Page 10 of 25 FA69372–2 English
Jun 2013
25
How To Install and Set Up the 5900 &
7900 Printer
Linx 5900 & 7900
3.1.2 Example calculation
The calculation below uses the following example:
• The message is a 16 Linear Quality Message Type.
• The printer has an Ultima 62 µm printhead, which requires 132 rasters for this message.
• The Print area is 50 mm long.
Step 1: Define the required Raster Pitch
To get the best print quality a 1:1 aspect ratio is needed—the vertical pitch (drop spacing)
must equal the horizontal pitch. This drop pitch is the ‘Ideal Raster Pitch’. The Ideal Raster
Pitch depends on the printhead type and the message type.
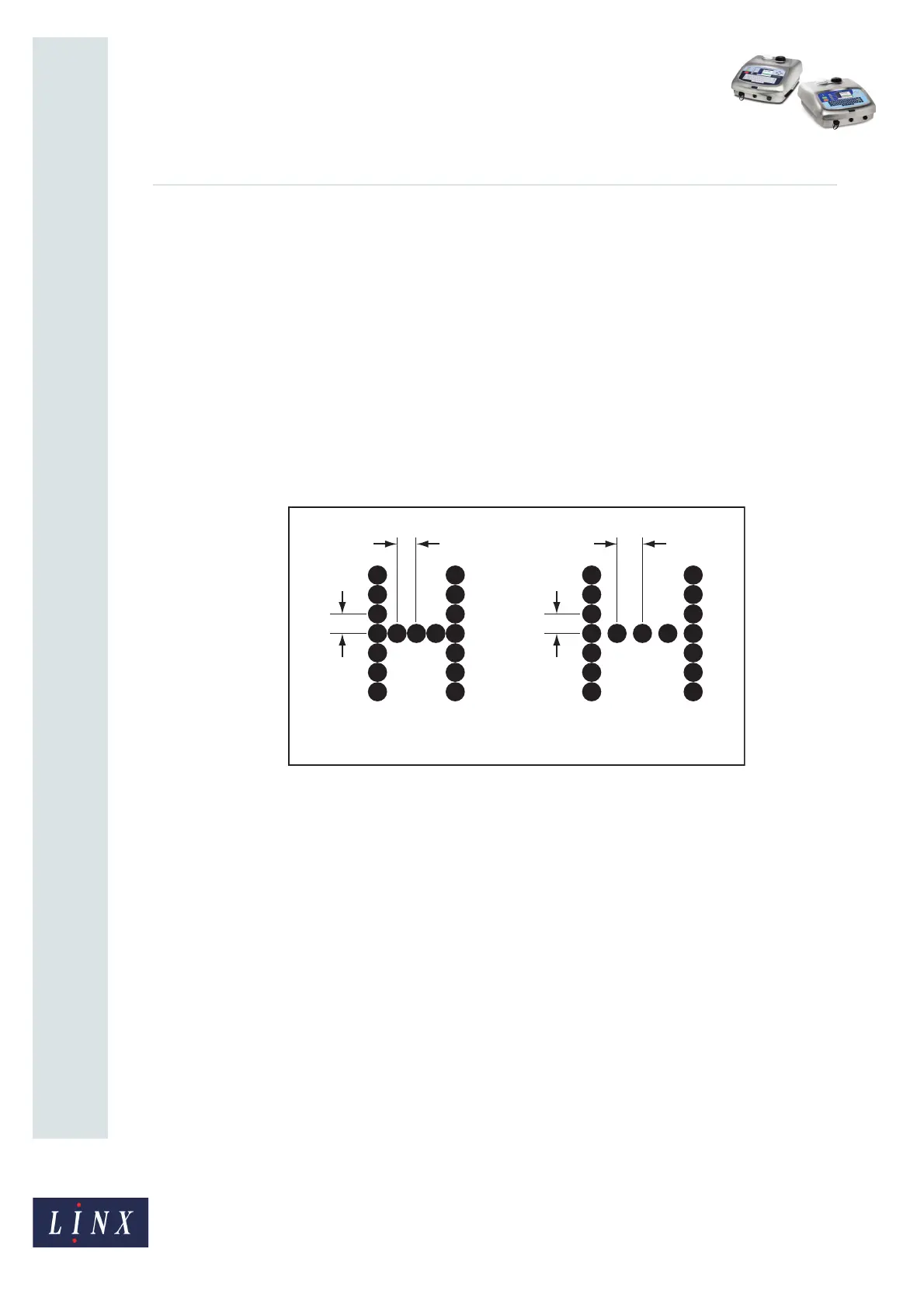
The effect of raster pitch is shown in Figure 8.
Figure 8. Raster Pitch
In Figure 8 (a) the letter ‘H’ is printed at the Ideal Raster Pitch—the horizontal spacing (X1)
is equal to the vertical spacing (Y). In Figure 8 (b), the raster pitch is larger than the Ideal
Raster Pitch—the horizontal spacing (X2) is larger than the vertical spacing (Y).
The section ‘Ideal Raster Pitch tables’ on page 18 contains tables that show the following
parameters for each combination of printhead and message type:
• Character matrices (character width)
• Ideal Raster Pitch (mm)
• Maximum raster rate (kHz)
• Maximum line speed for the ideal raster pitch
If the raster pitch in your application does not equal the Ideal Raster Pitch, you can adjust
the Print Height setting to make the aspect ratio 1:1.
NOTE: Not all message types listed in the Ideal Raster Pitch tables are available on the 5900
printer.
69462
(a) (b)
YY
X1 X2
 Loading...
Loading...