first document pixels so that the user documents will have an accurate placement of the image on
scans and copies. It reports a scanner error 6 message if the reference features are not found.
●
Calibration. This test, also known as scanner color calibration, enables the product to identify the black
and white on every pixel in the CCD. Calibration occurs in two major processes: a broad (analog)
adjustment of all pixels to bring them into the target output range, and a pixel-by-pixel adjustment
(digital) to fine tune the actual black and white response. The calibration process occurs under the left
side of flatbed image scanner where there is a special white calibration label.
Calibration is the most important step in creating a high quality image. Calibration problems can include
color inaccuracies, brightness inaccuracies, and vertical streaks through the image. The calibration
process identifies any bad pixels and enables the image formatter to recreate the lost information from
adjacent pixels. Extreme cases of this problem can appear as large vertical streaks or image smears.
The user has no control over the calibration process itself or this pixel-replacement process.
Copy or scan sequence of events
To create an accurate rendition of a document, the scanner must be calibrated for the requested operation. If
the user selects a scan at 600 ppi color, the flatbed image scanner calibrates for that specific operational
mode. Subsequently, the flatbed image scanner automatically re-calibrates for the next requested
operation. Calibration does not occur for every new copy request.
Normal sequence of operation for a flatbed copy or scan job includes the following.
1. LEDs illuminate.
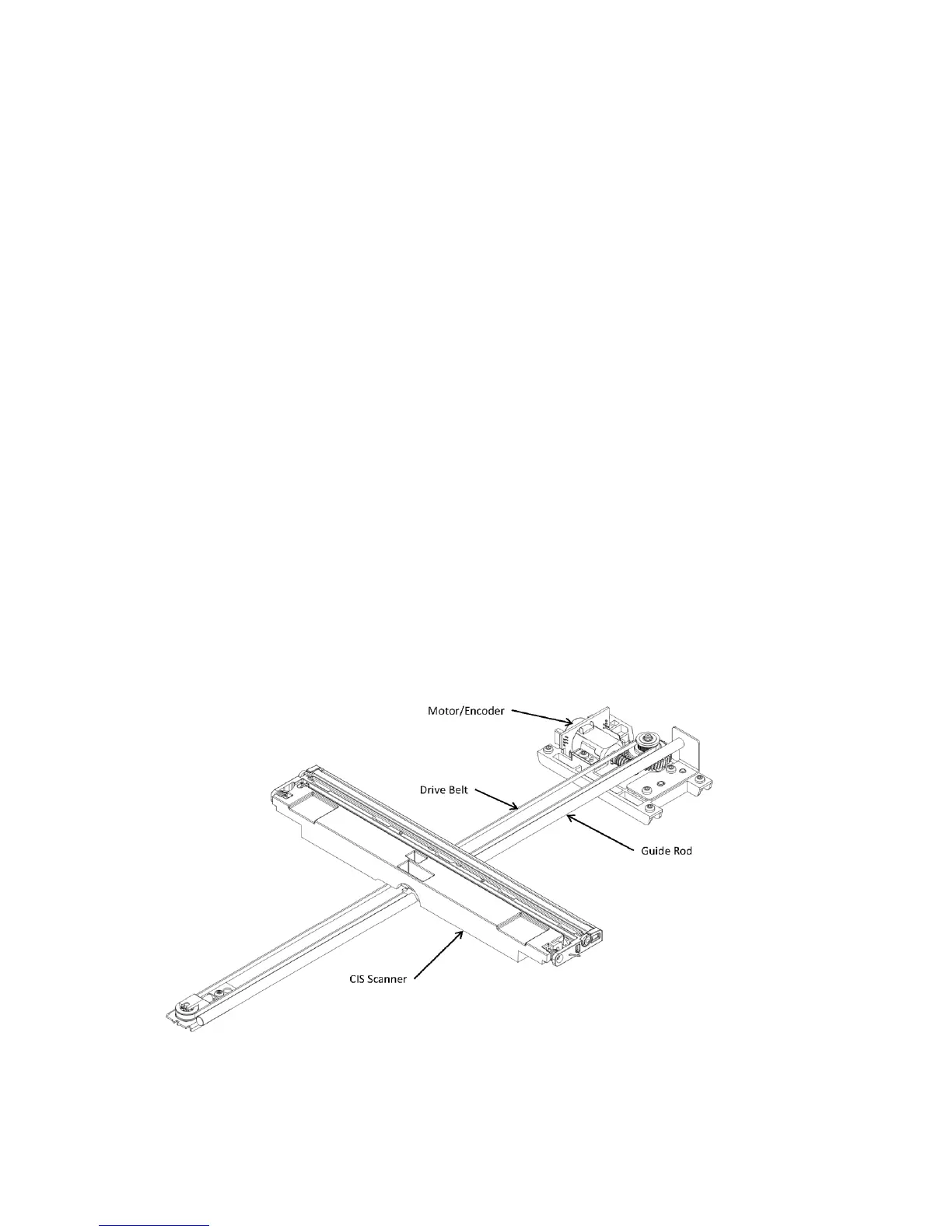
2. Carriage motion begins moving the CIS scanner toward the right.
3. Image capture continues for the entire page or length requested in a scan operation.
4. Carriage returns to the home position on the left.
Scanner operation
At power-on, the CIS scanner moves slowly to the left. The motor encoder is monitored to determine when
the scanner has found the left side wall. The scanner then moves to the right and identifies the document
origin (position of the original). If the document origin cannot be located, a default position is used.
28 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW

 Loading...
Loading...











