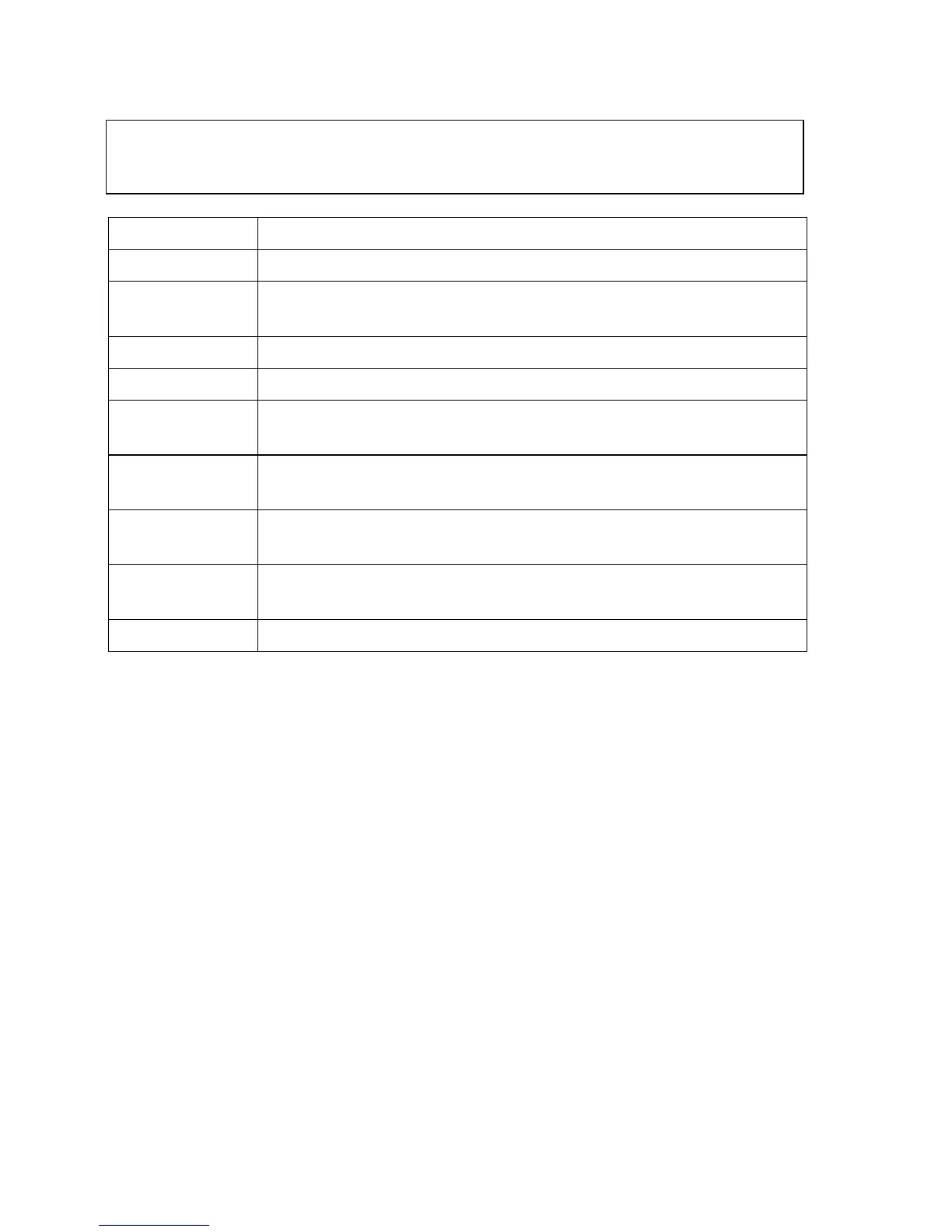
Effects of Carbon Monoxide (CO) poisoning
Warning: Ensure that the meter is powered, at room temperature, and in an area free of
Carbon Monoxide (CO) before starting measurements. If not, the meter will read
incorrectly when subsequently measuring CO.
0-1 PPM Normal background levels
9 PPM Maximum allowable short term exposure
50 PPM
Maximum allowable continuous exposure level in any 8-hour
period, according to OSHA
200 PPM Mild headache, fatigue, nausea and dizziness after 2-3 hours
400 PPM Frontal headache with 1-2 hours, life threatening after 3 hours
800 PPM
Dizziness, nausea, convulsions within 45 minutes. Unconsciousness
within 2 hours. DEATH WITHIN 2 TO 3 HOURS
1600 PPM
Headache, dizziness, nausea within 20 minutes, DEATH WITHIN 1
HOUR
3200 PPM
Headache, dizziness, nausea within 5-10 minutes. DEATH WITHIN
25-30 MINUTES
6400 PPM
Headache, dizziness, nausea within 1-2 minutes. DEATH WITHIN
10-15 MINUTES
12800 PPM DEATH WITHIN 1 TO 3 MINUTES
Regulatory exposure limits for Carbon Dioxide (CO
2
)
ASHRAE Standard 62-1989: 1000ppm: CO
2
concentration in occupied building should not
exceed 1000ppm.
OSHA: 5000ppm: Time weighted average over five 8-hour workday should not exceed
5000ppm.
Building bulletin 101 (BB101): 1500ppm. UK standards for schools state that CO
2
averaged
over the whole day (i.e. 9:00am to 3:30 pm) should not exceed 1500ppm.
Germany, Japan, Australia, UK: 5000ppm, 8 hours weighted average in occupational exposure
limit is 5000ppm.
EPA Taiwan (Type 1): Indoor areas such as department stores, theaters, restaurants, libraries
have acceptable CO
2
concentration of 1000ppm over an 8-hour average period.
EPA Taiwan (Type 2): Indoor areas with special requirements for good air quality such as
schools, hospitals, and day care centers have suggested CO
2
level of 600ppm.

 Loading...
Loading...











