Juniper Networks SSG 5 and SSG 20 Security Policy
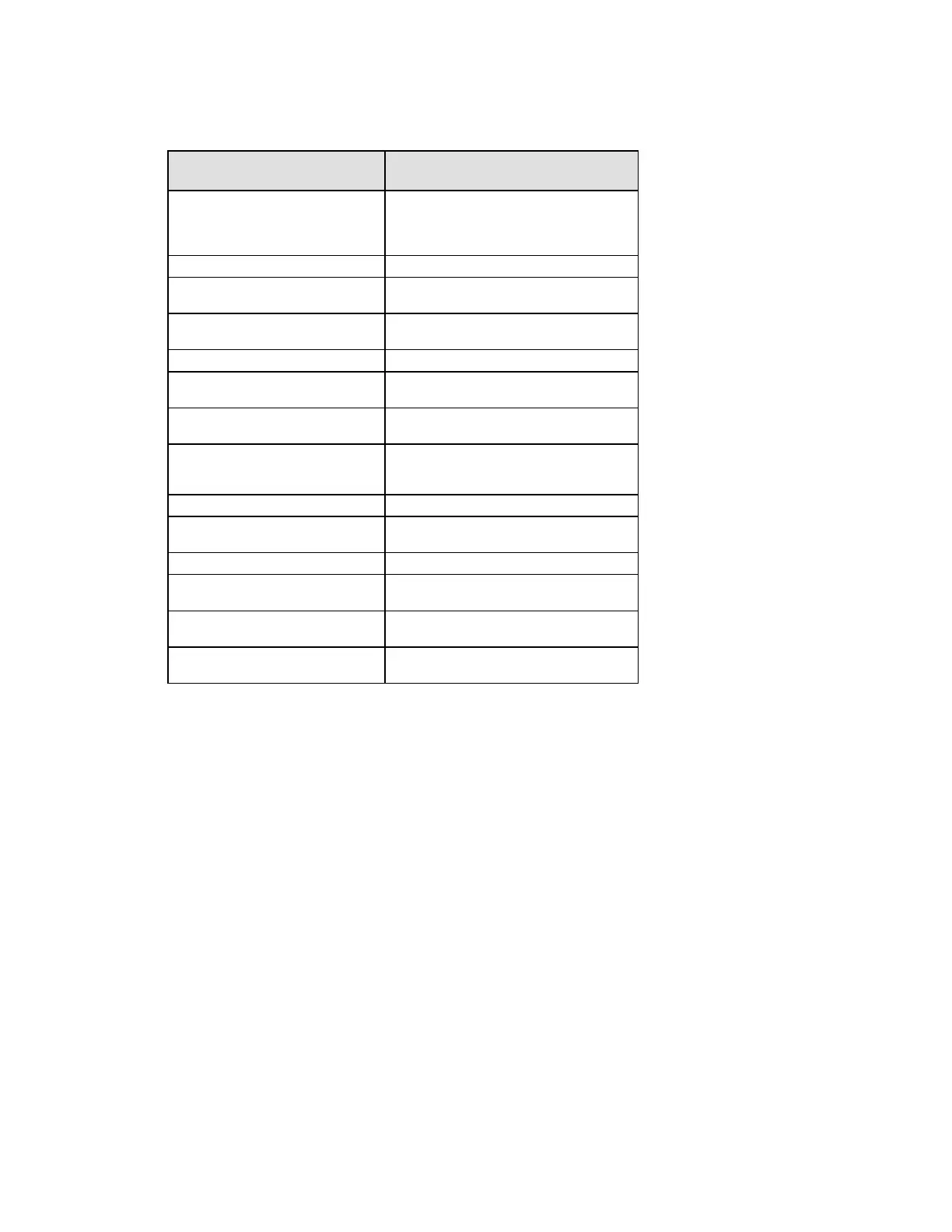
Table D: How Keys Are Generated
CSP Method of Generation
IPSEC HMAC SHA-1 Key May be either entered directly at the CLI
by the administrator, or generated
internally via ANSI X9.31 RNG as a result
of IKE protocol exchanges.
IPSEC ESP Key “
IKE Pre-shared Key Entered directly at the CLI by
administrator
IKE Encryption Key Internally via ANSI X9.31 RNG, as a result
of IKE protocol exchanges
IKE HMAC SHA-1 Key “
Password Entered directly at the CLI by
administrator
SSH Server/Host DSA Private Key Internally via ANSI X9.31 RNG when DSA
key-pair is generated.
SSH Encryption Key Internally via ANSI X9.31 RNG, as a result
of Diffie-Hellman key exchange during
SSH session establishment.
SSH HMAC SHA-1 Key “
HA Key Entered directly at the CLI by
administrator
IKE RSA/DSA/ECDSA Private Key Internally via ANSI X9.31 RNG
Diffie Hellman Private Key
Components
“
PRNG Seed and Seed Key Initial generation via entropy gathered
from a variety of internal sources.
RADIUS Secret Key Entered directly at the CLI by
administrator
Mitigation of Other Attacks Policy
The module is not designed to mitigate against attacks which are outside of the scope of FIPS 140-2.
 Loading...
Loading...