IOM / ROOFTOP BALTIC Series - 0704-E Page 53
The actual resistance of ductwork systems is not always identical to the calculated theoretical values. To rectify this, it may
be necessary to modify the pulley and belt setting. To this effect, the motors are fitted with variable pulleys.
AIRFLOW BALANCING
Measure the absorbed amps
If the absorbed amps are greater than the rated values, the ventilation system has a lower pressure drop than
anticipated. Reduce the flow by reducing the rpm. If the system resistance is significantly lower than design, there is a
risk that the motor will overheat resulting in an emergency cut out.
If the absorbed amps are lower than the rated values, your system has a higher pressure drop than anticipated. Increase
the flow by increasing the rpm. At the same time you will increase the absorbed power which may result in having to
increase the motor size.
To carry out the adjustment and to avoid a time-consuming re-start, stop the machine and if necessary lock the main
switch.
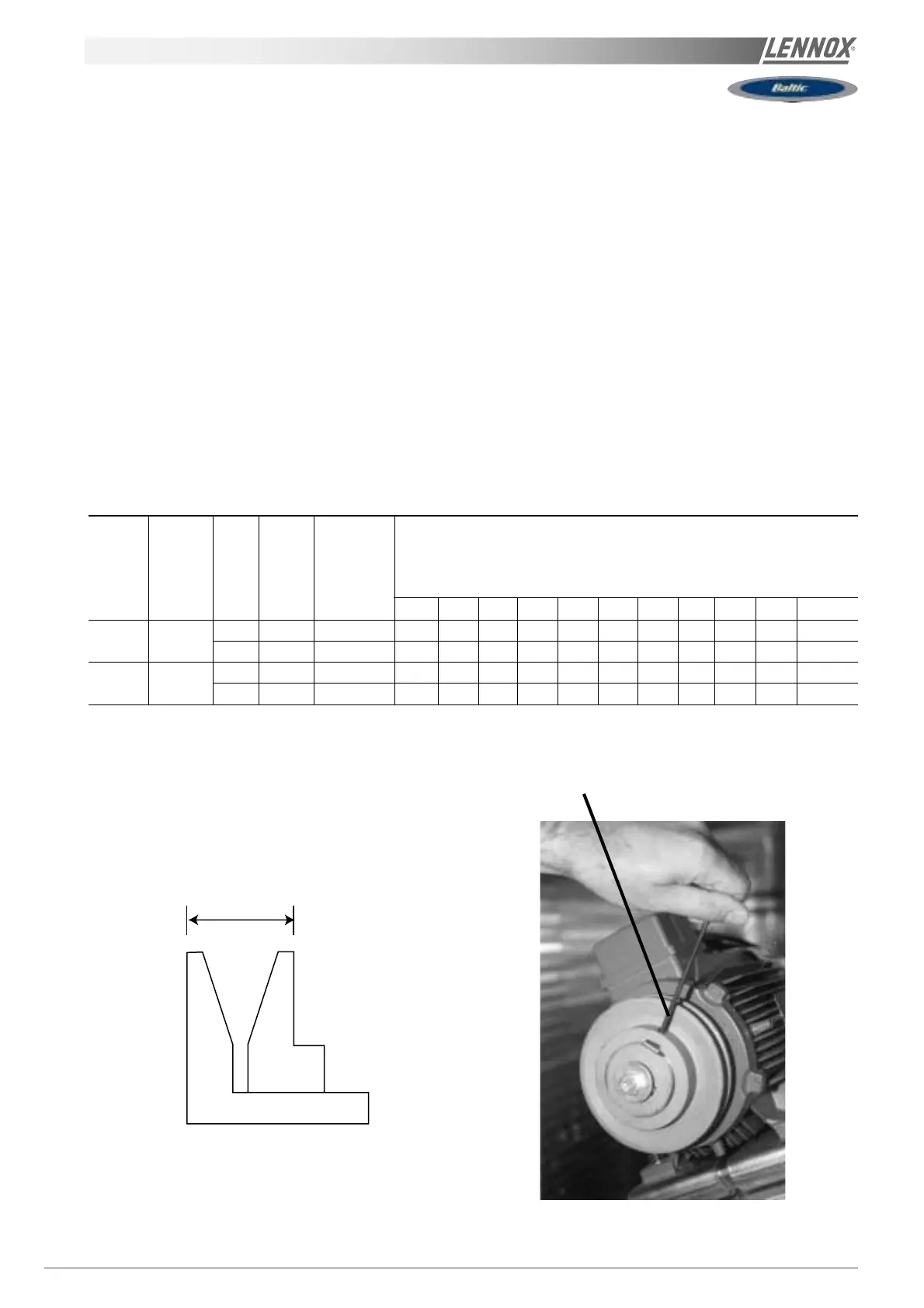
First unscrew the 4 Allen screw(s) on the pulley (see figure 15).
Min Max NB of turns
Pulley Pulley Dia / Dia / from fully Actual diameter (DM) or distance between faces for a given
type External Min Max closed to number of turns from fully closed with SPA belt in (mm)
Diameter Dist Dist fully open
0,5 1 1,5 2 2,5 3 3,5 4 4,5 5,0 5,5
8450 /
120
95 116 5 113,9 111,8 109,7 107,6 105,5 103,4 101,3 99,2 97,1 95,0 -
D8450 20,2 28 5 21,0 21,8 22,5 23,3 24,1 24,9 25,7 26,4 27,2 28,0 -
8550 /
136
110 131 5 128,9 126,8 124,7 122,6 120,5 118,4 116,3 114,2 112,1 110,0
D8550 20,6 31,2 5 21,6 22,7 23,8 24,8 25,9 26,9 28,0 29,1 30,1 31,2 -
Table 1
VENTILaTION : PULLEYS
The easiest way to determine the fan rotation speed is to
use a tachometer. If not available the fan rpm can be
estimated using the following two methods.
1st Method with the pulley secured in place:
L
Measure the distance between the two outside faces of the
pulley.
Using table 1 the motor pulley actual diameter can be
estimated
ALLEN WRENCH 4
Fig. 15

 Loading...
Loading...