75
8995B-eIFU-1115
10 20 30 40 50 60 70
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
0 < Number of Samples < 10
10 ≤ Number of Samples < 100
100 ≤ Number of Samples
Control (Respiration per Minute)
Capnograph (Respiration per Minute)
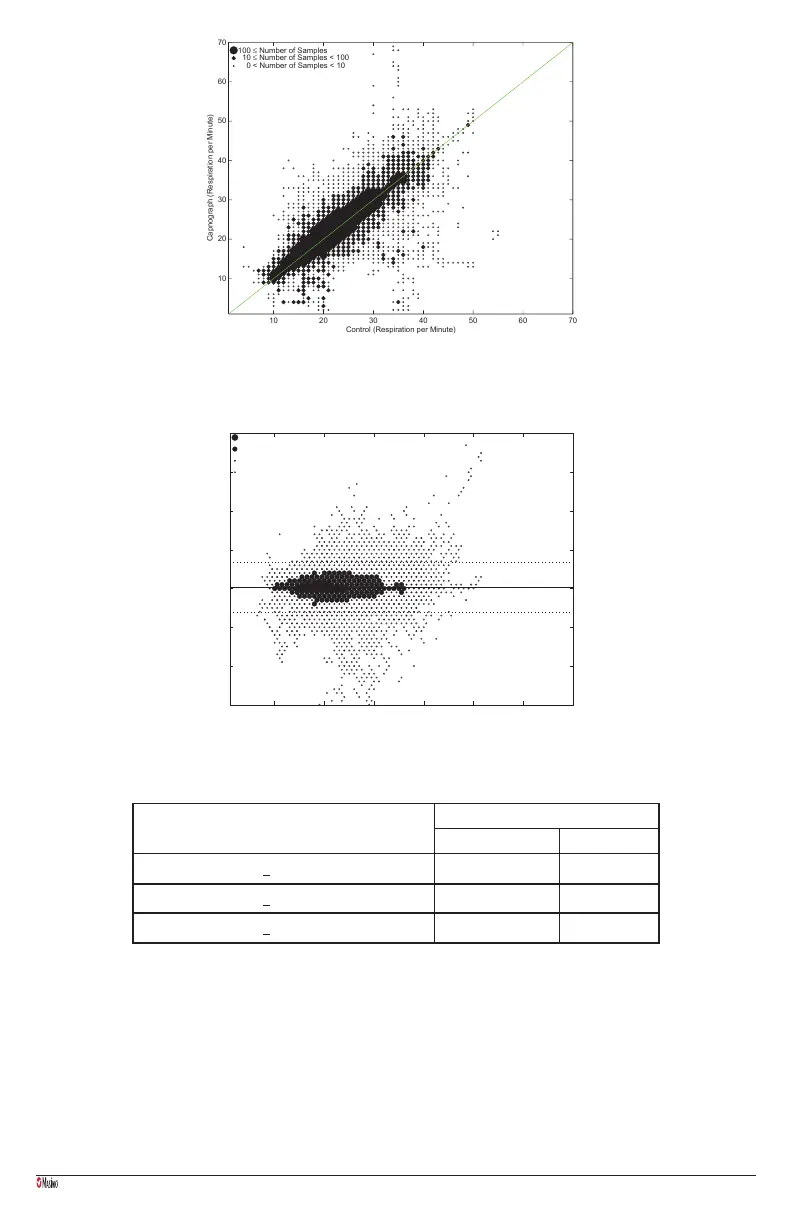
Hospitalized Pediatric Subjects: Capnograph vs. Control (manual count)
10 20 30 40 50 60 70
−30
−20
−10
0
10
20
30
40
Bias=0.23, STDEV=3.29
(Capnograph + Control)/2 (Respiration per Minute)
Capnograph − Control (Respiration per Minute)
0 < Number of Samples < 10
10 ≤ Number of Samples < 100
100 ≤ Number of Samples < 1000
1000 ≤ Number of Samples
Hospitalized Pediatric Subjects: Capnograph vs. Control (manual count)
Respiration Per Minute (RPM) Difference when Compared
to Control for Hospitalized Pediatric Subjects
Coverage
RAM Capnograph
+ 1 RPM 70.2% 51.8%
+ 2 RPM 83.4% 73.4%
+ 3 RPM 89.3% 84.3%
Outliers in the data from the healthy adult subjects and the hospitalized pediatric subjects were associated with subjects experiencing a fast
change in breath rate, breath in/breath out cycles that were very close to each other, or external noise interfering with the sensor (e.g., subject
movement or scratching on the sensor). Spot check data of less than 45 seconds should not be considered accurate: it is recommended to evaluate
more than one minute of trend data to obtain an accurate respiratory rate.
The accuracy of this device has not been validated for monitoring of respiratory rate in patients with specic medical conditions, e.g., asthma,
COPD or cystic brosis. The accuracy of the sensor has not been validated in infants or neonates.
 Loading...
Loading...