Multimedia Traffic Control with IP Multicast (IGMP)
How IGMP Operates
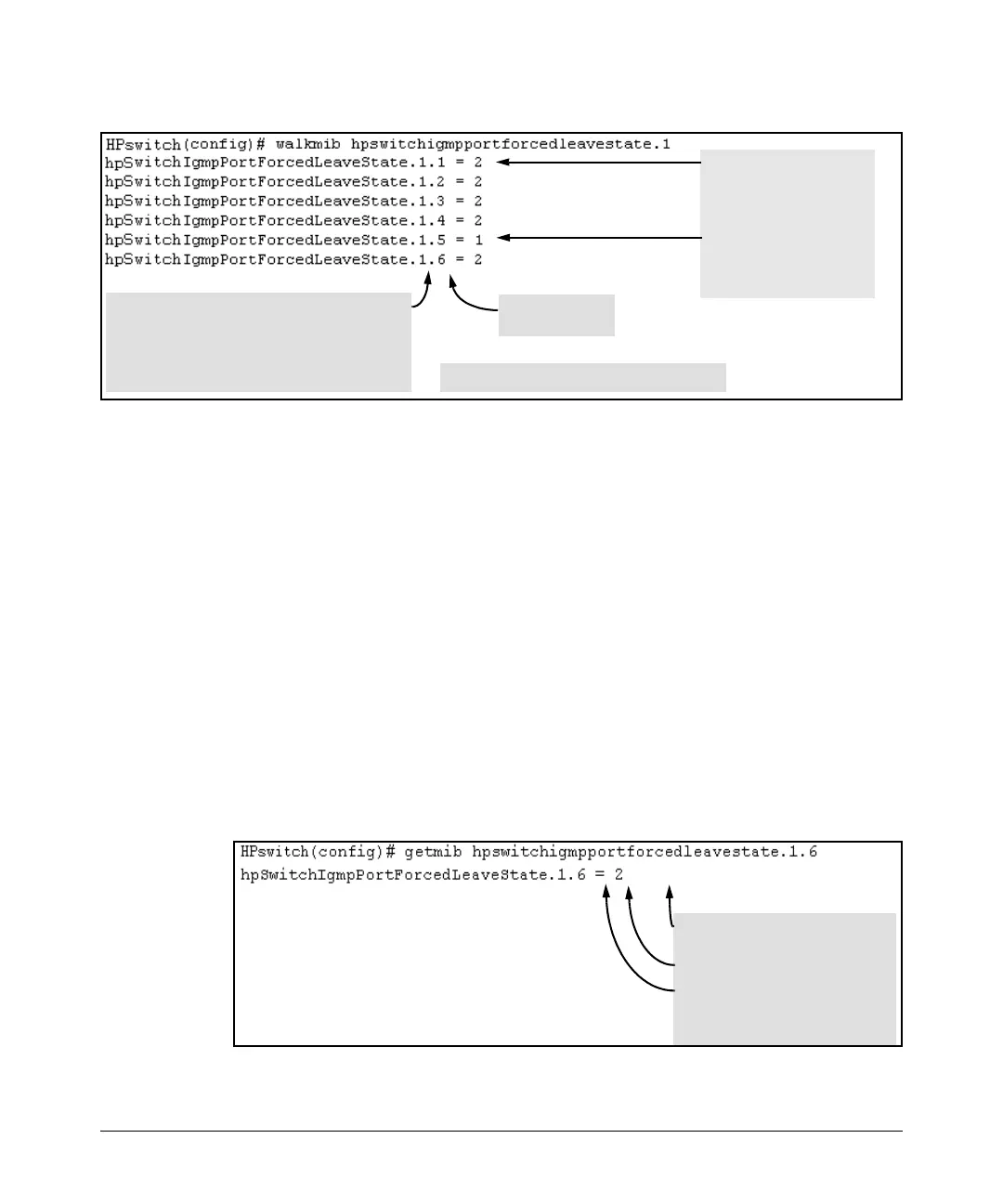
The 2 at the end of a port
listing shows that Forced
Fast-Leave is disabled on
the corresponding port.
The
1 at the end of a port
listing shows that Forced
Fast-Leave is enabled on
the corresponding port.
Ports 1-6: 6- Port 109/1000T Module in Slot A
Internal VLAN Number for the Default VLAN
Note: Internal VLAN numbers reflect the sequence
in which VLANs are created, and are not related to
the unique VID assigned to each VLAN. (See the
“Note on VLAN Numbers on page 4-15.)
Sequential Port
Numbers
Figure 4-4. Example of a Forced Fast-Leave Listing where all Ports are Members of the Default VLAN
To List the Forced Fast-Leave State for a Single Port. (See the “Note
on VLAN Numbers” on page
4-15.)
Use the switch’s CLI and use the
getmib command, as shown below.
Syntax: getmib hpSwitchIgmpPortForcedLeaveState.< vlan number >< .port
number >
- OR -
getmib 1.3.6.1.4.1.11.2.14.11.5.1.7.1.15.3.1.5.< vlan number >< .port number >
For example, the following command to list the state for port A6 (which, in
this case, belongs to the default VLAN) produces the indicated listing:
The 2 shows that Fast Forced-Leave
is disabled on port 7.
The
6 specifies port A6.
The 1 indicates the default VLAN.
(See the “Note on VLAN Numbers”
on page 4-15.)
Figure 4-5. Example Listing the Forced Fast-Leave State for a Single Port on the Default
VLAN
4-17

 Loading...
Loading...











