English
© 2001 PROCEQ SA Appendix 19
8 Appendix
8.1 Derivation of the PROCEQ Standard
Conversion Curves
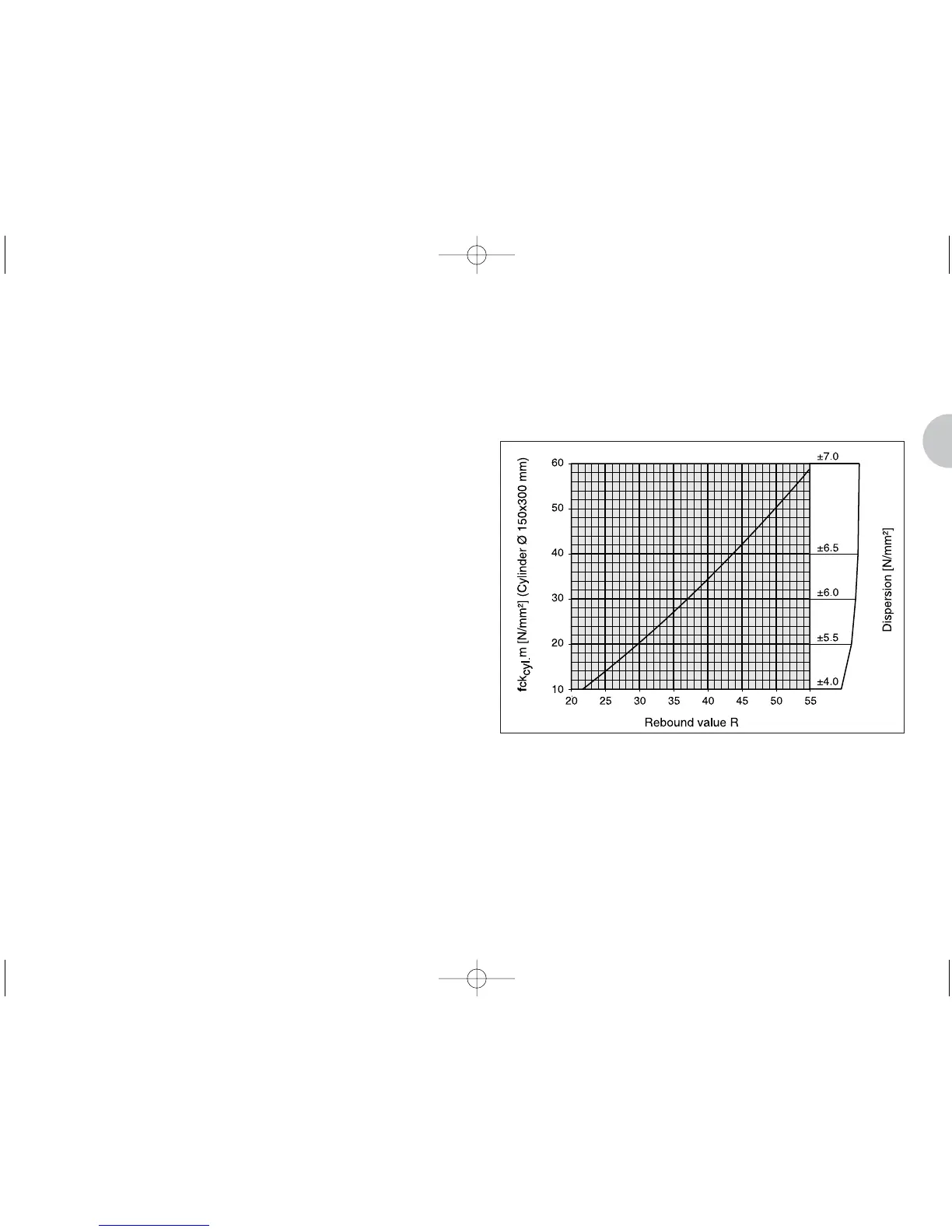
The conversion curves Fig. 8.1 and Fig. 8.2 for the con-
crete test hammer are based on measurements taken on
very many sample cubes.
The rebound values R of the sample cubes were measu-
red using the concrete test hammer. The compressive
strength was then determined with the pressure testing
machine. In each test, at least 10 test hammer impacts
were performed on one side of the sample cube which
was lightly clamped in the press.
Material of the sample cubes:
All cubes were made from concrete consisting of good
quality fine gravel (maximum particle size Ø 32 mm) and
Portland cement.
Empirical values:
The conversion curve is practically independent of the:
- Cement content of the concrete
- Particle gradation
- Diameter of the largest particle in the fine gravel mix-
ture, providing the diameter of the maximum particle is
< 32 mm
- Water/cement ratio
8.2 Standard Conversion Curves
Standard Conversion Curve for Concrete Test
Hammer Model ND
Mean value has already been corrected in relation to
the impact direction
Fig. 8.1 Model ND: Conversion curve based on the average
compressive strength of a cylinder and the rebound
value R
fck
cyl.
m: average compressive strength of a cylinder
(probable value)

 Loading...
Loading...