[
14
]
EINSTEIN
™
by Paul C. Buff
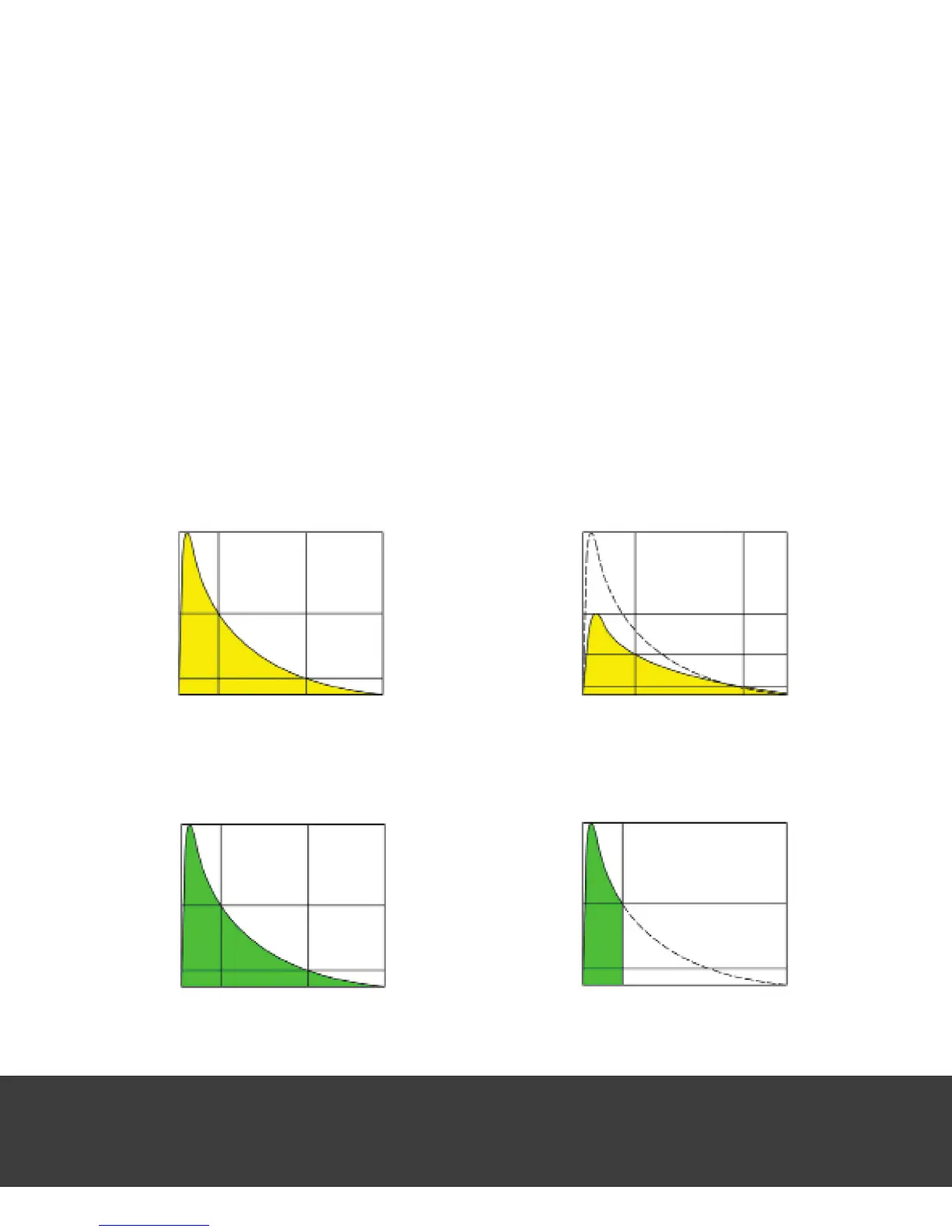
CONVENTIONAL FLASH VS. IGBT CONTROL
Conventional Variable Voltage Control: Figures 1 and 2 show the ash waveform from a conven-
tional variable voltage monoash. As power is reduced, both the t.5 and t.1 ash durations
become longer as power is reduced. Note that even beyond the t.1 point the ash continues
to trail off slowly, adding motion blur. The color temperature drops as power is reduced.
Einstein
TM
E640 IGBT Control: In Figures 3 and 4 below, notice the ash abruptly shuts off at
whatever point is needed to produce the desired output. The t.1 ash durations can be as fast
as 1/13,500 second at low power, producing crisp action freezing. But the color temperature
rises as power is reduced. This depicts the Einstein
TM
Action Mode. In the Constant Color
Mode, the Einstein
TM
processor compensates by adjusting both the shutoff time and the
voltage such that a constant 5600ºK color is achieved. The ash duration drops less rapidly
as power is reduced, but still produces very short t.1 times (1/8000 second at minimum
power) and extremely sharp action freezing. See the graphs below and on the following page.
Figure 2: Variable Voltage at Half Power
100%
50%
10%
t.5
1/1600
t.1
1/470
Figure 4: IGBT Control at Half Power
100%
50%
10%
t.1
1/2050
Figure 3: IGBT Control at Full Power
100%
50%
10%
t.1
1/588
t.5
1/2000
Figure 1: Variable Voltage at Full Power
100%
50%
10%
t.5
1/2000
t.1
1/588

 Loading...
Loading...