Chapter 12 Description of Parameter SettingsCP2000
12.1-09-6
ASCII Mode
Command Message: Response Message
STX ‘:’ STX ‘:’
ADR 1
ADR 0
‘0’
ADR 1
ADR 0
‘0’
‘1’ ‘1’
CMD 1 ‘1’ CMD 1 ‘1’
CMD 0 ‘0’ CMD 0 ‘0’
Target register
‘0’
Target register
‘0’
‘4’ ‘4’
‘0’ ‘0’
‘0’ ‘0’
Number of register
(count by word)
‘0’
Number of register
(count by word)
‘0’
‘0’ ‘0’
‘0’ ‘0’
‘2’ ‘2’
Number of register
(count by byte)
‘0’
LRC Check
‘E’
‘4’ ‘9’
The first data content
‘1’
END
CR
‘3’ LF
‘8’
‘8’
The second data
content
‘0’
‘F’
‘A’
‘0’
LRC Check
‘9’
‘B’
END
CR
LF
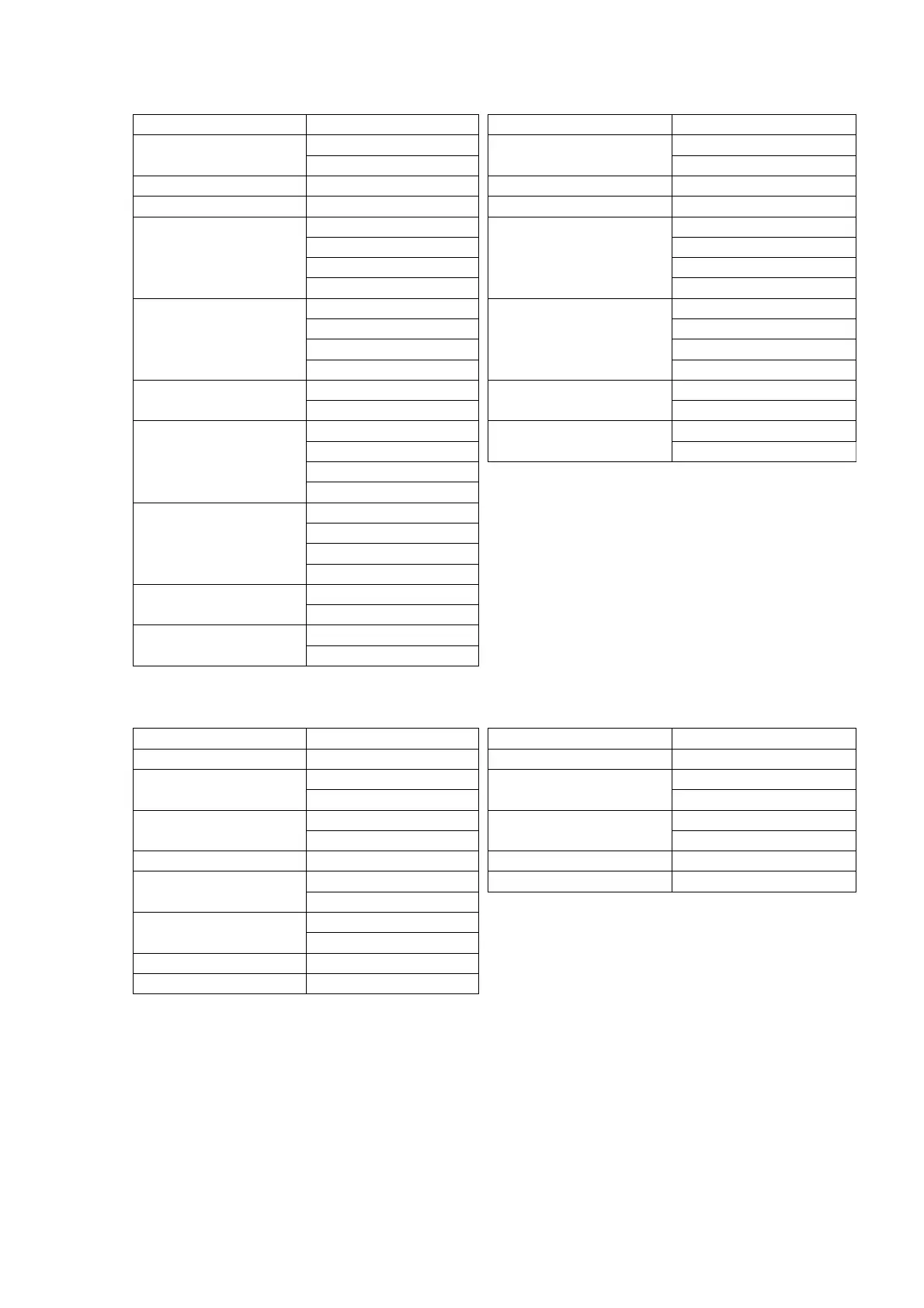
RTU mode:
Command Message: Response Message:
ADR 01H ADR 01H
CMD 10H CMD 1 10H
Target register
04H
Target register
04H
00H 00H
Number of register
(Count by word)
00H Number of register
(Count by word)
00H
02H 02H
Quantity of data (byte) 04 CRC Check Low 40H
The first data content
13H CRC Check High F8H
88H
The second data
content
0FH
A0H
CRC Check Low ‘9’
CRC Check High ‘A’
Check sum
ASCII mode:
LRC (Longitudinal Redundancy Check) is calculated by summing up the values of the bytes from
ADR1 to last data character then calculating the hexadecimal representation of the
2’s-complement negation of the sum.
For example,
01H+03H+21H+02H+00H+02H=29H, the 2’s-complement negation of 29H is D7H.
 Loading...
Loading...











