1/0
INTERFACING
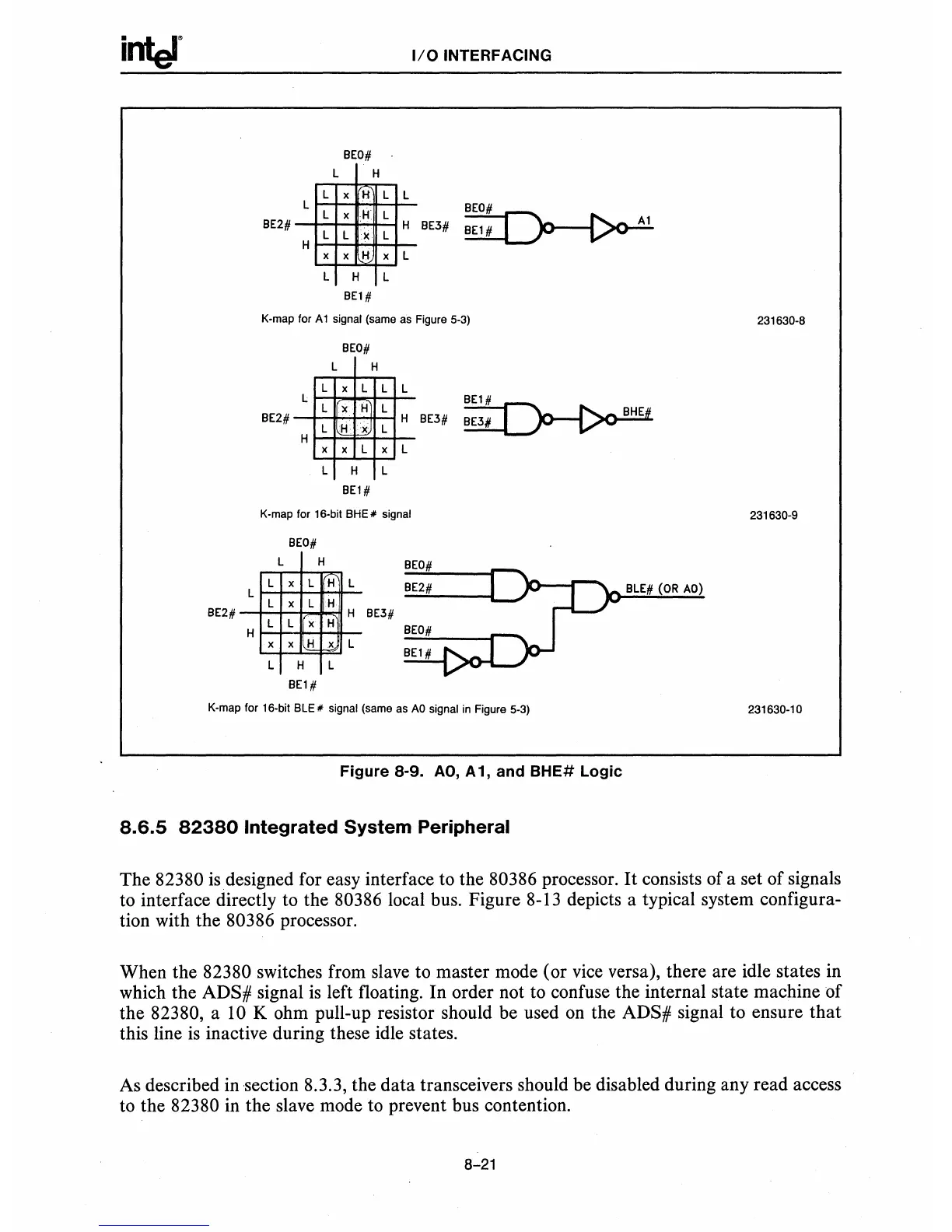
BEO#
L H
L
x H L
L
L
L
x H L
H
L L
X
L
H
BEO#
L~
Al
BE3# BEl #
--,,--~
BE2#
x
x
H x L
L
H L
BE1#
K-map for A 1 signal (same as Figure 5-3)
231630-8
BEO#
L H
L x L
L L
L
L x H
L
H
L H x L
H
BE1#
[~
BHE
BE3# BE3#
---
BE2#
x
x
L x L
L
H L
BE1#
K-map for 16-bit
BHE
lI' signal
231630-9
BEO#
L H
L
x
L
H
L
L
BLE#
(OR
AO)
L
x
L
H
H
L L x H
BE3#
BE2#
H
x x H x L
L
H L
BE1#
K-map for 16-bit BLE .. signal (same as
AO
signal in Figure 5-3)
231630-10
Figure 8-9.
AO,
A 1, and
BHE#
Logic
8.6.5
82380
Integrated System Peripheral
The 82380
is
designed for easy interface to the 80386 processor.
It
consists of a set of signals
to interface directly to the 80386 local bus. Figure 8-13 depicts a typical system configura-
tion with the 80386 processor.
When the 82380 switches from slave to master mode (or vice versa), there are idle states
in
which the ADS# signal
is
left floating. In order not to confuse the internal state machine
of
the 82380, a
10
K ohm pull-up resistor should be used
on
the ADS# signal to ensure that
this line
is
inactive during these idle states.
As described in section 8.3.3, the data transceivers should be disabled during any read access
to the 82380 in the slave mode to prevent bus contention.
8-21
 Loading...
Loading...











