Access Control Lists (ACLs) for the Series 3400cl and Series 6400cl Switches
ACL Operation
Note on Implicit For ACLs configured to filter inbound packets, note that Implicit Deny filters
Deny
any packets, including those with a DA specifying the switch itself. This
operation helps to prevent management access from unauthorized IP sources.
Is there a
match?
Perform action
(permit or deny).
No
Test a packet against
criteria in first ACE.
Yes
No
Yes
Deny the packet
(invoke implicit
deny any).
End
Perform action
(permit or deny).
End
End
Test the packet against
criteria in second ACE.
Is there a
match?
Test packet against
criteria in Nth ACE.
Is there a
match?
No
Yes
End
Perform action
(permit or deny).
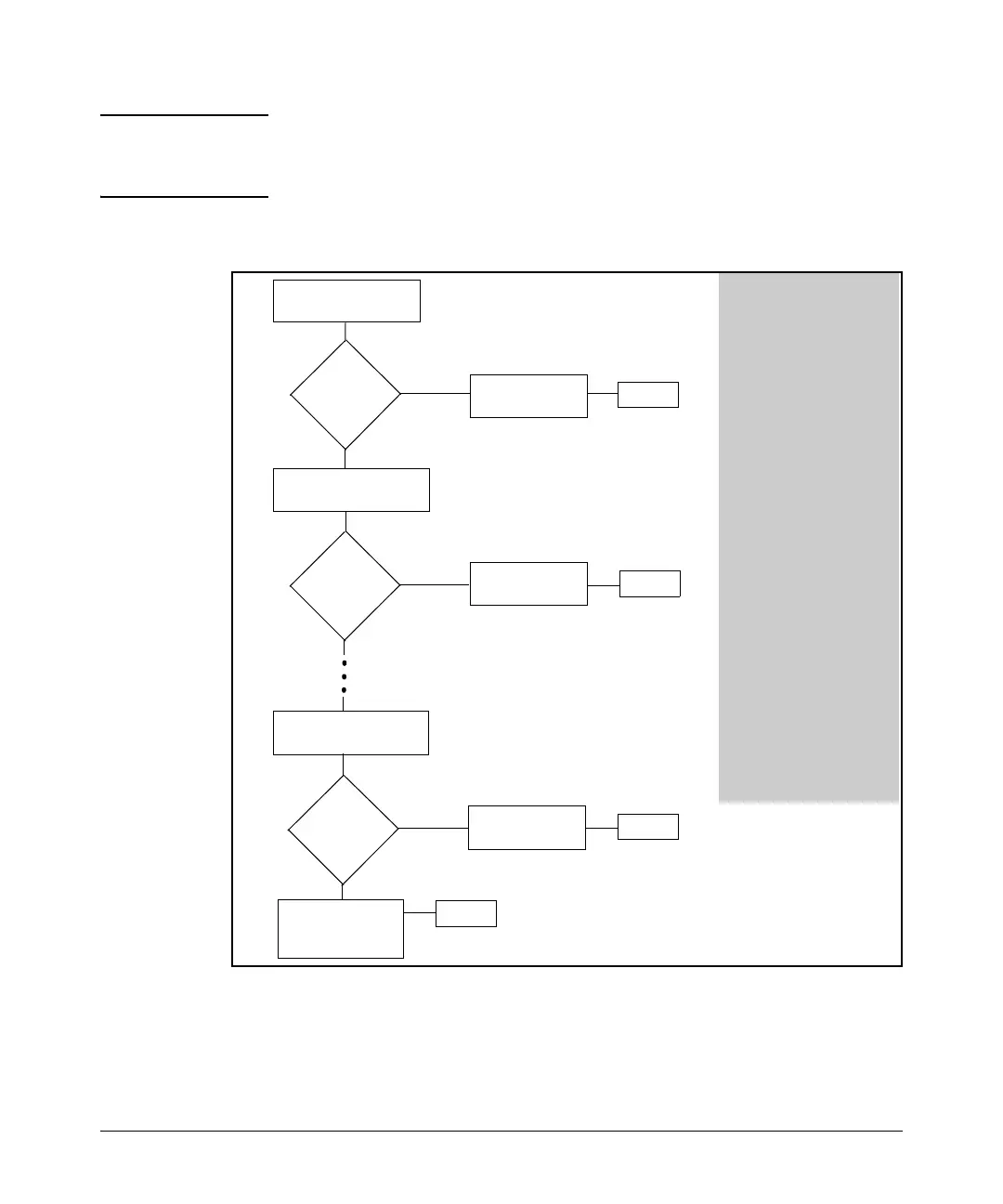
1. If a match is not found with
the first ACE in an ACL, the
switch proceeds to the next
ACE and so on.
2. If a match with an explicit
ACE is subsequently found,
the packet is either permit-
ted (forwarded) or denied
(dropped), depending on
the action specified in the
matching ACE. In this case
the switch ignores all sub-
sequent ACEs in the ACL.
3. If a match is not found with
any explicit ACE in the ACL,
the switch invokes the
implicit deny any at the end
of every ACL, and drops the
packet.
Note: If the list includes a
permit any entry, no
packets can reach the
implicit deny any at the end
of the list. Also, a permit
any ACE at any point in an
ACL defeats the purpose of
any subsequent ACEs in the
list.
Figure 10-4. The Packet-Filtering Process in an ACL with N Entries (ACEs)
10-14

 Loading...
Loading...











