• Keep hands away from cutting area. Never reach underneath
the material for any reason. Hold front of saw by grasping the
contoured gripping area. Do not insert fingers or thumb into the
vicinity of the reciprocating blade and blade clamp. Do not stabilize
the saw by gripping the shoe.
• Keep blades sharp. Dull blades may cause the saw to swerve or
stall under pressure.
• When cutting pipe or conduit ensure that they are free from
water, electrical wiring, etc.
• Allow the motor to come to a complete stop before
withdrawing the blade from the kerf (the slot created by
cutting). A moving blade may impact the workpiece causing a
broken blade, workpiece damage or loss of control and possible
personal injury.
• Never hold work in your hand, lap or against parts of your
body when sawing. The saw may slip and the blade could
contact the body causing injury.
• Keep handles dry, clean, free from oil and grease. This will
enable better control of the tool.
• Clean out your tool often, especially after heavy use. Dust
and grit containing metal particles often accumulate on interior
surfaces and could create an electric shock hazard.
• Do not operate this tool for long periods of time. Vibration
caused by the operating action of this tool may cause permanent
injury to fingers, hands, and arms. Use gloves to provide extra
cushion, take frequent rest periods, and limit daily time of use.
• Avoid prolonged contact with dust from power sanding,
sawing, grinding, drilling, and other construction activities.
Wear protective clothing and wash exposed areas with
soap and water. Allowing dust to get into your mouth, eyes, or
lay on the skin may promote absorption of harmful chemicals.
WARNING: Wear appropriate hearing protection during use.
Under some conditions and duration of use, noise from this product
may contribute to hearing loss.
• Air vents often cover moving parts and should be avoided.
Loose clothes, jewelry or long hair can be caught in moving parts.
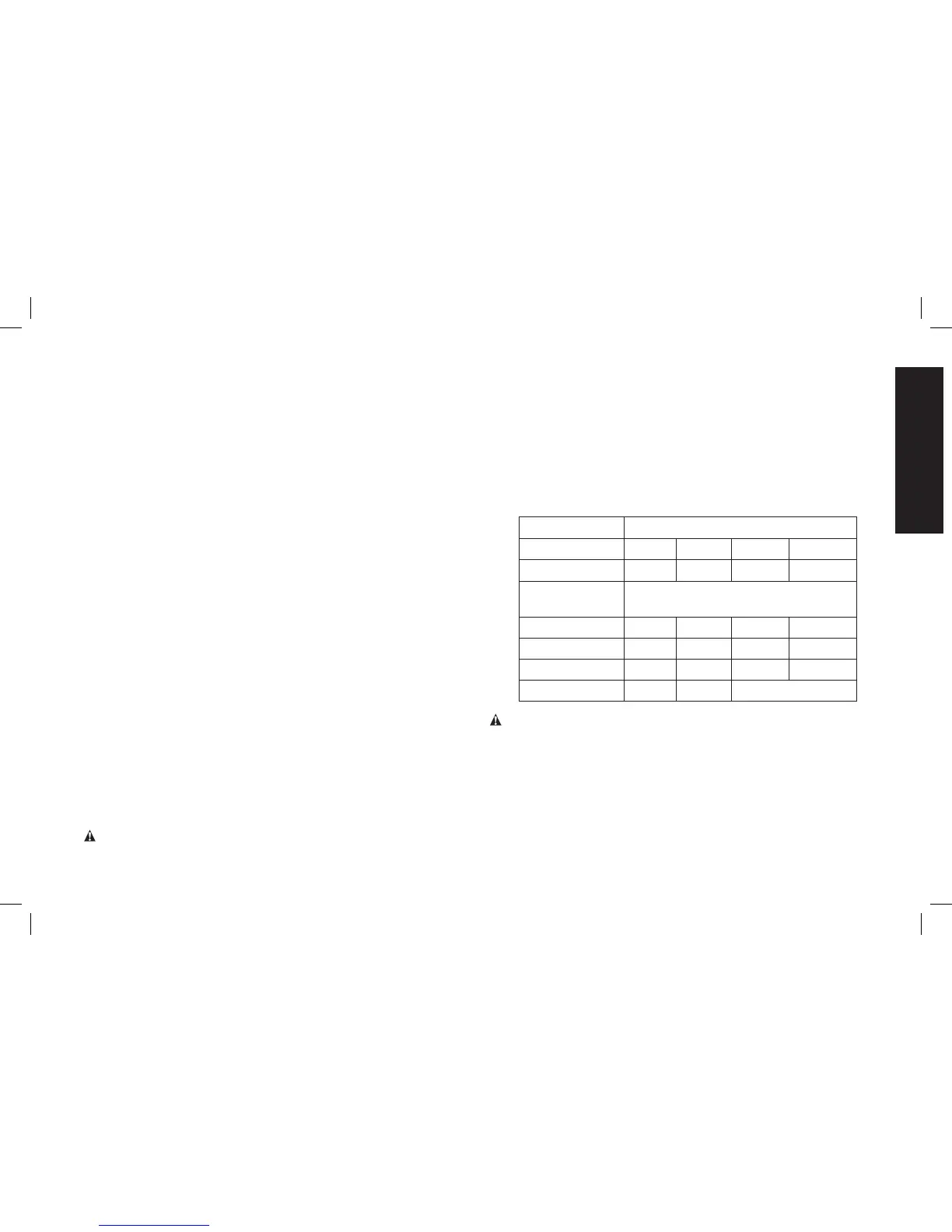
• An extension cord must have adequate wire size for safety.
An undersized cord will cause a drop in line voltage resulting in loss
of power and overheating. When using more than one extension
to make up the total length, be sure each individual extension
contains at least the minimum wire size. The following table shows
the correct size to use depending on cord length and nameplate
ampere rating. If in doubt, use the next heavier gauge. The smaller
the gauge number, the heavier the cord.
Voltage (Volts)
Total length of cord in meters (m)
120–127V 0–7 7–15 15–30 30–50
220–240V 0–15 15–30 30–60 60–100
Rated Ampere
range
Minimal cross-sectional area of the
cord in meters (mm
2
)
0–6A 1.0 1.5 1.5 2.5
6–10A 1.0 1.5 2.5 4.0
10–12A 1.5 1.5 2.5 4.0
12–16A 2.5 4.0 Not Recommended
WARNING: Some dust created by power sanding, sawing,
grinding, drilling, and other construction activities contains chemicals
known to cause cancer, birth defects or other reproductive harm.
Some examples of these chemicals are:
• lead from lead-based paints,
• crystalline silica from bricks and cement and other masonry
products, and
• arsenic and chromium from chemically-treated lumber.
Your risk from these exposures varies, depending on how often you
do this type of work. To reduce your exposure to these chemicals:

 Loading...
Loading...