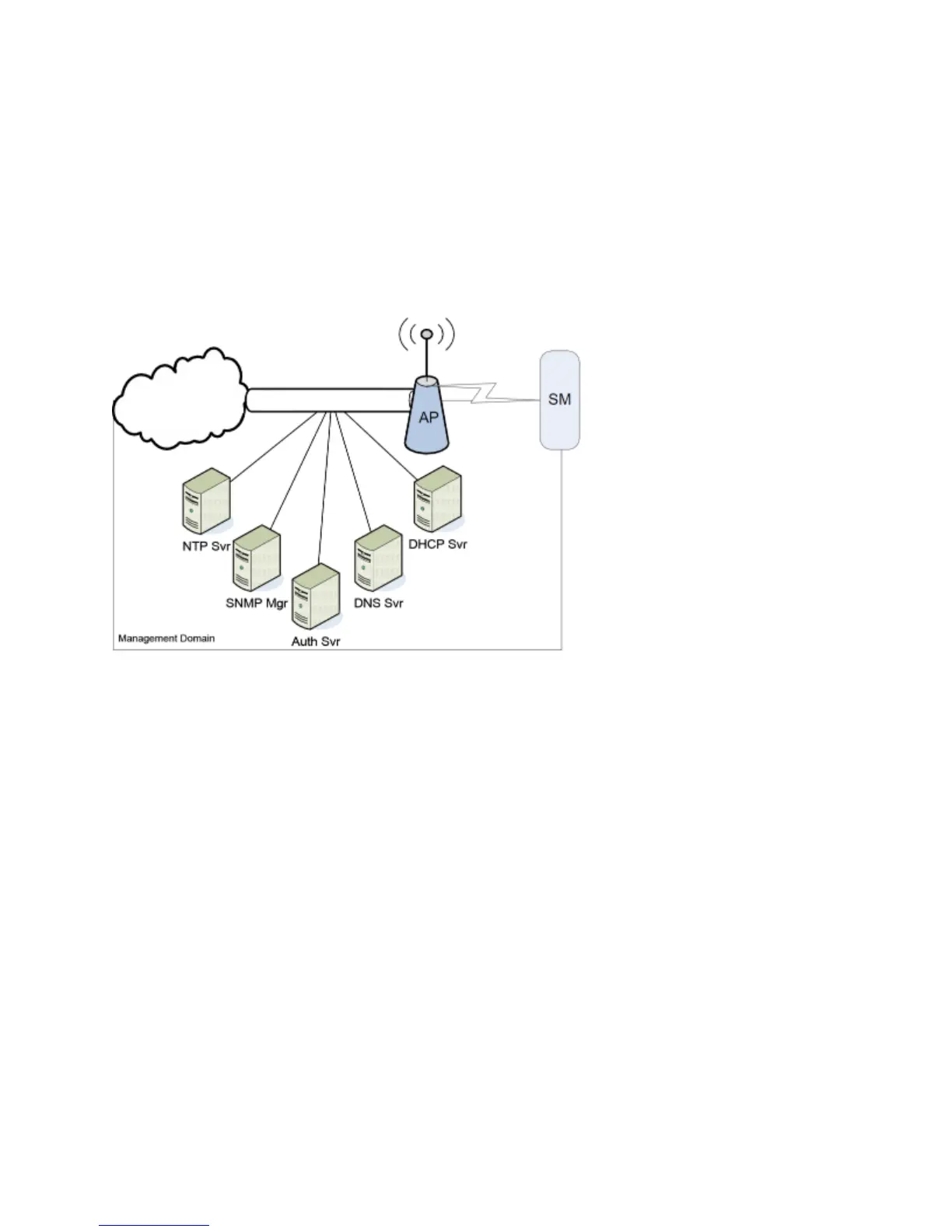
DNS Client
The DNS Client is used to resolve names of management servers within the operator’s
management domain (see Figure 46). This feature allows hostname configuration for NTP servers,
Authorization Servers, DHCP relay servers, and SNMP trap servers. Operators may choose to
either enter in the FQDN (Fully Qualified Domain Name) for the host name or to manually enter the
IP addresses of the servers
.
Figure 46 Cambium networks management domain
Network Address Translation (NAT)
NAT, DHCP Server, DHCP Client and DMZ in SM
The system provides NAT (network address translation) for SMs in the following combinations of
NAT and DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol):
NAT Disabled
NAT with DHCP Client (DHCP selected as the Connection Type of the WAN interface) and DHCP
Server
NAT with DHCP Client(DHCP selected as the Connection Type of the WAN interface)
NAT with DHCP Server
NAT without DHCP
NAT
NAT isolates devices connected to the Ethernet/wired side of a SM from being seen directly from
the wireless side of the SM. With NAT enabled, the SM has an IP address for transport traffic
(separate from its address for management), terminates transport traffic, and allows you to assign
a range of IP addresses to devices that are connected to the Ethernet/wired side of the SM.

 Loading...
Loading...











