1/0
INTERFACING
Only two peripherals
do
not meet the bus controller specifications: the
8041
and 8042 UPls
(Universal Peripheral Interface 8-bit Microcomputers). These intelligent peripherals meet
all but the command recovery specification,
so
they can be used if this delay
is
implemented
in
software.
8.5
BASIC
1/0
EXAMPLES
In this section, two examples of the interface to slave
I/O
devices are presented. Typically,
several of these devices exist
on
the 80386 local bus. The basic
I/O
interface presented above
is
used for both examples.
8.5.1
8274
Serial Controller
The 8274 Multi-Protocol Serial Controller (MPSC)
is
designed to interface high-speed serial
communications lines using a variety of communications protocols, including asynchronous,
IBM bisynchronous, and
HDLC/SDLC
protocols. The 8274 contains two independent full-
duplex channels and can serve
as
a high-performance replacement for two 8251A Universal
Synchronous/ Asynchronous Receiver Transmitters (USARTs).
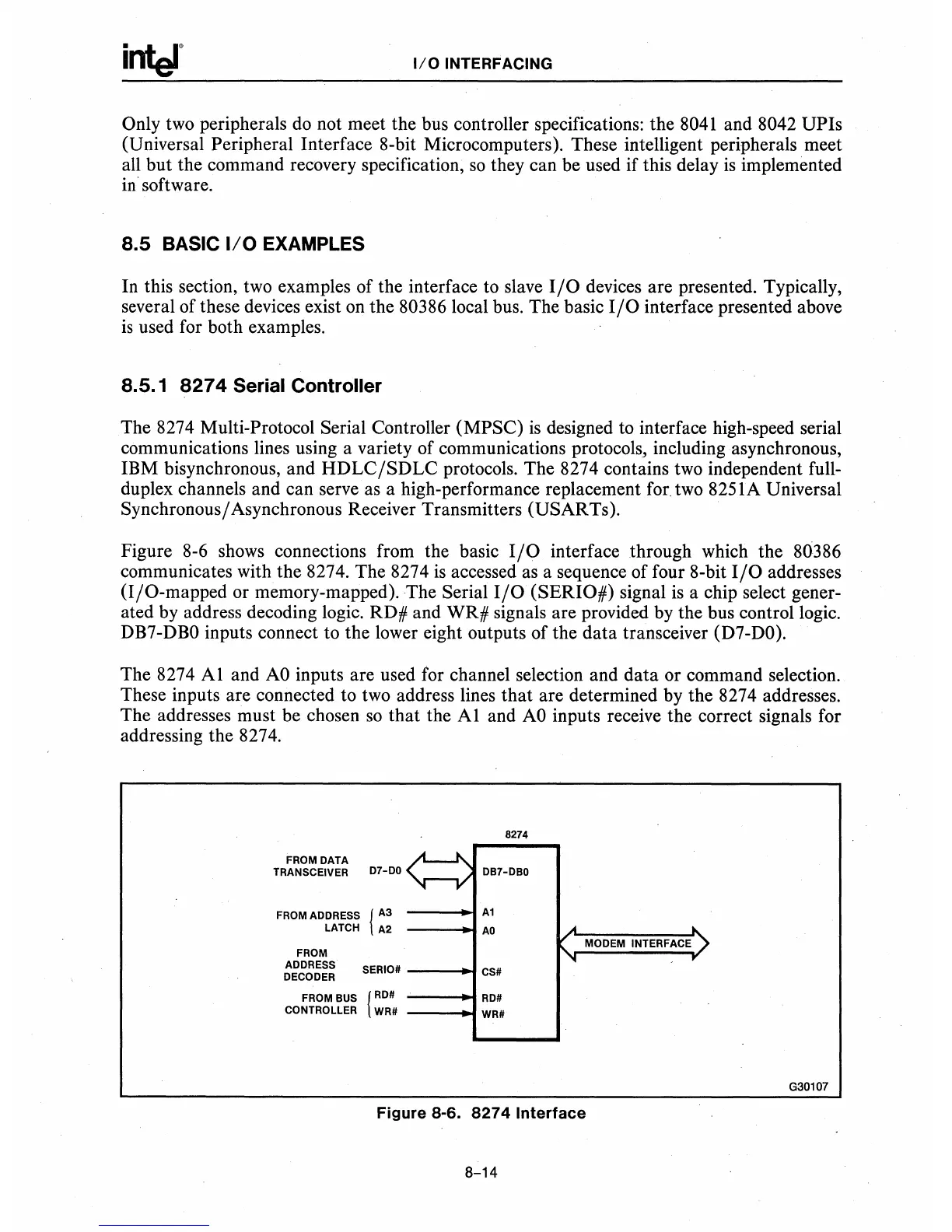
Figure
8-6
shows connections from the basic
I/O
interface through which the 80386
communicates with the 8274. The 8274
is
accessed as a sequence of four 8-bit
I/O
addresses
(I/O-mapped or memory-mapped).
The
Serial
I/O
(SERIO#) signal
is
a chip select gener-
ated by address decoding logic. RD# and WR# signals are provided by the bus control logic.
DB7-DBO
inputs connect to the lower eight outputs of the data transceiver (D7-DO).
The 8274
Al
and
AO
inputs are used for channel selection and data or command selection.
These inputs are connected to two address lines that are determined by the 8274 addresses.
The addresses must be chosen
so
that the
Al
and
AO
inputs receive the correct signals for
addressing the 8274.
8274
FROM DATA
D7-DD~
TRANSCEIVER
DB7-DBD
~
V
FROM ADDRESS i A3
A1
LATCH
A2
AD
....
MODEM INTERFACE
FROM
~
"
ADDRESS
DECODER
SERIO#
CS#
FROM BUS
i RD#
RD#
CONTROLLER WR#
WR#
G30107
Figure
8-6.
8274
Interface
8-14
 Loading...
Loading...











