69
Disassembly/Inspection and Service
24 690 06 Rev. C KohlerEngines.com
NOTE: Rings must be installed correctly. Ring
installation instructions are usually included with
new ring sets. Follow instructions carefully. Use
a piston ring expander to install rings. Install
bottom (oil control) ring fi rst and top
compression ring last.
Scuffi ng and scoring of pistons and cylinder walls occurs
when internal engine temperatures approach welding
point of piston. Temperatures high enough to do this are
created by friction, which is usually attributed to improper
lubrication and/or overheating of engine.
Normally, very little wear takes place in piston boss-
piston pin area. If original piston and connecting rod can
be reused after new rings are installed, original pin can
also be reused but new piston pin retainers are required.
Piston pin is included as part of piston assembly – if pin
boss in piston or pin are worn or damaged, a new piston
assembly is required.
Ring failure is usually indicated by excessive oil
consumption and blue exhaust smoke. When rings fail,
oil is allowed to enter combustion chamber where it is
burned along with fuel. High oil consumption can also
occur when piston ring end gap is incorrect because
ring cannot properly conform to cylinder wall under this
condition. Oil control is also lost when ring gaps are not
staggered during installation.
When cylinder temperatures get too high, lacquer and
varnish collect on pistons causing rings to stick, which
results in rapid wear. A worn ring usually takes on a
shiny or bright appearance.
Scratches on rings and pistons are caused by abrasive
material such as carbon, dirt, or pieces of hard metal.
Detonation damage occurs when a portion of fuel charge
ignites spontaneously from heat and pressure shortly
after ignition. This creates two fl ame fronts which meet
and explode to create extreme hammering pressures on
a specifi c area of piston. Detonation generally occurs
from using low octane fuels.
Preignition or ignition of fuel charge before timed spark
can cause damage similar to detonation. Preignition
damage is often more severe than detonation damage.
Preignition is caused by a hot spot in combustion
chamber from sources such as glowing carbon deposits,
blocked cooling fi ns, an improperly seated valve, or
wrong spark plug(s).
Replacement pistons are available in STD bore size, and
in 0.25 mm (0.010 in.), and 0.50 mm (0.020 in.) oversize.
Replacement pistons include new piston ring sets and
new piston pins.
Replacement ring sets are also available separately
for STD, 0.25 mm (0.010 in.), and 0.50 mm (0.020 in.)
oversize pistons. Always use new piston rings when
installing pistons. Never use old rings.
Some important points to remember when servicing
piston rings:
1. Cylinder bore must be deglazed before service ring
sets are used.
2. If cylinder bore does not need reboring and if old
piston is within wear limits and free of score or scuff
marks, old piston may be reused.
3. Remove old rings and clean up grooves. Never
reuse old rings.
4. Before installing new rings on piston, place top two
rings, each in turn, in its running area in cylinder
bore and check end gap. Compare ring gap to
tolerances listed in Specifi cations.
5. After installing new compression (top and middle)
rings on piston, check piston-to-ring side clearance.
Compare clearance to tolerance listed in
Specifi cations. If side clearance is greater than
specifi ed, a new piston must be used.
To install new piston rings, proceed as follows:
1. Oil control ring (bottom groove): Install expander and
then rails. Make sure ends of expander are not
overlapped.
2. Middle compression ring (center groove): Install
center ring using a piston ring installation tool. Make
sure identifi cation mark is up or dye colored stripe (if
contained) is to left of end gap.
3. Top compression ring (top groove): Install top ring
using a piston ring expender. Make sure
identifi cation mark is up or dye colored stripe (if
contained), left of end gap.
Connecting Rods
Offset, stepped-cap connecting rods are used in all
these engines.
Inspection and Service
Check bearing area (big end) for excessive wear,
score marks, running and side clearances (refer to
Specifi cations). Replace rod and cap if scored or
excessively worn.
Service replacement connecting rods are available in
STD crankpin size and 0.25 mm (0.010 in.) undersize.
An 0.25 mm (0.010 in.) undersized rod can be identifi ed
by a drilled hole located in lower end of rod shank.
Always refer to appropriate parts information to ensure
correct replacements are used.
Remove Crankshaft
Inspection and Service
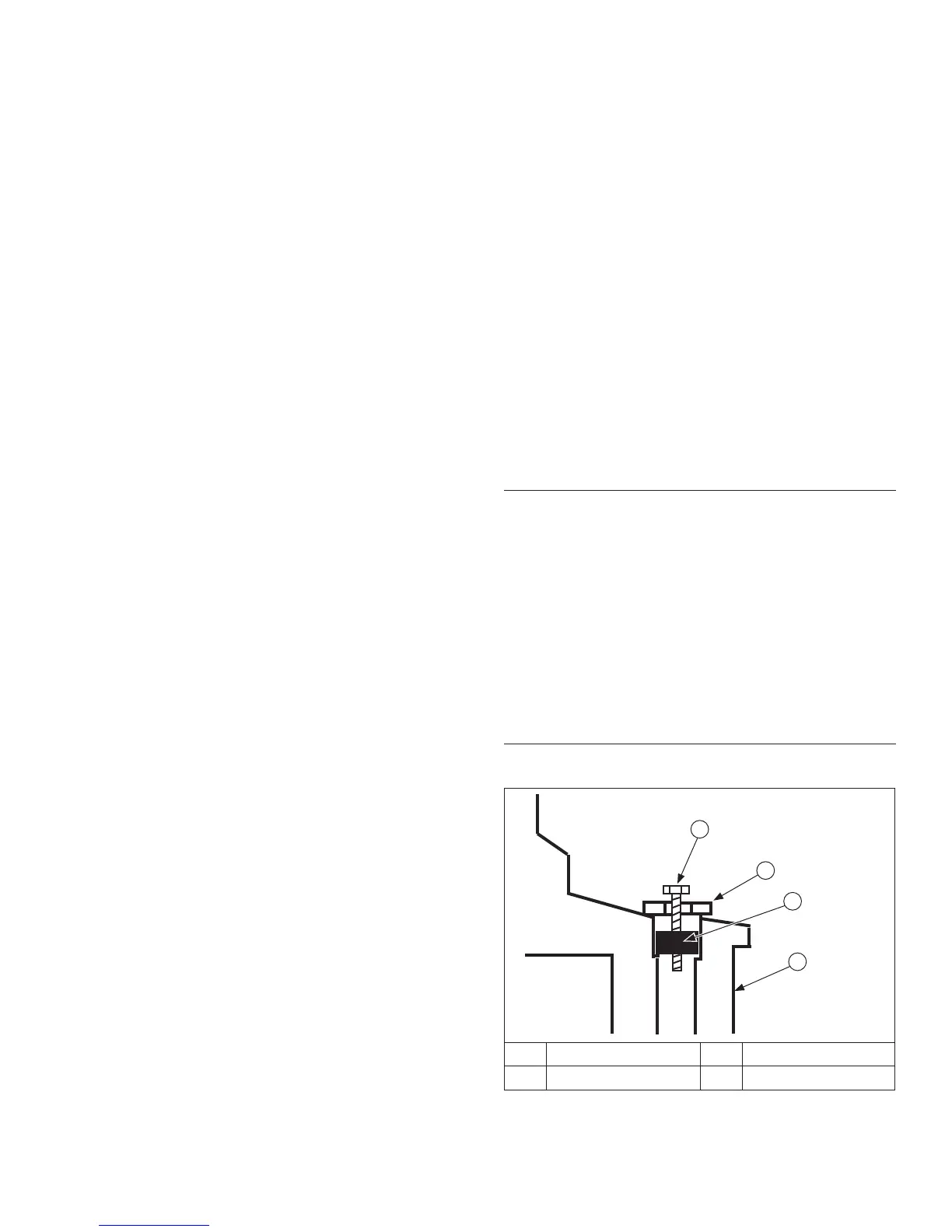
Crankshaft Components and Details
A
B
C
D
A Self-Tapping Screw B Flat Washer
C Plug D Crankshaft
 Loading...
Loading...