2
2
.
.
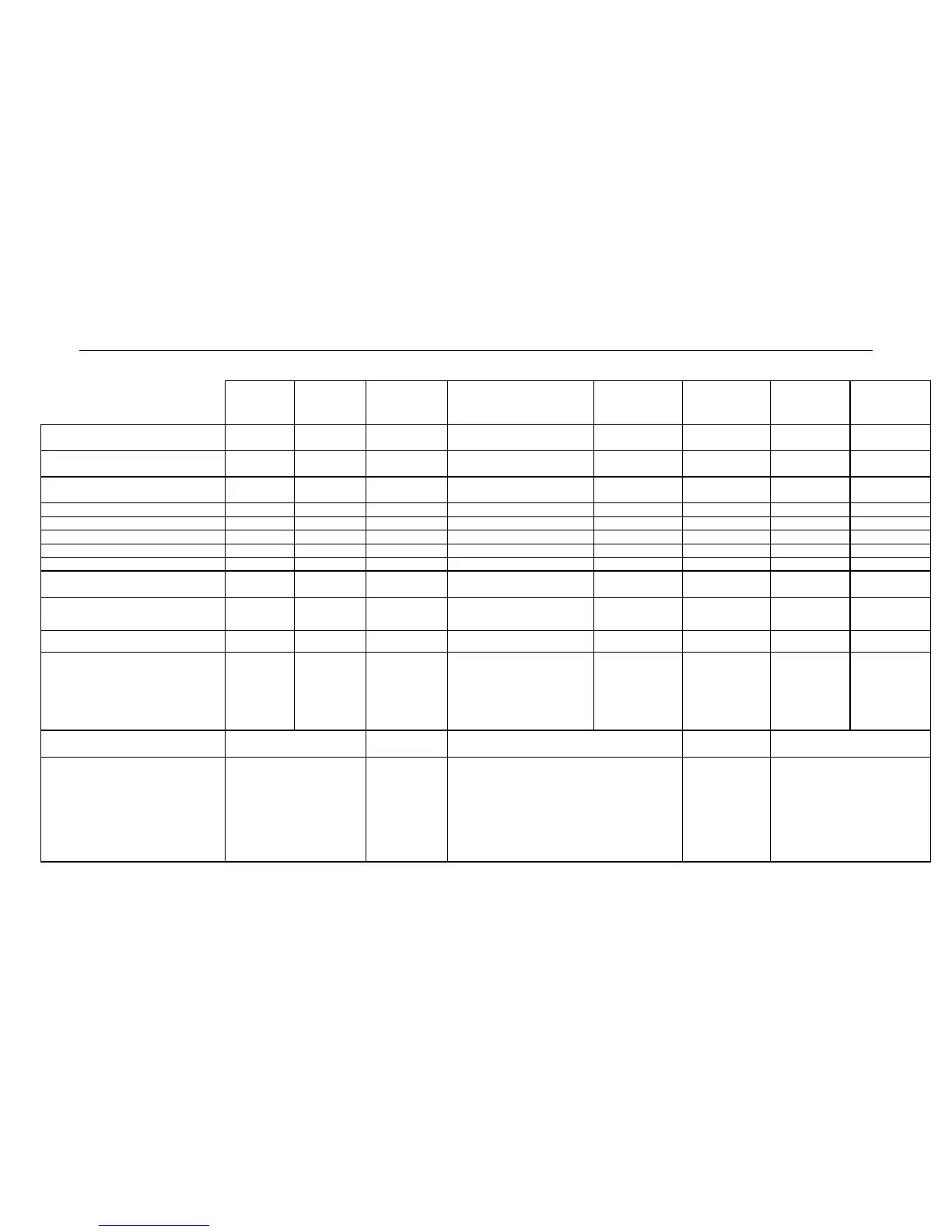
Sensors (non-exhaustive list)
Table No. 1
Methane
CH4
Propane
C
3
H
8
Methane
CH4
Oxygen
O
2
2 years
Oxygen
O
2
1 year
Carbon Dioxide
CO
2
Carbon
Monoxide
CO
Hydrogen
sulphide H
2
S
Sensor reference
6 313 888 6 313 888 6 313 889 6 313 780 6 313 817 6 313 818 6 313 787 6 313 788
Standard range (1) 0 - 100%
LEL CH4
0 - 100%
LEL C
3
H
8
0 - 100% vol 2 - 30 % volume 2 – 30 % volume
0 - 5 % v/v 1000 100
Measurement principle Thermo-
catalytic
Thermo-
catalytic
Catharo
metric
Electrochemical Electrochemical Infrared
absorption
Electrochemica
l
Electrochemica
l
Display resolution (1) 1 % LEL 1 % LEL 1% v/v 0,1 % v/v 0,1 % v/v 0,1 % v/v 1 1
Accuracy (2) 2 2 2 0.3 % v/v 0.3 % v/v 0.2 % v/v 15 3
Repeatability (3) ± 1 % LEL ± 1 % LEL ± 1 % vol 0,1 % v/v 0,1 % v/v 0.1 % v/v 1 1
Deviation of zero/sensitivity (4) 0,5 / 5 0,5 / 5 0,.2 / 2 0,2 / 2 0.2 / 2 0,2 / 2 0.5 / 1,5 0.5 / 2,5
Response time (5) < 20 seconds
< 20 seconds < 10 < 10 < 30 < 30 < 25
Temperature (6) -20°C to
+50°C
-20°C to
+50°C
-20°C to +50°C
-20°C to +40°C -20°C to +40°C -10°C to40°C -20°C to40°C -20°C to40°C
Relative humidity and pressure
range (7)
0 – 95 % RH
1 bar ± 20 %
0 – 95 % RH
1 bar ± 20 %
10 – 95 % RH
1 bar ± 20 %
10 – 95 % RH
1 bar ± 20 %
10 – 95 % RH
1 bar ± 20 %
10 – 95 % RH
1 bar ± 20 %
10 – 95 % RH
1 bar ± 20 %
Service life (8) 48 months 48 months 60 months 28 16 60 36 36
Storage conditions and maximum
storage time (9)
-40°C to +40
°C
10-60 % RH
1 bar ± 10 %
6 months
maximum
-40°C to +40
°C
10-60 % RH
1 bar ± 10 %
6 months
maximum
-40°C to +40
°C
10-60 % RH
1 bar ± 10 %
6 months
maximum
4 – 20 °C
10 – 60 % RH
1 bar ± 10 %
3 months
4 – 20 °C
10 – 60 % RH
1 bar ± 10 %
3 months
0 – 40 °C
10 – 60 % RH
1 bar ± 20 %
6 months
4 – 20 °C
10 – 60 % RH
1 bar ± 10 %
2 months
4 – 20 °C
10 – 60 % RH
1 bar ± 10 %
2 months
Response time (10) 30 s 30 s Sensors functional immediately after start up of
device
120 s Sensors functional immediately
after start up of device
Notes: - Measurement is
underestimated if oxygen
level is < 10%
- Exposure to high levels of
silicon or sulphur vapors
may damage the detector.
- The detector is sensitive to
a majority of explosive gases
- Presence of high levels of CO
2
can lead to an
over estimation of O
2
concentration
- Exposure to high levels of
organic solvents can damage the
sensors.
- Exposure to gases at higher
levels than detector’s range can
damage it Recalibrate sensors if
they go out of range.
 Loading...
Loading...