Output
Specifications
38
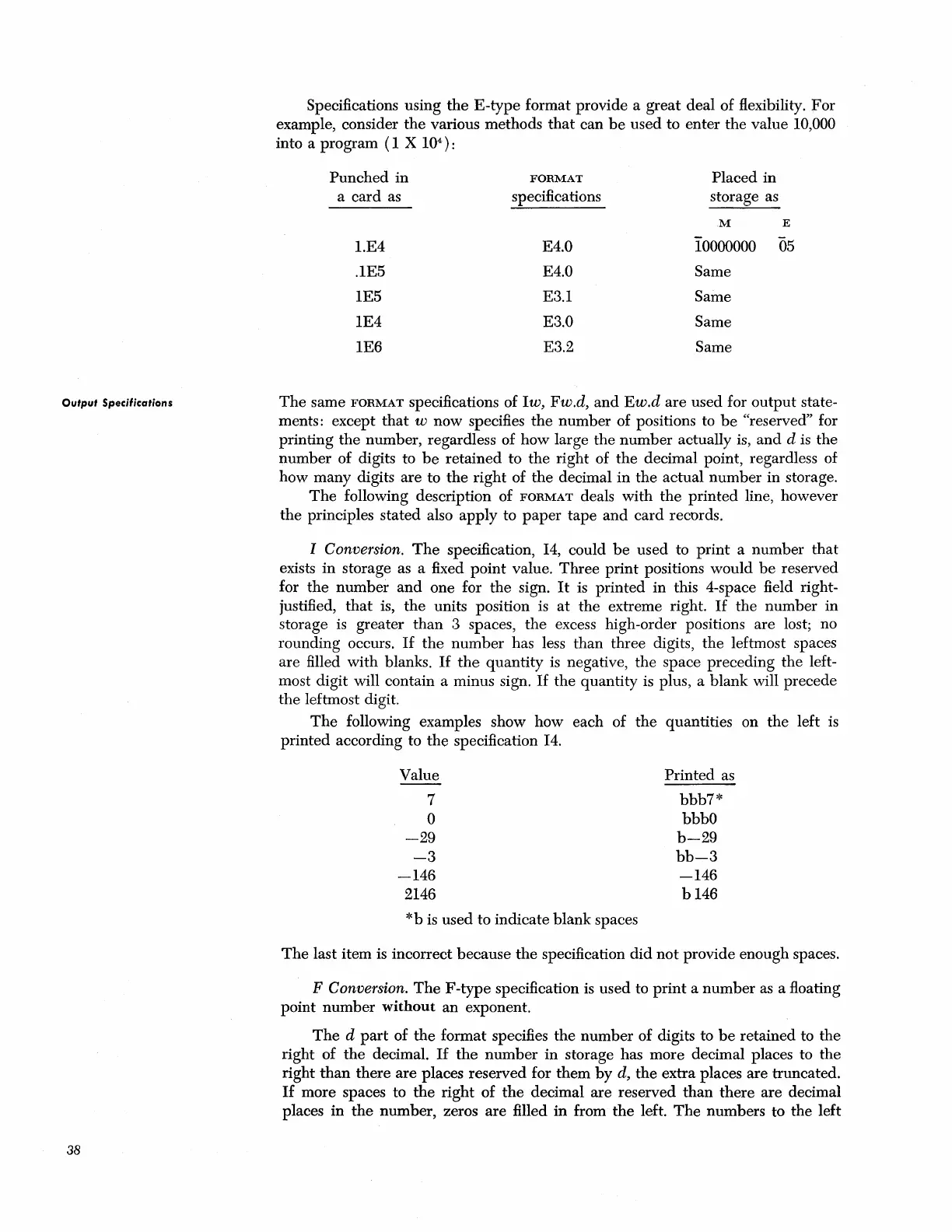
Specifications using
the
E-type
format provide a
great
deal of flexibility.
For
example, consider
the
various methods
that
can
be
used to
enter
the
value 10,000
into a
program
(1 X 10
4
):
Punched
in
FORMAT
Placed in
a
card
as specifications storage as
M
E
l.E4
E4.0 10000000
os
.lE5
E4.0
Same
1E5 E3.1 Same
1E4 E3.0 Same
1E6
E3.2
Same
The
same
FORMAT
specifications of Iw, Fw.d,
and
Ew.d
are
used for
output
state-
ments: except
that
w now specifies
the
number
of positions to
be
"reserved" for
printing
the
number, regardless of how large the
number
actually is,
and
d
is
the
number
of digits to
be
retained
to
the
right of
the
decimal point, regardless of
how
many
digits are to
the
right
of
the
decimal in
the
actual
number
in storage.
The
following description of
FORMAT
deals
with
the
printed
line, however
the
principles
stated
also
apply
to
paper
tape
and
card
records.
I Conversion.
The
specification,
14,
could
be
used to
print
a
number
that
exists
in
storage as a fixed
point
value.
Three
print
positions
would
be
reserved
for
the
number
and
one for
the
sign.
It
is
printed
in
this 4-space field right-
justified,
that
is,
the
units position is
at
the extreme right.
If
the
number
in
storage
is
greater
than
3 spaces,
the
excess high-order positions are lost; no
rounding occurs.
If
the
number
has less
than
three digits,
the
leftmost spaces
are
filled
with
blanks.
If
the
quantity
is
negative,
the
space
preceding
the
left-
most digit will contain a minus sign.
If
the
quantity
is
plus, a
blank
will precede
the
leftmost digit.
The
following examples show
how
each of
the
quantities on
the
left is
printed
according to
the
specification
14.
Value
7
o
-29
-3
-146
2146
*b
is
used to indicate
blank
spaces
Printed
as
bbb7*
bbbO
b-29
bb-3
-146
b146
The
last item is incorrect
because
the
specification
did
not
provide enough spaces.
F Conversion.
The
F-type
specification is used to
print
a
number
as a floating
point
number
without
an exponent.
The
d
part
of
the
format specifies
the
number
of digits to
be
retained to
the
right of
the
decimal.
If
the
number
in
storage has
more
decimal places to
the
right
than
there
are
places reserved for
them
by
d,
the
extra places are truncated.
If
more spaces to
the
right
of
the
decimal are reserved
than
there
are decimal
places
in
the
number, zeros are filled
in
from
the
left.
The
numbers to the left
 Loading...
Loading...