CACHE SUBSYSTEMS
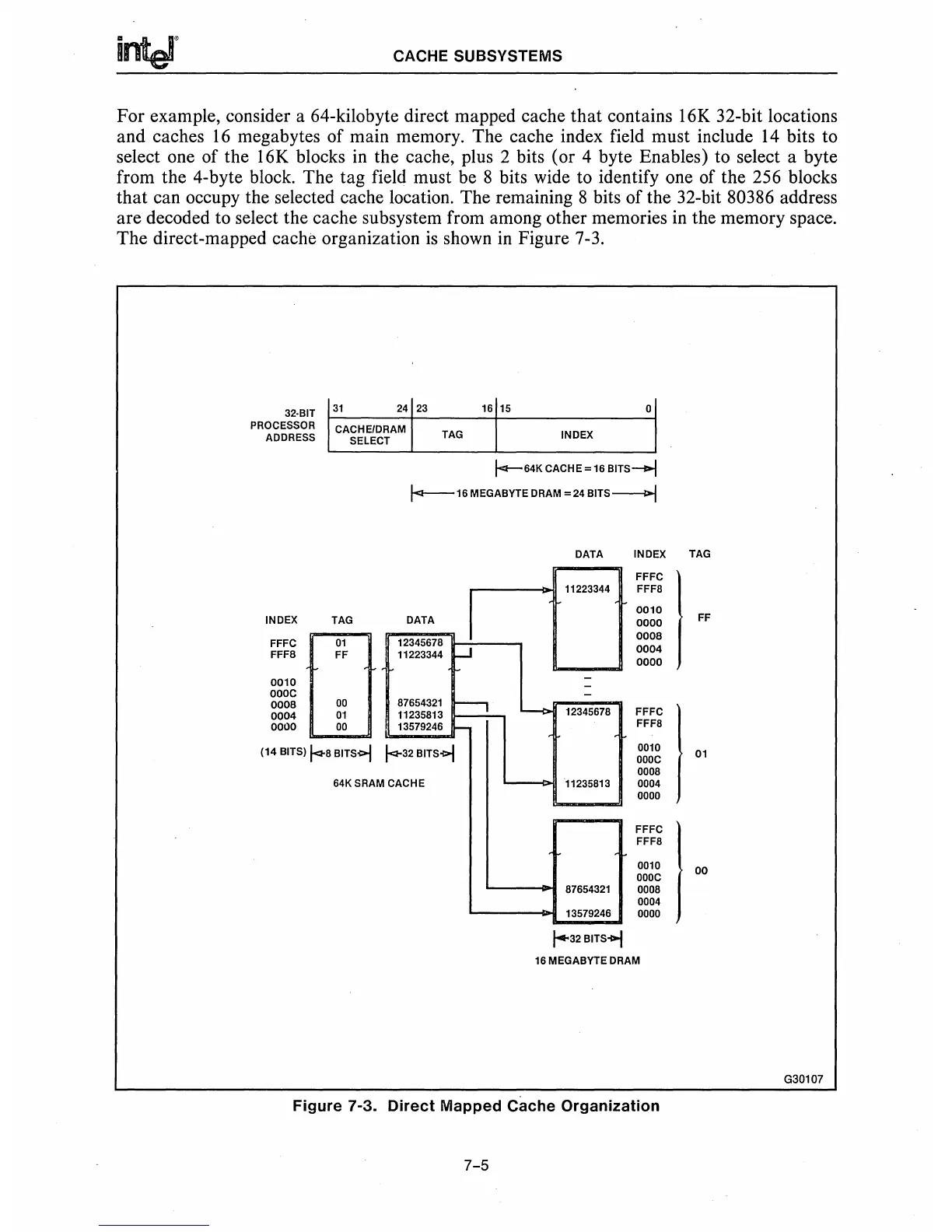
For example, consider a 64-kilobyte direct mapped cache
that
contains
16K
32-bit locations
and caches
16
megabytes of main memory. The cache index field must include
14
bits to
select one of the 16K blocks in the cache, plus 2 bits (or 4 byte Enables) to select a byte
from the 4-byte block. The tag field must
be
8 bits wide to identify one of the 256 blocks
that can occupy the selected cache location. The remaining 8 bits of the 32-bit
80386 address
are decoded to select the cache subsystem from among other memories in the memory space.
The direct-mapped cache organization
is
shown
in
Figure 7-3.
32·BIT
PROCESSOR
ADDRESS
INDEX
TAG
FFFC
01
FFF8 FF
0010
OOOC
0008
00
0004
01
0000
00
(14 BITS)
r--8
BITS<>j
64KSRAM
INDEX
f<t--64KCACHE=16
BITS~
1--16
MEGABYTE
DRAM
=
24
BITS~
DATA INDEX
FFFC
11223344 FFFB
0010
DATA
0000
12345678
---I
11223344
0008
0004
0000
-
-
-
87654321
:::::::!..-
----<>
11235813
12345678 FFFC
13579246
-
FFF8
f<!-32 BITS<>j
0010
OOOC
0008
CACHE
--
11235813 0004
0000
FFFC
FFF8
0010
OOOC
87654321
0008
0004
13579246
0000
r--32BITS~
16
MEGABYTE DRAM
Figure 7-3. Direct Mapped Cache Organization
7-5
TAG
I
FF
01
00
G30107
 Loading...
Loading...











