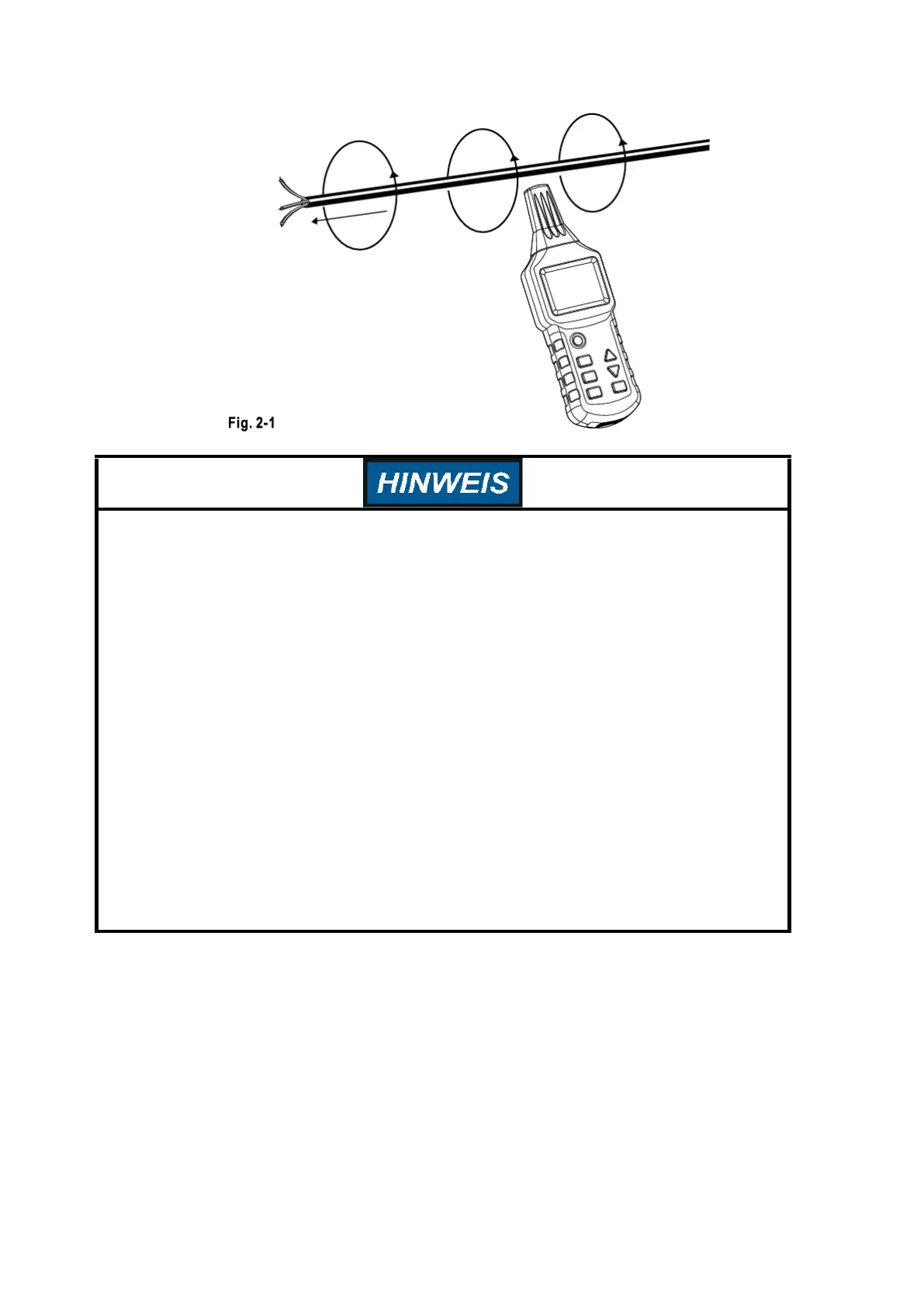
Optional connection types
1. Single-pole use: Connect the transmitter with just one lead. The high frequency signal generated by
the transmitter can detect and track only one conductor. The second conductor is ground. This
configuration generates a high frequency current that flows through the conductor and on to
ground, similar to a radio or receiver.
2. Double-pole use: The transmitter is connected to the conductor by two test leads. This configuration
can detect live and voltage-free lines.
The transmitter is connected to live wires:
Connect the + terminal of the transmitter to the grid conductor phase and the ground terminal of the
transmitter to the grid neutral conductor. If the grid wire is not live, the modulated current from the
transmitter will pass through the distributed capacity in the grid line to the neutral wire and return to
the transmitter.
The transmitter is connected to voltage-free wires:
Connect the + terminal of the transmitter to a grid neutral connection. Connect the ground terminal to
another parallel grid wire and connect the two other grid connections to each other. In this case the
modulated current returns directly to the transmitter through the grid wire. Optionally, the two
transmitter test leads can be connected to the two ends of the conductor. The + terminal of the
transmitter can be connected to the grid line, and the ground terminal of the transmitter to the grid’s
protective ground lead.
 Loading...
Loading...