070.610-IOM (JUL 21)
Page 41
RWF II Rotary Screw Compressor Units
Maintenance
Vibration analysis
Periodic vibration analysis can be useful in detecting
bearing wear and other mechanical failures. If vibration
analysis is used as a part of your preventive main tenance
program, take the following guidelines into consideration.
1. Always take vibration readings from exactly the same
places and at exactly the same percentage of load.
2. Use vibration readings taken from the new unit at
start-up as the base line reference.
3. Evaluate vibration readings carefully as the instru ment
range and function used can vary. Findings can be eas-
ily misinterpreted.
4. Vibration readings can be inuenced by other equip-
ment operating in the vicinity or connected to the
same piping as the unit.
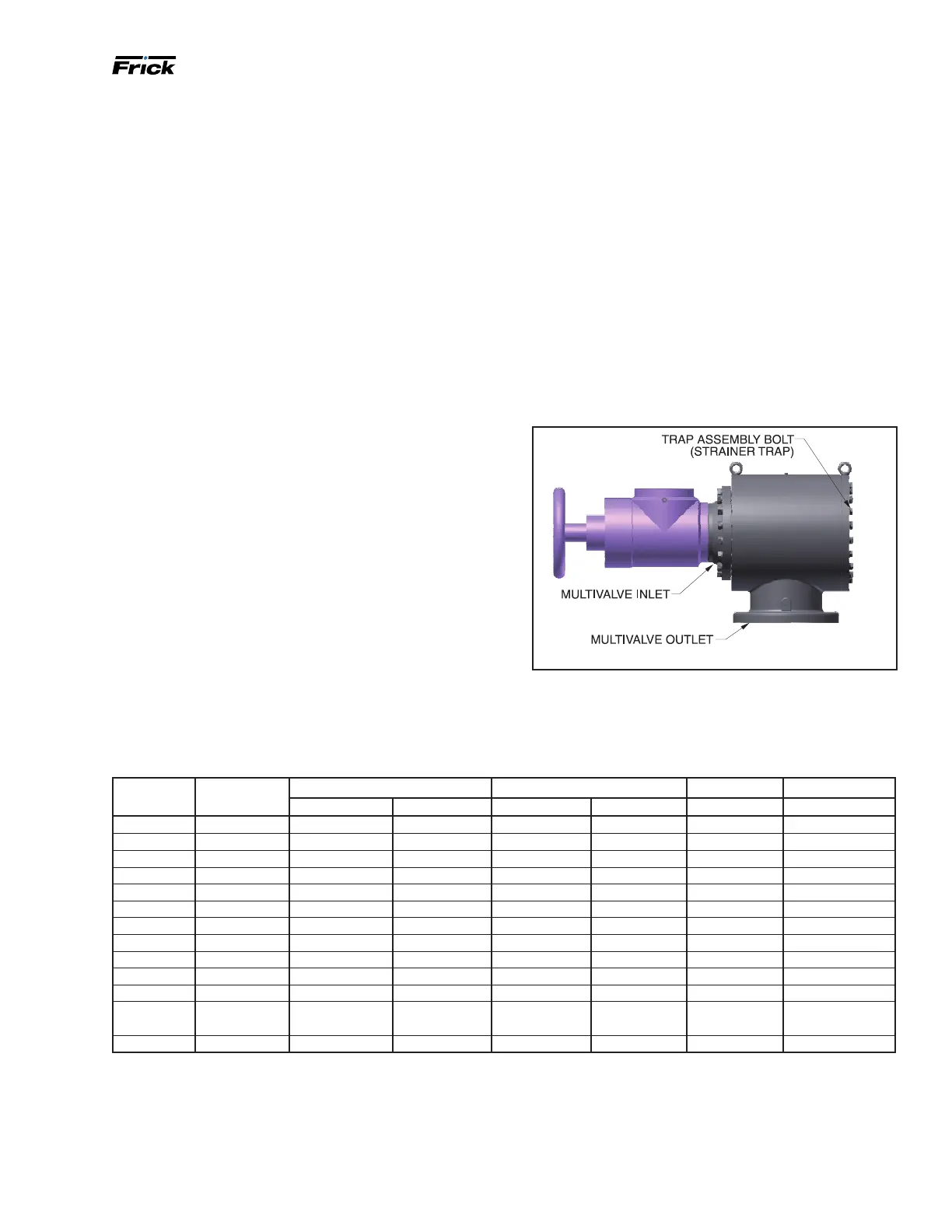
Figure 45: Multivalve Arr. - 496, 676, 856 and 1080
the head may have increased through wear to the point
where the pump is losing capacity or pressure. Resetting
end clear ance will normally improve pump performance.
See Technical Service Manual on particular model series
for procedure on adjusting end clear ance for the pump
involved.
Maintenance program
To obtain maximum compressor unit perform ance and
ensure reliable operation, follow a regular main tenance
program.
Check the compressor unit daily for leaks, abnormal vibra-
tion, noise, and proper operation. A log should also be
maintained. Initial oil analysis and vibration analysis should
be done at start-up and continued per the maintenance
schedule.
Vibration analysis is recommended every 6 months to
ensure that the internal components of the screw com-
pressor are in compliance with expected vibration levels,
based on the initial, full spectrum baseline performed at
start-up. If the Frick PhD on-board vibration monitoring
system is utilized, the 6 month vibration analysis is not re-
quired. Frick PhD provides continuous vibration monitoring
that fullls the maintenance requirement. If the Frick PhD
has an alarm or shut down event, a full spectrum vibration
analysis would then be required to specically identify the
cause of the alarm or shut down.
In addition, a Frick compressor package without PhD
monitoring already in operation can be retrotted with the
Frick PhD on-board vibration monitoring system to fulll
the vibration maintenance recommendation. However, it is
also necessary to establish a current baseline vibration with
a full spectrum analysis in order for the PhD retrot to be
compliant.
Table 13: RWF II bolt sizes and torque values
RWF II
model
Compressor
model
Disch. ange to separator ange
Compressor suction ange Strainer trap
Multi-valve inlet
Bolt size (mm) Torque* (ft-lb) Bolt size (mm) Torque* (ft-lb) Torque* (ft-lb)
Torque* (ft-lb)
100/119 SS SGC 1913 M20 X 2.5 180 M20 X 2.5 180 180 —
134/159 SS SGC 1918 M20 X 2.5 180 M20 X 2.5 180 180 —
177/209 SS SGC 2313 M20 X 2.5 180 M20 X 2.5 180 180 —
222/264 SS SGC 2317 M20 X 2.5 180 M22 X 2.5 280 280 —
270 SGC 2321 M20 X 2.5 180 M22 X 2.5 280 280 —
316/375 SS SGC 2813 M22 X 2.5 280 M22 X 2.5 280 280 —
399/472 SS SGC 2817 M22 X 2.5 280 M24 X 3.0 300 300 —
480 SGC 2821 M22 X 2.5 280 M24 X 3.0 300 300 —
546 SGC 2824 M22 X 2.5 280 M24 X 3.0 300 300 —
496 SGCB/H 3511 M24 X 3.0 300 M30 X 3.5 350 250 250
676 SGCB/H 3515 M24 X 3.0 300 M30 X 3.5 350 250 250
856
SGCB/H 3519
SGXB/H 3519
M24 X 3.0 300 M30 X 3.5 350 250 250
1080 SGXB 3524 M24 X 3.0 300 M30 X 3.5 350 250 250
* Based on: Gaskets-Garlock
®
Blue-Gard
®
3300; Bolts-class 8.8 or stronger hex head bolts, lightly oiled and clean

 Loading...
Loading...