19
Cisco 1841 Integrated Services Router with AIM-VPN/BPII-Plus and Cisco 2801 Integrated Services Router with AIM-VPN/EPII-Plus
OL-8719-01
Cisco 1841 and Cisco 2801 Routers
Self-Tests
In order to prevent any secure data from being released, it is important to test the cryptographic
components of a security module to insure all components are functioning correctly. The router includes
an array of self-tests that are run during startup and periodically during operations. All self-tests are
implemented by the software. An example of self-tests run at power-up is a cryptographic known answer
test (KAT) on each of the FIPS-approved cryptographic algorithms and on the Diffie-Hellman algorithm.
Examples of tests performed at startup are a software integrity test using an EDC, and a set of Statistical
Random Number Generator (RNG) tests. Examples of tests run periodically or conditionally include: a
bypass mode test performed conditionally prior to executing IPSec, and a continuous random number
generator test. If any of the self-tests fail, the router transitions into an error state. In the error state, all
secure data transmission is halted and the router outputs status information indicating the failure.
Examples of the errors that cause the system to transition to an error state:
• IOS image integrity checksum failed
• Microprocessor overheats and burns out
• Known answer test failed
• NVRAM module malfunction.
• Temperature high warning
Enable secret r
w
d
RADIUS secret r
w
d
TACACS+ secret r
w
d
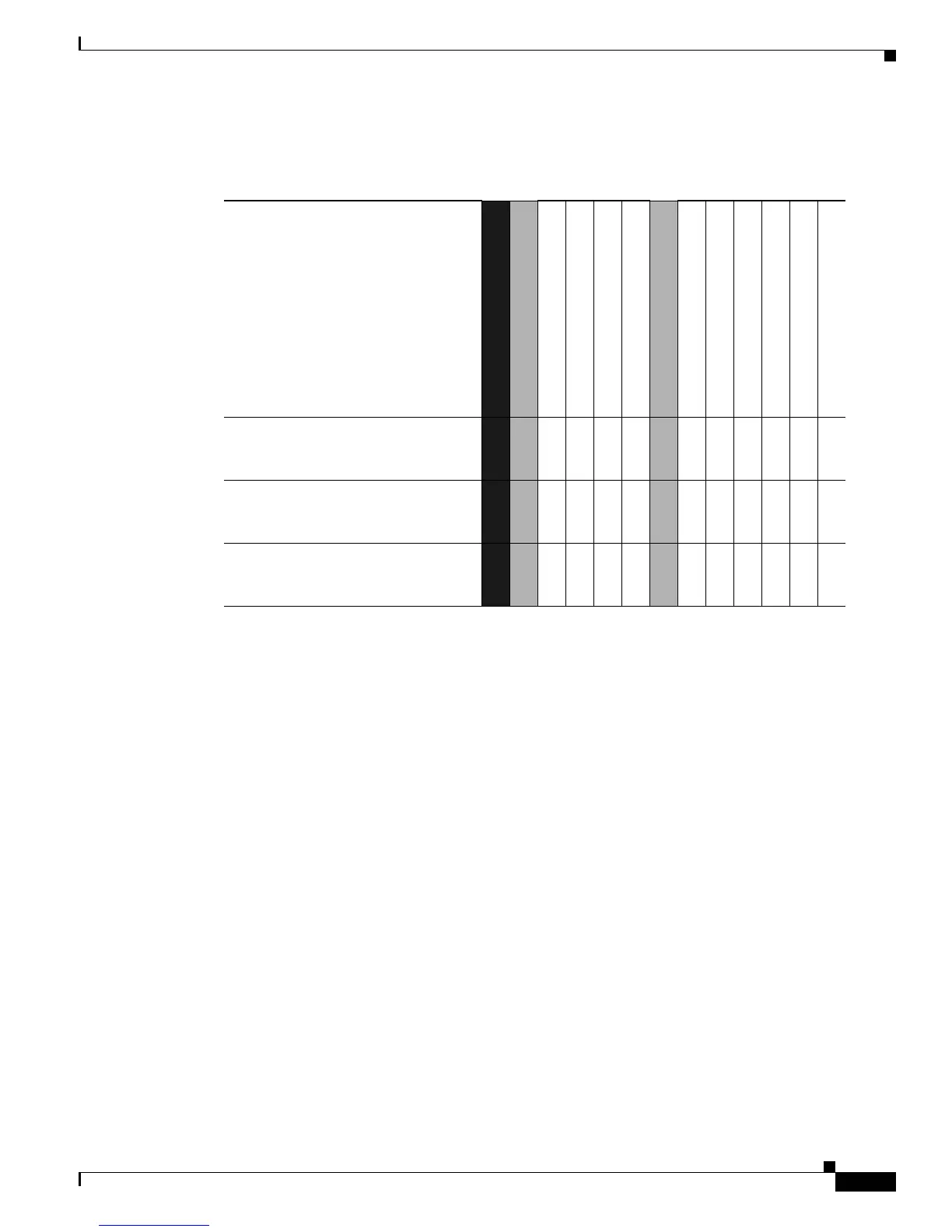
Table 9 Role and Service Access to CSP (Continued)
Note: An enpty entry indicates that a particular SRDI is not accessible by the corresponding service.
SRDI/Role/Service Access Policy
Role/Service
User Role
Status Functions
Network Functions
Terminal Functions
Directory Services
Crypto-Officer Role
Configure the Router
Define Rules and Filters
Status Functions
Manage the Router
Set Encryptions/Bypass
Change WAN Interface Cards
 Loading...
Loading...