5B.5
Section 5B
EFI Fuel System
Two different ECU styles have been used in CV EFI
production. Each has a plastic case, but they differ in
having a 24 pin or 32 pin connector block, and are
identified as MSE 1.0 or MSE 1.1 respectively. See
Figures 5B-1 and 5B-2. Basic function and operating
control remains the same between the two, however
due to differences in the internal circuitry as well as the
wiring harness, the ECU’s are not interchangeable.
Certain service/troubleshooting procedures will also
differ, so where applicable, they are covered
individually as: “24 Pin” (MSE 1.0) Plastic-Cased
ECU, or “32 Pin” (MSE 1.1) Plastic-Cased ECU.
General
The ECU is the brain or central processing computer
of the entire EFI system. During operation, sensors
continuously gather data which is relayed through the
wiring harness to input circuits within the ECU. Signals
to the ECU include: ignition (on/off), crankshaft
position and speed (RPM), throttle position, oil
temperature, exhaust oxygen levels, and battery
voltage. The ECU compares the input signals to the
programmed maps in its memory to determine the
appropriate fuel and spark requirements for the
immediate operating conditions. The ECU then sends
output signals to set the injector duration and ignition
timing.
The ECU continually performs a diagnostic check of
itself, each of the sensors, and the system
performance. If a fault is detected, the ECU turns on
the Malfunction Indicator Light (MIL) on the equipment
control panel, stores the fault code in its fault memory,
and goes into a default operating mode. Depending on
the significance or severity of the fault, normal
operation may continue, or “limp home” operation
(slowed speed, richer running) may be initiated. A
technician can access the stored fault code using a
“blink code” diagnosis flashed out through the MIL. An
optional computer software diagnostic program is also
available, order Kohler Part No. 25 761 23-S.
The ECU requires a minimum of 7.0 volts to operate.
The adaptive memory in the ECU is operational
whenever the required voltage is present, however the
adapted values are lost if the power supply is disrupted
for any reason. The ECU will “relearn” the adapted
values if the engine is operated for 10-15 minutes at
varying speeds and loads after the oil temperature
exceeds 55°C (130°F).
To prevent engine over-speed and possible failure, a
“rev-limiting” feature is programmed into the ECU. If the
maximum RPM limit (4500) is exceeded, the ECU
suppresses the injection signals, cutting off the fuel
flow. This process repeats itself in rapid succession,
limiting operation to the preset maximum.
Service
Never attempt to disassemble the ECU. It is sealed to
prevent damage to internal components. Warranty is
void if the case is opened or tampered with in any way.
All operating and control functions within the ECU are
preset. No internal servicing or readjustment may be
performed. If a problem is encountered, and you
determine the ECU to be faulty, contact your source of
supply. Do not replace the ECU without factory
authorization.
The relationship between the ECU and the throttle
position sensor (TPS) is very critical to proper system
operation. If the TPS or ECU is changed, or the
mounting position of the TPS is altered, the
appropriate “TPS Initialization Procedure” (see pages
5B.8 and 5B.9) must be performed to restore the
synchronization.
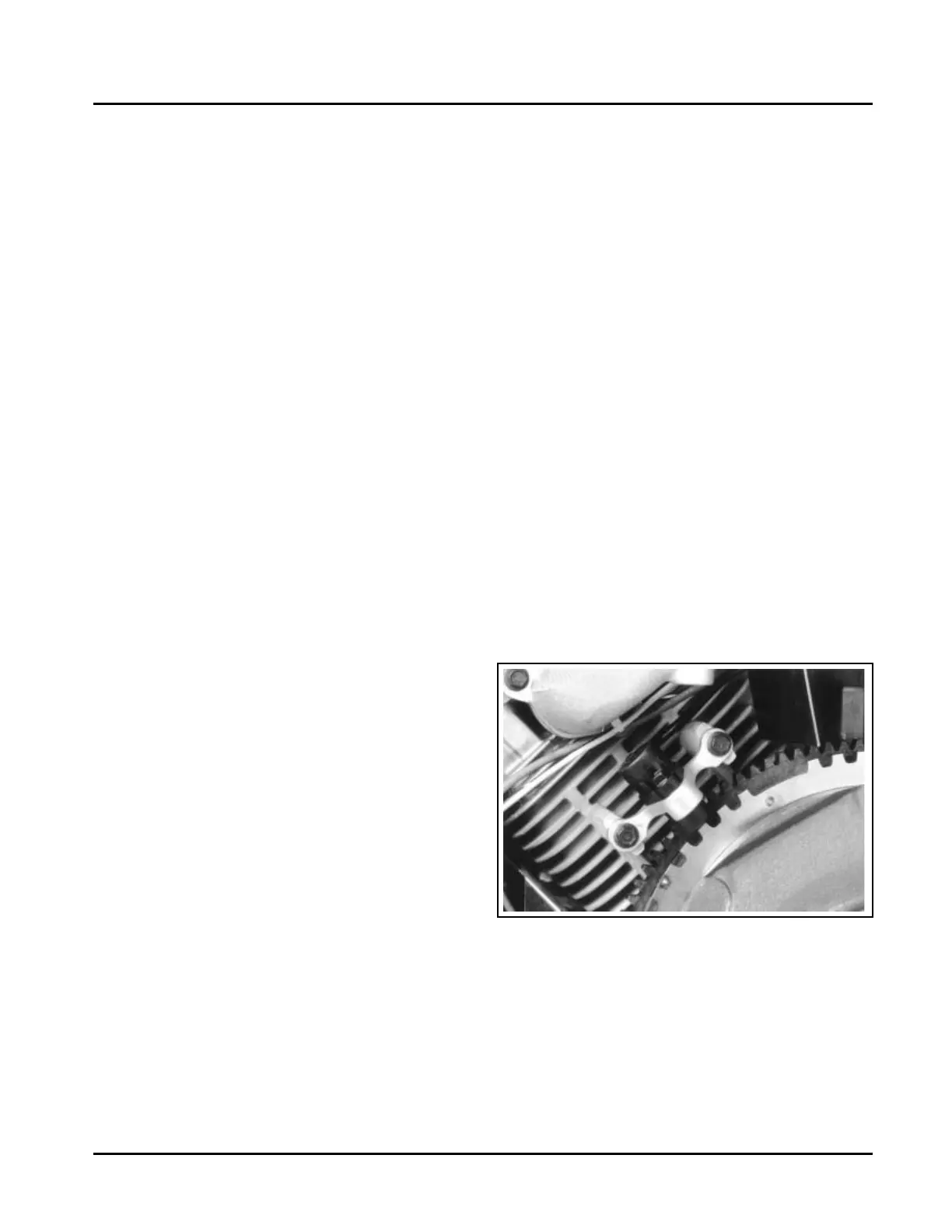
Engine Speed Sensor
Figure 5B-3. Engine Speed Sensor.
Kohler Engine Parts Call K&T 606-678-9623 or 606-561-4983
www.mymowerparts.com
 Loading...
Loading...











