Next
Home
Back
4
1. Introduction
1.3 How the intraocular pressure (IOP) is measured
The cornea is flattened by an acrylic measuring prism on a
ring support at the end of the Tonometer sensor arm assembly.
It is flat with smooth or rounded margins to avoid any damage
to the cornea.
The measuring prism is brought into contact with the patient’s
eye by moving the slit lamp forward. The measurement drum is
then turned to increase the pressure on the eye until a continuous,
uniform applanated surface 3.06 mm in diameter (7,354 mm² area)
is obtained. The doubling prism divides the image and presents
the two opposing semicircular halves at 3.06mm (see section 7.4.2
Measurement procedure for further details).
1.4 Advantages of using a Goldmann Type Tonometer
• Intraocular pressure can be measured during a routine
examination with the Slit Lamp.
• The standard deviation among single measurements is
approximately ≤ 0,5 mmHg*.
• The value is expressed in mmHg and is read directly on the
instrument.
• Scleral rigidity need not be taken into consideration because
the small volume moved (0,56 mm
3
) increases intraocular
pressure by only about 2.5%.
*Please Note: Whilst the D-KAT has a Digital read-out that can indicate
decimal point measurement, it is not intended to imply higher accuracy.
The D-KAT instrument has been validated to a measurement deviation
of ±0.49mN (~0.5mmHg) or 1.5%, whichever is greater, in accordance
with ISO 8612.
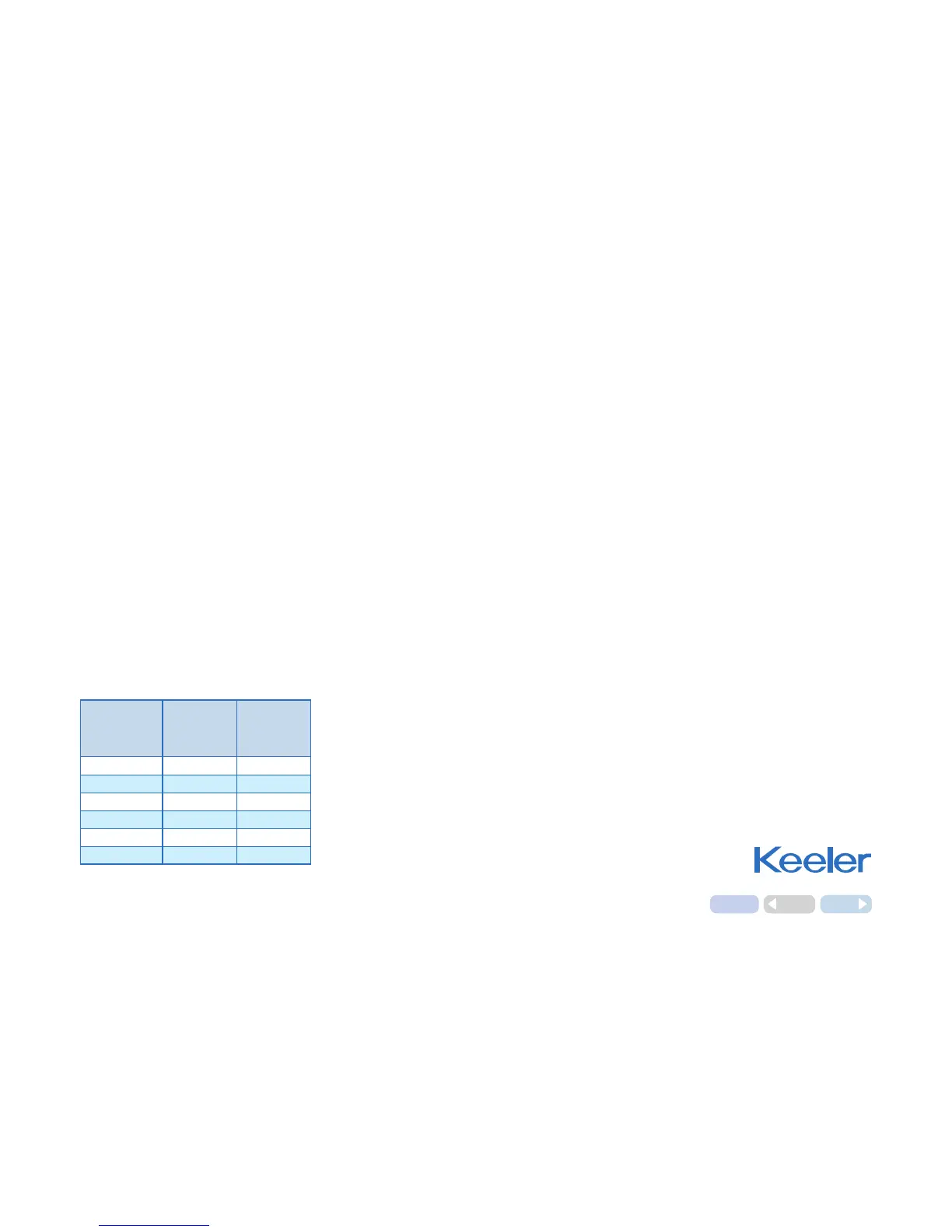
LED
Display
mmHg
Force
mN
Pressure
kPa
10
9.81
1.33
20 19.62 2.66
30 29.43 3.99
40 39.24 5.32
50 49.05 6.65
60 58.86 7.98
Relationship between the LED display
and the force and pressure on the
applanated surface.
 Loading...
Loading...