3. Instruction Set
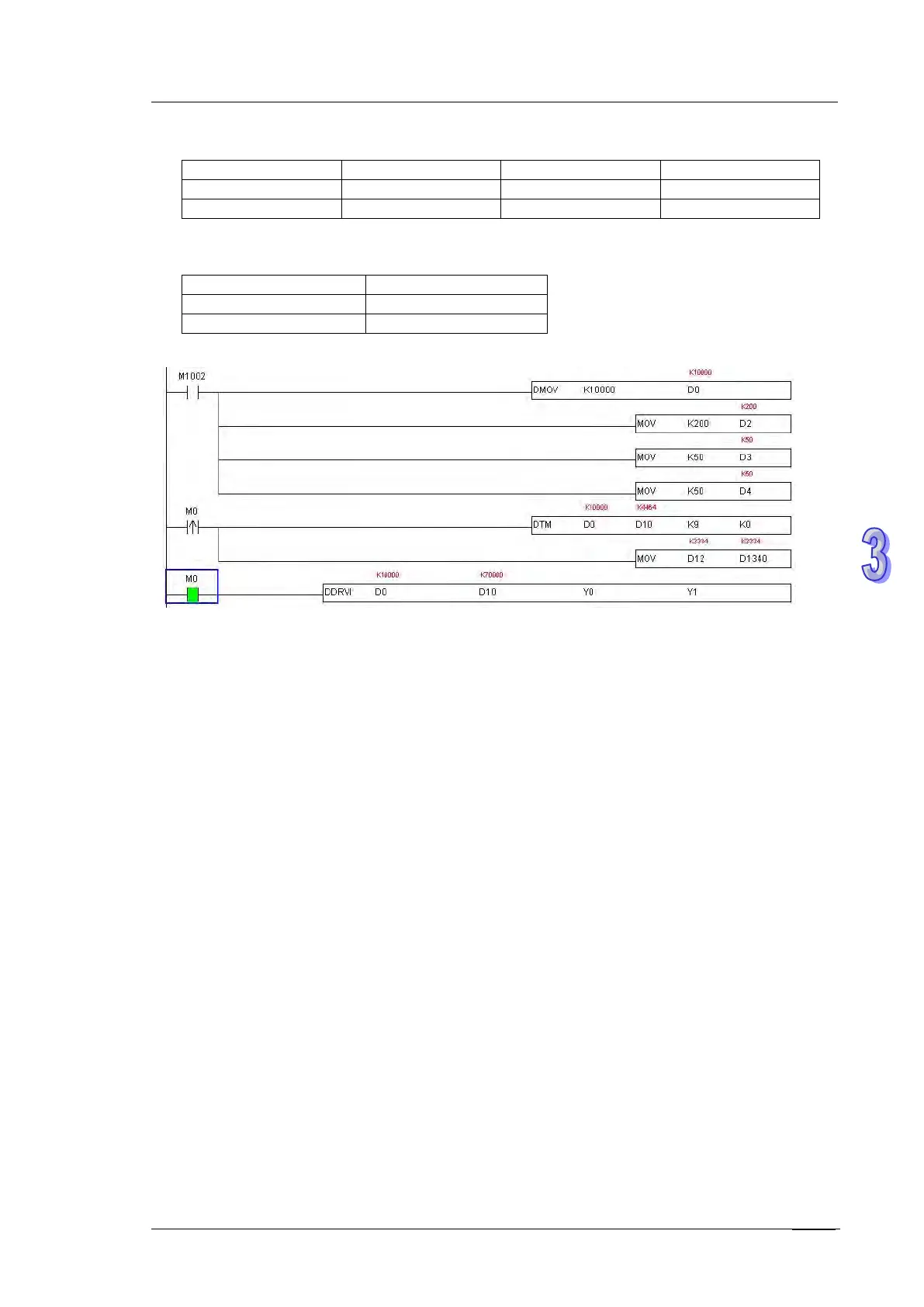
2. Assume the data of source device is set up as below:
3. The optimal positioning results can be obtained as below:
K11: Conversion from Local Time to Local Sidereal Time
Unlike the common local time defined by time zones, local sidereal time is calculated based on
actual longitude. The conversion helps the user obtain the more accurate time difference of
each location within the same time zone.
Explanation on operands:
S+0, S+1: Longitude (32-bit floating point value; East: positive, West: negative)
S+2: Time zone (16-bit integer; unit: hour)
S+3~ S+8: Year, Month, Day, Hour, Minute, Second of local time (16-bit integer)
D+0~D+5: Year, Month, Day, Hour, Minute, Second of the converted local sidereal time (16-bit
integer)
n: Reserved
Example:
Input: Longitude F121.55, Time zone: +8, Local time: AM 8:00:00, Jan/6/2011
Conversion results: AM 8:06:12, Jan/6/2011
K12: Proportional Value Calculation Function of Multi-point Areas (16-bit values)
Explanation on operands (16-bit values):
S: input value

 Loading...
Loading...