11
Natural conditions that can cause a tree to
fall in a particular direction include:
S The wind direction and speed.
S The lean of the tree. The lean of a tree
might not be apparent due to uneven or
slopingterrain. Useaplumborlevel tode-
termine the direction of tree lean.
S W eight and branches on one side.
S Surrounding trees and obstacles.
Look for decay and rot. If thetrunk is rotted,
it can snap and fall toward the operator.
Make sure there is enough room for the tree to
fall. Maintain a distance of
2-1/2 tree lengths
from the nearest person or other objects. En-
gine noise can drown out a warning call.
Remove dirt, stones, loosebark, nails, staples,
and wire from the tree where cuts are to be
made.
Direction of Fall
45_
Plan a clear retreat path
FELLING LARGE TREES
(15cmindiameterorlarger)
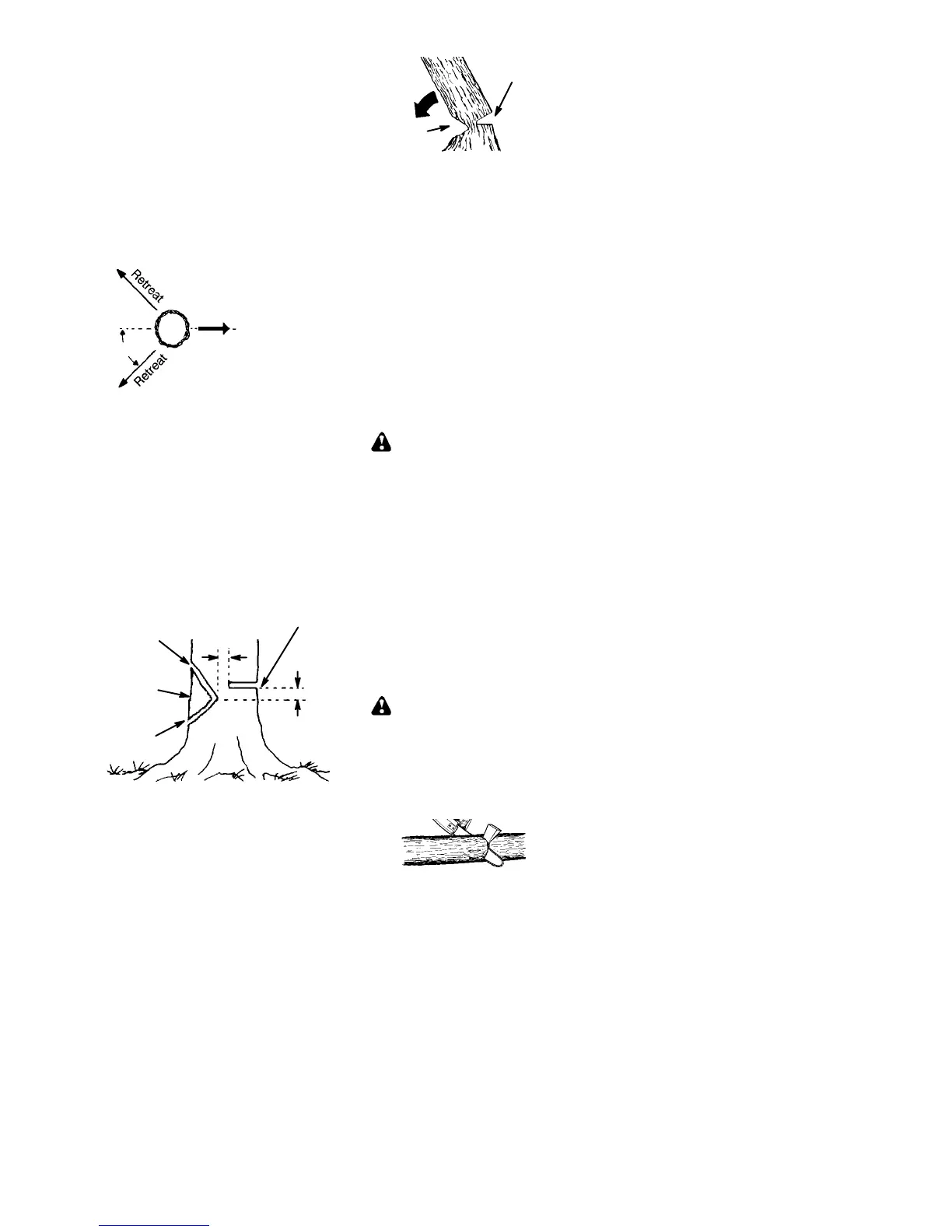
The notch method is used to fell large trees.
Anotchiscutonthesideofthetreeinthede-
sired direction of fall. After a felling cut is
made on the opposite side of tree, the tree
will tend to fall into the notch.
NOTCH CUT AND FELLING THE
TREE
S Make notch cut by cutting the top of the
notch first. Cut through
1/3 of the diameter
ofthetree. Nextcompletethenotchbycut-
ting the bottom of the notch. See illustra-
tion. Once the notch is cut remove the
notch of wood from the tree.
Notch
First cut
Second cut
Final cut here. 5 cm above
center of notch.
5cm
5cm
S After removing the wood from the notch,
make the felling cut on the opposite side of
thenotch. This isdonebymakinga cutabout
5 cm higher than the center of the notch.
This will leave enough uncut wood between
the felling cut and the notch to form a hinge.
This hinge will helpprevent the tree from fall-
ing in the wrong direction.
Opening
of felling
cut
Closing
of notch
Hinge holds tree on stump and helps
control fall
NOTE: Before felling cut is complete, use
wedges to open the cut when necessary to
controlthedirectionoffall. Toavoidkickback
or chain damage, use wood or plastic
wedges, but never steel or iron wedges.
S Bealerttosignsthatthetreeisreadytofall:
cracking sounds, widening of the felling cut,
or movement in the upper branches.
S As treestarts to fall,stop saw, put it down,
and get away quickly on your planned re-
treat path.
S DO NOT cut down a partially fallen tree with
your saw . Be extremely cautious with par-
tially fallen trees that may be poorly sup-
ported. When a tree doesn’t fall completely,
set thesaw aside andpull down the treewith
a cable winch, block and tackle, or tractor .
CUTTING A F ALLEN TREE
(BUCKING)
Bucking is the term used for cutting a fallen
tree to the desired log length.
WARNING: Do not stand on the log
being cut. Any portion can roll causing loss
of footing and control. Do not stand downhill
of the log being cut.
Important points
S Cut only one log at a time.
S Cut shattered wood very carefully; sharp
piecesofwoodcouldbeflungtowardoper-
ator.
S Use a sawhorse to cut small logs. Never
allow another person to hold the log while
cuttingandnever holdthelogwithyour leg
or foot.
S Do not cut in an area where logs, limbs,
and roots are tangled.Drag thelogs into a
clear area before cutting by pulling out ex-
posed and cleared logs first.
TYPES OF CUTTING USED FOR
BUCKING
WARNING: If saw becomes pinched
or hung in a log, don’t try to force it out. You
can lose control of thesaw resulting ininjury
and/or damage to the saw. Stop the saw ,
drive a wedge of plastic or wood into the cut
untilthesawcanberemovedeasily. Restart
thesawandcarefully reenterthe cut. Donot
attempttorestartyoursawwhenitispinched
or hung in a log.
Turn saw OFF and use a plastic or
wooden wedge to force cut open.
 Loading...
Loading...