• This will display the Matrix Editor with the contents of the copy
destination.
Matrix Calculation Examples
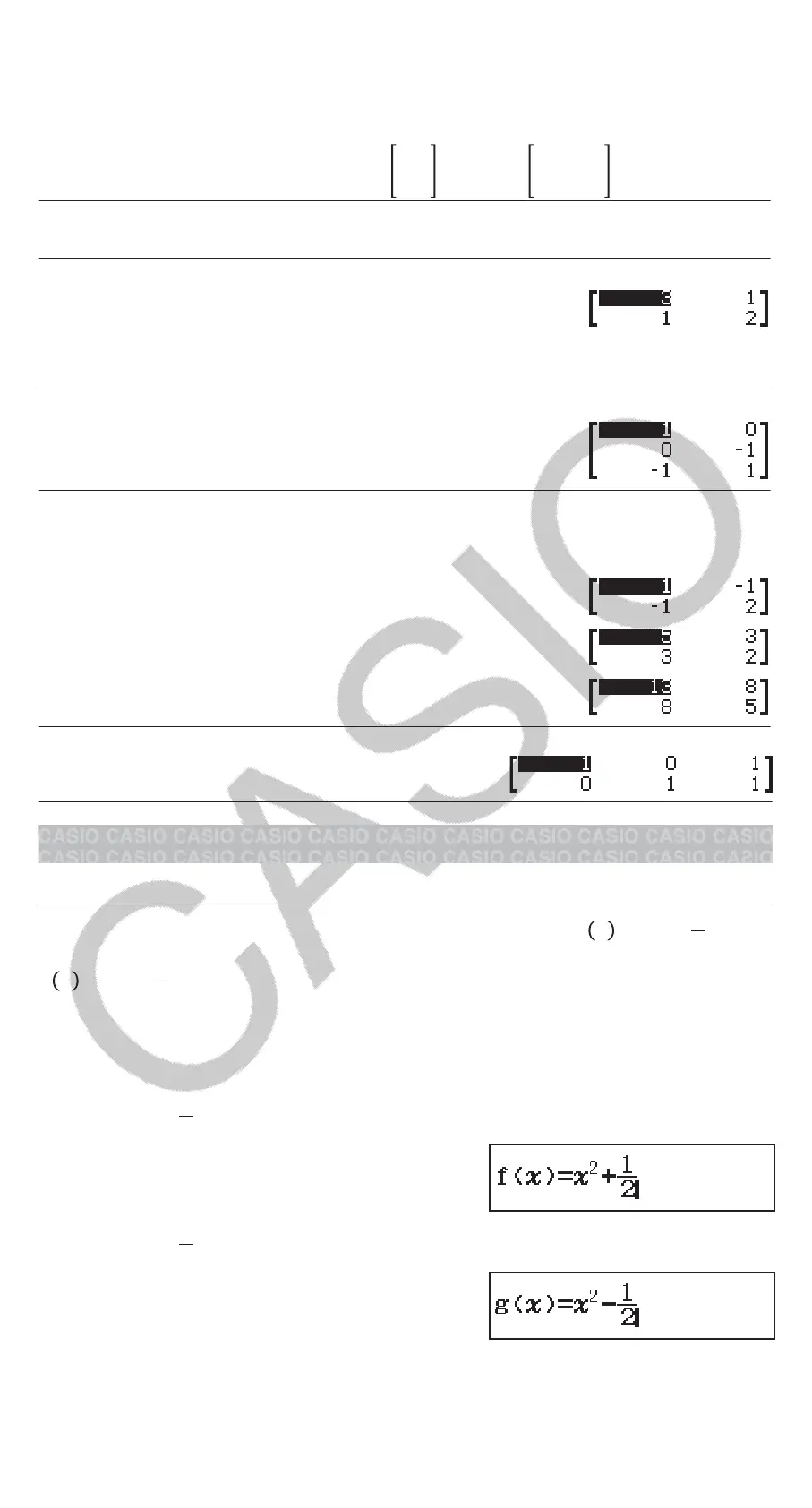
The following examples use MatA =
21
11
, MatB =
10-1
0-1 1
.
To obtain the determinant of MatA (Det(MatA))
(Determinant) MatA
1
To create a 2 × 2 identity matrix and add it to MatA (Identity(2) + MatA)
(Identity) MatA
Note: You can specify a value from 1 to 4 as the Identity command
argument (number of dimensions).
To obtain the transposition of MatB (Trn(MatB))
(Transposition) MatB
To invert, square, and cube MatA (MatA
-1
, MatA
2
, MatA
3
)
Note: You cannot use for this input. Use to input “
-1
”, to specify
squaring, and (x
3
) to specify cubing.
MatA
MatA
MatA (x
3
)
To obtain the absolute value of each element of MatB (Abs(MatB))
(Abs) MatB
Creating a Number Table
The Table Mode generates a number table based on one or two functions.
Example: To generate a number table for the functions 𝑓
𝑥 =𝑥
2
+
1
2
and
g
𝑥 =𝑥
2
−
1
2
for the range -1 ≦ 𝑥 ≦ 1, incremented in steps of 0.5
1. Press , select the Table Mode icon, and then press .
2. Configure settings to generate a number table from two functions.
(SETUP)(Table)(f(x),g(x))
3. Input 𝑥
2
+
1
2
.
(x)12
4. Input 𝑥
2
−
1
2
.
(x)12
5. Press . On the Table Range dialog box that appears, input values for
Start (Default: 1), End (Default: 5), and Step (Default: 1).
27
 Loading...
Loading...