5
trapuls – EtherCAT® Fieldbus Interface
Chapter 2 – Basic information about EtherCAT®
Chapter 2 - BASIC INFORMATION ABOUT
EtherCAT®
EtherCAT® (“Ethernet for Controller and Automation Technology”) is a real-time Ethernet-based fieldbus.
2.1 - MAIN ETHERCAT® SLAVE FUNCTIONS
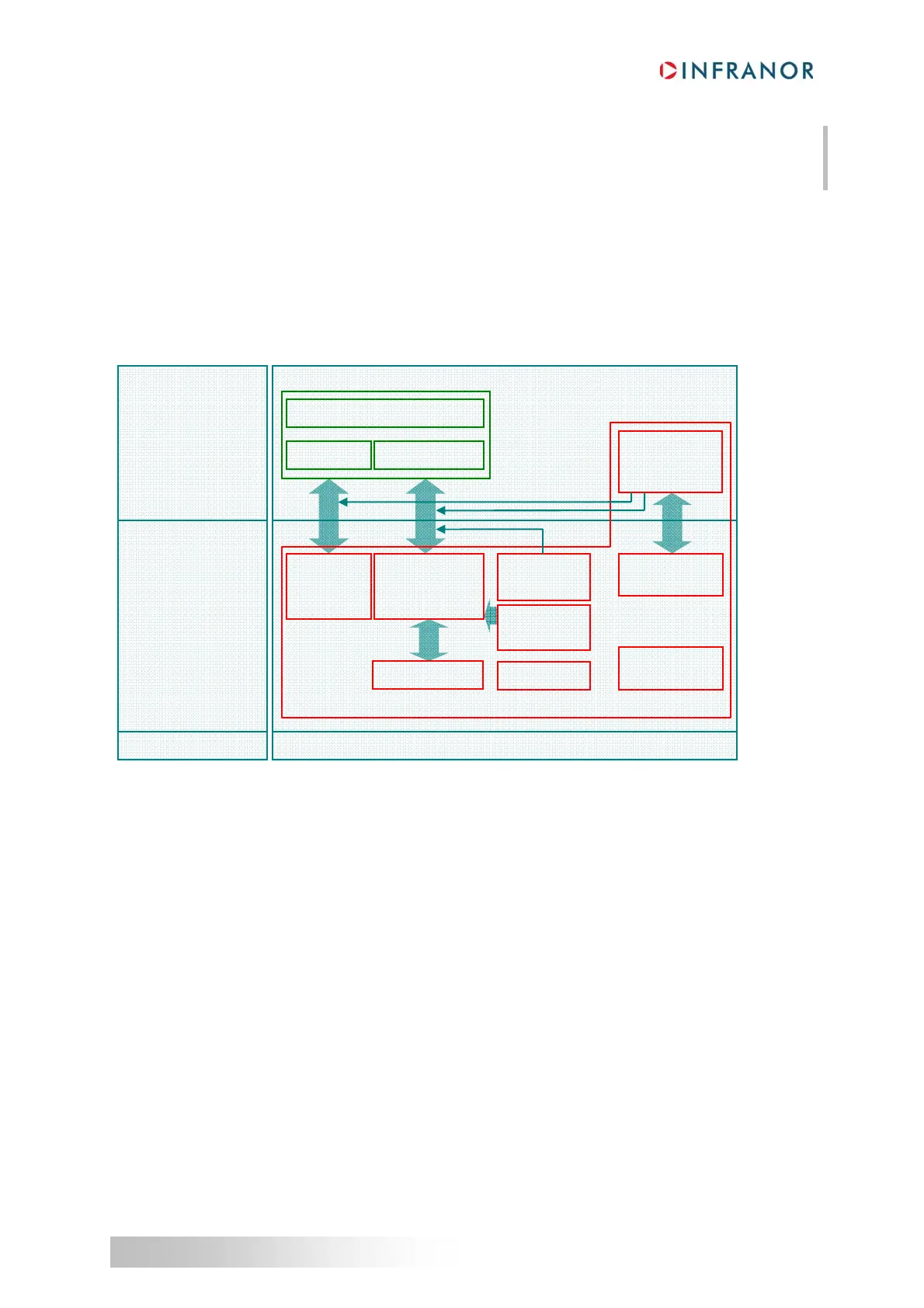
The following EtherCAT® slave node reference model makes it easy to locate the impact of the EtherCAT®
specific functions on the communication architecture.
The green box contains the modules belonging to the CANopen communication profile. This profile is
implemented in the Xtrapuls drives (please see “Xtrapuls User Guide” for more details about this communication
profile).
The red box contains the modules that belong to the EtherCAT® Slave Controller (ESC) on the EtherCAT®
Extension Board.
The EtherCAT® frame is initiated by the EtherCAT® master which sends this frame to the first EtherCAT®
slave. An EtherCAT® frame can contain several telegrams. If one of the telegrams is assigned the first slave, it
will process this telegram by inserting or extracting data respectively in or from the frame. The frame is then
transmitted to the next EtherCAT® slave which makes the same. The last EtherCAT® slave receiving the frame,
will also process it, and then returns the frame to the master via all slaves. To perform such a processing, two full-
duplex communication ports are controlled.
FMMUs
Mailbox
SM0 : out
SM1 : in
Process Data
SM2 : out
SM3 : in
AL Control/
AL Status
Distributed
Clock
DL Control/
DL Status
DL Info
EtherCAT®
State
Machine
SDO PDO
Ob
ect Dictionar
SM
Settin
s
Ph
sical La
e
Data Link Layer
Application Layer
Ethernet Ph
sical La
er
100Base-TX or 100Base-FX
or LVDS
CANopen Profile
EtherCAT® Data Link Layer
 Loading...
Loading...