7
Amplitude – The strength of a sound’s vibration measured in Decibels (dB). This
corresponds to the musical term Loudness (figure 4).
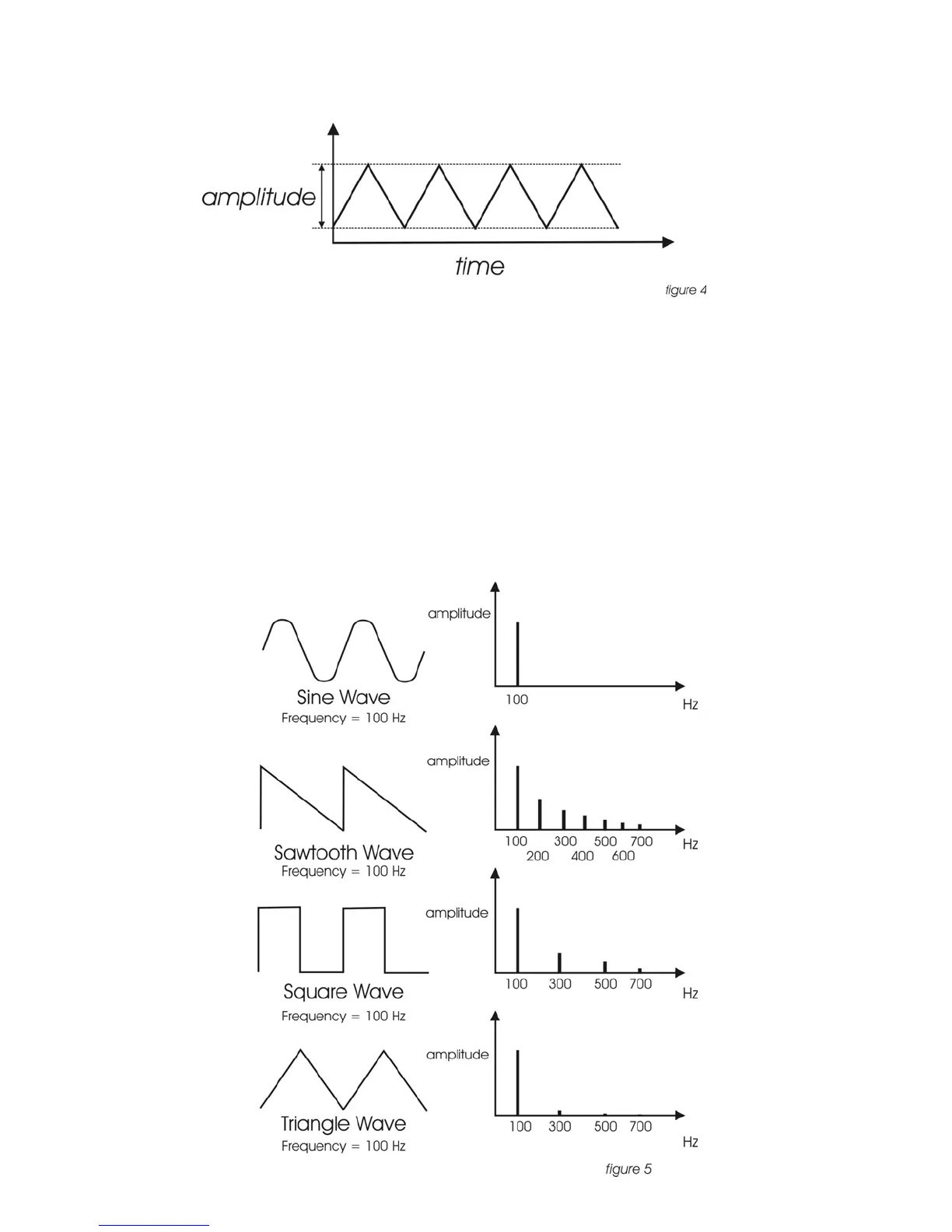
Harmonic Content – A sound is made up of simple vibrations at many different
frequencies (called harmonics) which give a sound its particular character. This
corresponds to the musical term timbre or tone color. A harmonic sound, such as a
vibrating string, is one in which the harmonics are mathematically related by what is
called the harmonic series. These sounds are typically pleasing to the ear and
generally the consecutive vibrations have the same characteristic shape or
waveform. An inharmonic sound, such as a crash cymbal, is one in which the
harmonics are not mathematically related. Their waveforms look chaotic. White
noise is an inharmonic sound that contains equal amounts of all frequencies. A
frequency spectrum is a graph of harmonics vs. their amplitude; a waveform is a
graph of the amplitude of a sound vs. time (figure 5).
 Loading...
Loading...