Gree GMV6 DC Inverter VRF Units Service Manual
184
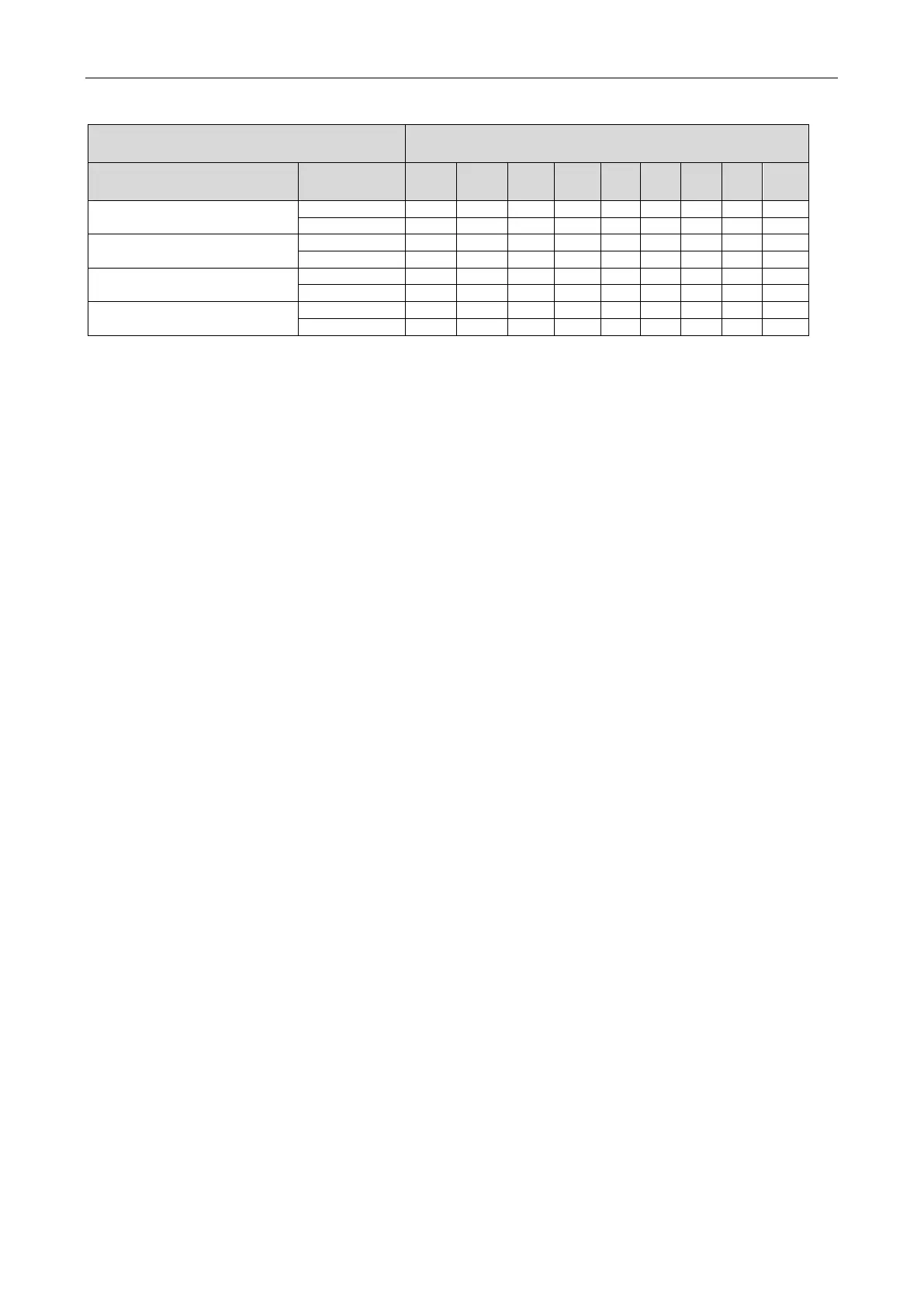
2.2 Refrigerant charging amount B of every module
Refrigerant charging amount B of every module
②
Module capacity (kW)
IDU/ODU rated capacity
①
Quantity of
22.4 28.0 33.5 40.0 45.0 50.4 56.0 61.5 68.0
50%≤C≤70%
70%<C≤90%
90%<C≤105%
105%<C≤135%
Notes:
① Rated capacity configuration rate of indoor unit and outdoor unit C = sum of indoor unit rated
cooling capacity / sum of outdoor unit rated cooling capacity.
② If all indoor units are all fresh air indoor units, the added refrigerant amount for each module B
is 0kg.
③ If all fresh air indoor units are mixed with the general VRF indoor units, charge the refrigerant
according to the refrigerant-charging method of the general indoor unit.
For example1:
Outdoor unit consists of one 28kW module and one 45kW module. Five 14kW duct type units are
used as indoor units.
IDU/ODU rated capacity collocation ratio C=14.0×5/(28.0+45.0)=96%. The quantity of included IDUs
is more than 4 sets. Please refer to the above table.
Additional refrigerant quantity B for 28kW module is 2.0 kg.
Additional refrigerant quantity B for 45kw module is 4 kg.
So, ∑Refrigerant charging amount B of every module=2.0+4=6 kg.
Suppose the Pipeline charging amount A=∑Liquid pipe length×refrigerant charging amount of every
1m liquid pipe=20kg.
Total refrigerant charging amount R=20+6=26kg.
For example 2:
Outdoor unit is a 45kW module and the indoor unit is a 45kW fresh air unit. The quantity (B) of
refrigerant added to this module is 0kg.
So, ∑Refrigerant charging amount B of every module= 0kg.
Suppose the Pipeline charging amount A=∑Liquid pipe length×refrigerant charging amount of every
1m liquid pipe = 5kg.
Total refrigerant charging amount R = 5+0=5kg.
Modular combination of outdoor unit subjects to combinations that is currently available.

 Loading...
Loading...











