VC Pro VRF 50/60Hz
179
Part 3 - System Design and Installation
8 Charging Refrigerant
8.1 Calculating Additional Refrigerant Charge
The additional refrigerant charge required depends on the lengths and diameters of the outdoor and indoor liquid pipes.
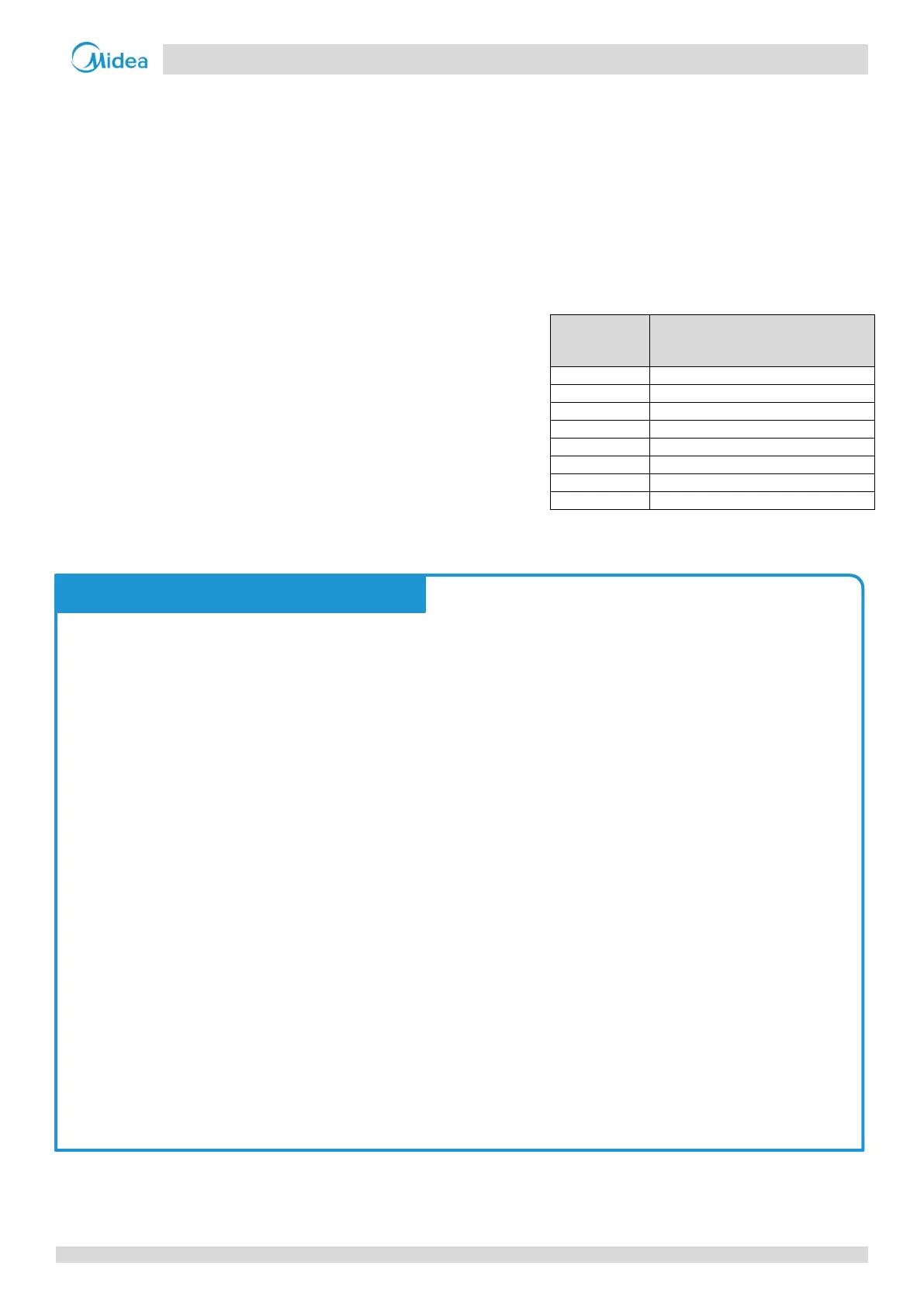
Table 3-8.1 shows the additional refrigerant charge required per meter of equivalent pipe length for different diameters of
pipe. The total additional refrigerant charge is obtained by summing the additional charge requirements for each of the
outdoor and indoor liquid pipes, as in the following formula, where L
1
to L
8
represent the equivalent lengths of the pipes of
different diameters. Assume 0.5m for the equivalent pipe length of each branch joint.
Additional refrigerant charge R (kg) = L
1
(Φ6.35) × 0.022
+ L
2
(Φ9.53) × 0.057
+ L
3
(Φ12.7) × 0.110
+ L
4
(Φ15.9) × 0.170
+ L
5
(Φ19.1) × 0.260
+ L
6
(Φ22.2) × 0.360
+ L
7
(Φ25.4) × 0.520
+ L
8
(Φ28.6) × 0.680
8.2 Adding Refrigerant
Box continued on next page …
Table 3-8.1: Additional refrigerant charge
Additional refrigerant charge per
meter of equivalent length of
piping (kg)
Caution
Only charge refrigerant after performing a gastightness test and vacuum drying.
Never charge more refrigerant than required as doing so can lead to liquid hammering.
Only use refrigerant R410A - charging with an unsuitable substance may cause explosions or accidents.
Use tools and equipment designed for use with R410A to ensure required pressure resistance and to prevent
foreign materials from entering the system.
Refrigerant must be treated in accordance with applicable legislation.
Always use protective gloves and protect your eyes when charging refrigerant.
Open refrigerant containers slowly.
Procedure
The procedure for adding refrigerant is as follows:
Step 1
Calculate additional refrigerant charge R (kg) (see Part 3, 8.1 “Calculating Additional Refrigerant Charge”)
Step 2
Place a tank of R410A refrigerant on a weighing scale. Turn the tank upside down to ensure refrigerant is charged
in a liquid state. (R410A is a blend of two different chemicals compounds. Charging gaseous R410A into the
system could mean that the refrigerant charged is not of the correct composition).
After vacuum drying (see Part 3, 5.10 “Vacuum Drying”), the blue and red pressure gauge hoses should still be
connected to the pressure gauge and to the master unit stop valves.
Connect the yellow hose from the pressure gauge to the R410A refrigerant tank.
 Loading...
Loading...











