7
Eclipse Ratio Regulator, V1, Instruction Manual 742, 5/1/2009
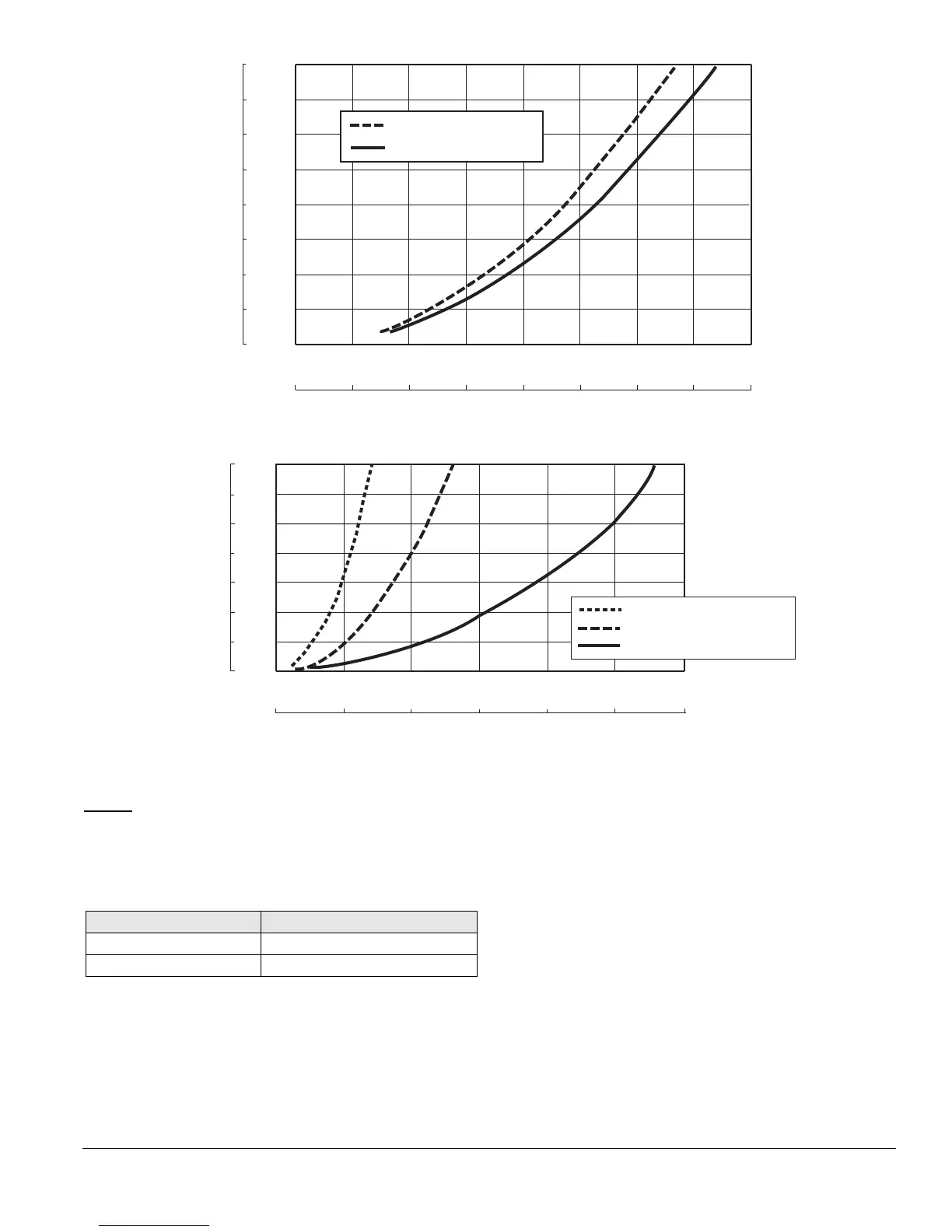
Figure 3.1. Flow vs Pressure Drop, 3/4" & 1" NPT (Rp) Models
Figure 3.2. Flow vs Pressure Drop, 1-1/2", 2" & 3" NPT (Rp) Models
NOTE:
Above graphs are for natural gas (0.60 s.q.). For
propane or butane, multiply the gas flow by the factors
listed below, to calculate the equivalent natural gas flow,
then find the pressure drop from the previous graphs.
Example: Find the pressure drop created by 15,000 scfh
of propane through an ES369 ratio regulator.
1. Convert propane to the equivalent natural gas flow:
15,000 x 1.58 = 23,700 scfh
2. Plot the point where 23,700 scfh crosses the ES369
curve on the above graph.
3. Translate the intersection point back to the pressure
drop axis.
4. The pressure drop at 23,700 scfh natural gas,
equivalent to 15,000 scfh propane, is approximately
23.5" w.c.
10.0
8.75
7.5
6.25
5.0
3.75
2.5
1.25
0.0
0200
5.66
400
11.33
600
16.99
800
22.66
1000
28.32
1200
33.99
1400
39.66
1600
45.32
Model ES365 & ES365M
Model ES366 & ES366M
Capacity, scfh
∆P "wc
4.0
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
∆P mbar
0.0
Capacity, Nm³/hr
0
05,000
141.6
10,000
283.3
15,000
424.9
20,000
566.5
25,000
708.2
30,000
849.8
Model ES363, ES363M
Model ES368, ES368M
Model ES369, ES369M
Capacity, scfh
∆P "w.c.
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
∆P mbar
0
12.5
25
37.5
50
62.5
75
87.5
0
Capacity, Nm
3
/hr
Table 3.3 Conversion Factors
Gas Conversion Factor
Propane (1.5 s.g.) 1.58
Butane (2.0 s.q.) 1.82

 Loading...
Loading...