267Section 14 Load ManagementTP-6953 7/19
14.5.6 Under Frequency Shed Logic
Under Frequency Shed uses the output frequency of the
generator system and the under Frequency Shed Level
to compute a Frequency Droop. The output frequency of
the generator system is taking from the generator
metering in a single-generator application and from the
bus metering in a paralleling application.
Frequency Droop is computed according to the
following formula:
Frequency Droop = (Generator Rated Frequency –
(Generator System Frequency + Under Frequency
Shed Level))
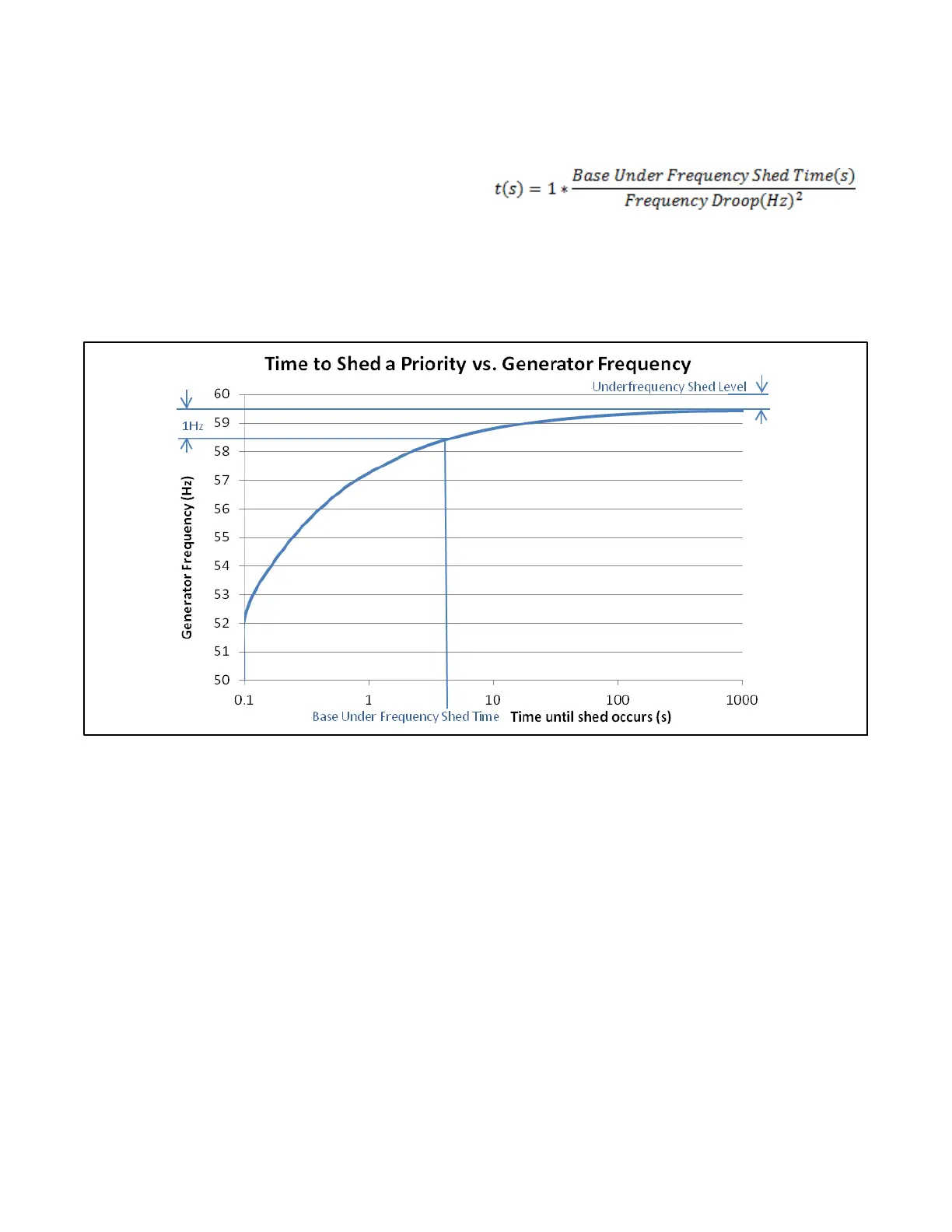
The under Frequency Shed Accumulator fills at a rate
that is dependent on the Frequency Droop and the Base
Under Frequency Shed Time such that the time to shed
the first priority after the overload condition occurred is
defined as:
Figure 14 -13 Generator Under Frequency Shed Timing With Default Configuration
The Base Under Frequency Shed Time sets the shed
time at a 1 Hz frequency droop, while the time decreases
as the f requency decreases (indicating additional
generator load).
The time to shed subsequent priorities decreases by a
fixed 0.5 acceleration factor for each priority shed,
hence if the first priority shed in 10 seconds, the second
priority will shed in 5 seconds, while the third priority will
shed in 2.5 seconds and the fourth priority in 1.3
seconds with the same maintained frequency.
Note: The shed function is performed by an
accumulator and the timing is determined by the
rate that the accumulator fills, hence a varying
load will fill the accumulator at varying rates,
causing the load to shed at a time that can’t be
calculated directly with the equation above, but
canbeestimatedbyit.

 Loading...
Loading...