E-21
EQN Mode Calculation Examples
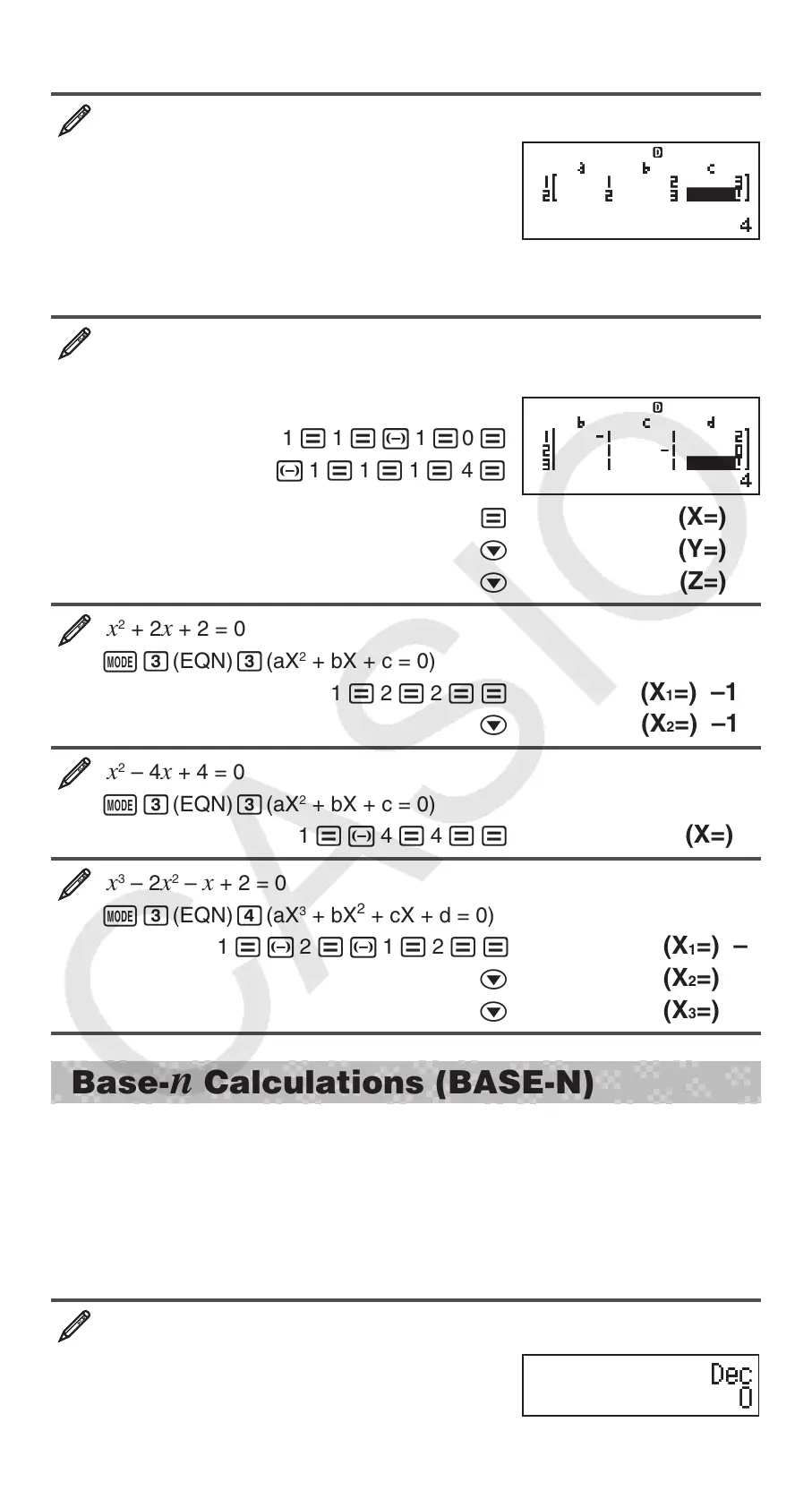
x + 2 y = 3, 2 x + 3 y = 4
N3(EQN) 1(a
n
X + b
n
Y = c
n
)
1 = 2 = 3 =
2 = 3 = 4 =
=
(X=) –1
c (Y=) 2
x – y + z = 2, x + y – z = 0, –x + y + z = 4
N3(EQN) 2(a
n
X + b
n
Y + c
n
Z = d
n
)
1 =- 1 = 1 = 2 =
1 = 1 =- 1 =0 =
- 1 = 1 = 1 = 4 =
=
(X=) 1
c (Y=) 2
c (Z=) 3
x
2
+ 2x + 2 = 0
N3(EQN)3(aX
2
+ bX + c = 0)
1 = 2 = 2 ==
(X
1
=) –1+i
c (X
2
=) –1–i
x
2
– 4x + 4 = 0
N3(EQN)3(aX
2
+ bX + c = 0)
1 =- 4 = 4 ==
(X=) 2
x
3
– 2 x
2
– x + 2 = 0
N3(EQN) 4(aX
3
+ bX
2
+ cX + d = 0)
1 =- 2 =- 1 = 2 ==
(X
1
=) –1
c (X
2
=) 2
c (X
3
=) 1
Base-n Calculations (BASE-N)
Press N4(BASE-N) to enter the BASE-N Mode when you want to
perform calculations using decimal, hexadecimal, binary, and/or octal
values. The initial default number mode when you enter the BASE-N Mode
is decimal, which means input and calculation results use the decimal
number format. Press one of the following keys to switch number modes:
w(DEC) for decimal, 6(HEX) for hexadecimal, l(BIN) for binary, or
i(OCT) for octal.
To enter the BASE-N Mode, switch to the binary mode, and
calculate 11
2
+ 1
2
N4(BASE-N)
MathMath
MathMath
 Loading...
Loading...